On Differences about Public Sentiment Feedback of Public Policies Making in Major Public Health Emergencies——An Investigation about the Policy of "Delay of School Opening" Based on Social Media Data
-
摘要:
公共政策的出台往往引发公众形成相应的情绪反馈,该情绪反馈同时又影响公众对政策的态度和政策的执行效果。以“延迟开学”政策为例,运用文本分析法,探究新冠肺炎疫情期间中国34个省级行政区公众对“延迟开学”政策的情绪反馈差异并分析相关的影响因素。认为重大突发公共卫生事件背景下的公共政策,不仅需要关注如何解决客观问题,还应具备回应公众主观需求的社会属性。研究发现,重大突发公共卫生事件背景下的公共政策制定,是政府基于事件危机评判和公众总体需求对公众作出的回应,相关政策会在不同地区出现差异化的公众情绪反馈;在疫情形势较为严峻的背景下,大多数公众对“延迟开学”政策呈整体消极情绪,但消极情绪的程度和对政策的积极反馈程度存在地区差异,这一差异可能与地区受疫情影响程度、经济发展水平、教育发展水平等因素有关。因此,在突发公共卫生事件的背景下,政府公共政策的制定应瞄准公众需求、把脉公众感受,从而实现政策制定的科学化和精细化。
Abstract:The introduction of public policies often triggers the public to form corresponding sentiment feedback, which also affects the public′s attitude towards policies and the effect of policy implementation. Taking the "delay of school opening" policy as an example, the study used text analysis to explore the differences in the public′s emotional feedback on the " delay of school opening" policy in 34 provinces in China during the epidemic period, and analyzed the related influencing factors. It is believed that public policies under the background of major public health emergencies should not only focus on how to solve objective problems, but also have the social attributes of responding to the subjective needs of the public. The study found that public policy formulation in the context of major public health emergencies was the government′s response to the public based on the event crisis assessment and the general public needs. Relevant policies lead to differentiated public sentiment feedback in different regions: In the context of the severe epidemic situation, the majority of the public had an overall negative sentiment towards the " delay of school opening " policy, but there were regional differences in the degree of negative sentiment and positive feedback to the policy, which may be related to multiple factors such as the severity of the impact of the epidemic, economic development, and educational development in the region. Therefore, the formulation of public policies in the context of public health emergencies requires the government to target the needs of the public and take the pulse of the public′s feelings, so as to achieve scientific and refined policy formulation.
-
一. 问题提出
重大突发公共卫生事件的暴发将政府治理由常态切换至危机状态,危机状态下公共政策的制定不仅关注危机如何化解的事务属性问题,还具备围绕人进行沟通管理活动的社会属性[1]。在危机管理社会属性的视角下,公共政策制定与公众需求和感受之间的因果链条是一项值得关注的议题。通常,公共政策的制定是政府对公众热切关心话题的回应,会刺激公众对政策形成相应的公众情绪和反馈行为[2];公众的情绪反馈又会直接关系公众对政策的接纳程度和态度[3],同时也影响政策的执行效果和执行难度[4]。这些因素表明,公共政策制定需要关注社会属性的作用要素和逻辑[5],这既是政策能否高效实施的关键因素,也是政策完善方向的重要参考,并对政策制定的精准化和精细化具有重要的意义和价值。
这种现象在重大突发公共卫生事件治理过程中更为凸显。突发公共卫生事件具有突发性、危害性、不确定性、多变性等特征,事件本身及其衍生的一系列连锁反应和信息舆情往往会引发公众恐惧、焦虑、无助、抑郁等负面情绪[6],而这些情绪比较突出、激烈,且容易通过社交网络等平台传播汇聚,形成一定的社会情绪。因此,突发公共卫生背景下的公共政策是政府为应对事件危机和公众需求而迅速提出的解决方案,往往面临紧急度高、紧迫性强、舆情压力大等挑战。因此,这就要求政府在突发公共卫生事件暴发之后迅速反应,快速掌握事件信息、摸清公众需求、制定应急预案,并发布相应的应对措施,以指导公众有效应对突发公共卫生事件,降低其可能带来的危害和损伤。同时,政府政策措施能否精准匹配公众需求、解决公众痛点问题,能否得到公众的接受与认同[7],能否调动公众的积极性与主动性显得尤为重要。
近年来,学界也逐渐开始关注社会治理中公众对公共政策的主观情绪反馈,现有研究主要从政策态度的形成途径、影响因素、特定政策或特定群体的公众态度分析,以及政策态度与政策行为关系等四个方面展开,并基本形成了较为成熟的研究体系。与此同时,随着互联网的发展,学界相关的研究内容也逐渐向线上公众政策态度表达聚集,并聚焦于特定危机事件探讨在线公众的情感反馈。这种研究方式突破了传统线下研究过程中样本覆盖面小、代表性弱、样本量少、工作量大等问题,实现了大样本数据快速收集、分析和预测的效果,推动了相关领域研究的快速发展。然而,在特定突发公共卫生事件议题中,往往存在着许多不同的事件和主题,这使得研究很难区分危机事件中的公众情绪是对何种现象的反应。学界有关突发公共卫生情境下的公众情绪研究,大部分聚焦于危机事件本身对公众的情绪影响及其反馈特征,少有研究关注危机事件中政府公共政策对公众情绪的作用。因此,本文力图将突发公共卫生事件情景下的公众情绪反馈,更加聚焦于特定公共政策或特定危机阶段,由此更有利于理解公众在突发公共卫生事件中的情绪反馈,并将其精准应用于公众需求匹配以及应急政策和应急措施的指导中去,促进公共危机背景下治理体系和治理能力现代化建设。
2019年末,自全球新冠肺炎疫情多点暴发至今,各国政府不断尝试、积极应对,通过政策制定等形式以保障公众在疫情之下的生命安全。2020年初,从武汉“封城”到延迟开学、从复工复产到减税降费,我国在保障公众生命健康、保证经济持续发展上也因势而谋、应势而动。全国各地在疫情期间出台的各项政策中,“延迟开学”政策尤其具有出台时间紧迫、连续性强的特征。该政策大多出台于2020年春节假期之间,是对寒假后公众是否正常学习生活的及时回应;同时,从“延迟开学”、到“根据各地疫情实际情况安排高三学生有序开学”、再到“2020年高考推迟一个月开考”等,不同政策之间的内容具有连续性,政策的出台间隔也给予公众足够的讨论和情绪表达空间和互动条件;此外,“延迟开学”政策的目标对象具有特殊性。学校作为一个人口高度密度的地方,是重要的防疫阵地[8],而学生作为社会和国家未来的象征,其健康成长一直备受社会各界和各个家庭的关注。根据教育部2020年全国教育事业发展统计公报数据显示,2020年,我国共有各级各类学历教育在校生2.89亿人①,这一庞大群体及其背后的家庭几乎涵盖了我国大部分的人口。因此,我国相关部门与这一群体利益相关的政策更能够引起社会各界的关注和共鸣,也更容易激发公众的表达欲望和讨论热情。
① 中华人民共和国教育部,2020年全国教育事业发展统计公报。http://www.moe.gov.cn/jyb_sjzl/sjzl_fztjgb/202108/t20210827_555004.html。
基于此,本研究将议题聚焦于疫情期间的“延迟开学”政策,借助大数据采集分析技术获取社交媒体平台上公众对该政策的情绪表达和情感反馈信息,并对其可能的影响因素进行解释分析;同时,希望通过一种聚焦的研究方式,能够为突发公共卫生情景下快速掌握公众情绪、征求公众意见提供一种可能性,力图为危机情境下地方政府精准释放政策信号、因地制宜调整政策提供一份研究经验。
二. 理论基础与研究假设
一 政策态度
公众的政策态度是公众对于公共政策的认知、情感及其相应的行为表现[9]。公众对政策的认知,是公众基于自身既有经验对某一公共政策产生的理解、领悟和判断;对政策的情感,是公众对于某一特定政策产生的个人情绪、看法、评价、期望等,这种情绪复杂而多样,既包括开心、欣喜、接纳等积极情绪,也包括抗拒、厌恶、反感等消极情绪;公众对政策的行为,是公众对于某一特定政策所采取的行动,包括对政策实施的配合或阻挠等。三者息息相关、密不可分,其中政策认知是产生政策情感的基础,政策情感是导致公众具体实施行为的前提;反之,政策情感是对政策认知的表现,而政策行为也是政策情感的一种表达。政策情感作为公众对某一公共政策的综合情感表达,其积极性和消极性既可以直接关系公众对政策的接纳程度和认可程度[3],同时也影响政策的执行效果和执行难度。通常而言,公众会选择认同个人更倾向和愿意接受的政策,也会更加配合相关政策的要求和执行过程;相反,对于公众不认可的政策,其落地过程往往会遭遇更多来自公众的阻力和质疑,使得政策难以实现其真正的意义。由此,个体相似情绪在社会层面上汇集,当形成社会共同情绪和公共舆论时,甚至可以影响更多社会公众的认知,直至干涉政策的调整和执行。特别是在新时代背景下,公众对于政策有更多的自我思考和情绪传递。
一方面,公众在现代社会中的政治参与意识不断增强,对公共政策的态度也从被动接受逐渐向主动了解转变,更愿意主动关心时事和了解政策,也更愿意与他人分享自己对政策的理解和感受,表达自己对公共政策的情绪和态度;另一方面,在科技不断进步的时代,互联网也给公众提供了更多的情绪表达途径和意见表达平台,公众能够随时随地与全球公众交流互动;与此同时,互联网平台也促进了公众情绪在社会层面的汇聚,助于形成网络舆论并引起更多公众的关注和评论。不仅仅如此,政府更积极通过各种途径倾听民声、了解民情、征集民意、汇聚民智,了解公众对于政策的情绪反馈,以更好地为政策出台和政策调整做好基础,同时也更好服务公众需求和社会发展,促进共建共治共享社会治理新格局的实现。因此,在新时代背景下,我们如何有效引导公众正确理解公共政策,开展精准的情绪干预是至关重要的。
近年来,学界对于政策态度的研究也逐渐成熟,相比于前期从心理学和政治心理学领域出发探究政策态度的形成途径,现有更多研究从多个维度探究影响公众政策态度的相关因素,大部分学者从个体、政策与环境三个维度开展分析。有学者认为,公众的性别、年龄、经济收入水平、所处区域等个体特征[10]会影响其对于政策的认知和情感表达,进而影响其对政策的态度;同时,有学者认为,政策态度的最主要影响因素来自于政策本身,政策的合理性和可行性[11]是影响公众对其态度的关键因素;也有学者认为,个体外在环境如网络热点、意见领袖意见[12]等会左右公众自身对政策的认知和判断,从而影响政策态度;此外,还有学者从特定政策或特定群体公众出发,分析特定条件下公众政策态度的形成和演变,并探究公众政策态度对其实际行为的影响[13]。
二 社会情绪治理
社会情绪是在一定空间和时间范围内,一定数量社会个体对某件事情或某个社会现象所共同产生的相似情绪体验的集合体[14]。通常而言,社会情绪来自社会群体中每个个体在现实环境中的满足程度,在人际互动中,如果大部分个体的社会需求得到满足,则会产生较为积极的社会情绪;反之则可能产生较为消极的社会情绪。基于此,许多学者对社会情绪开展了深入的研究,主要研究维度包括两个方面。一是对社会情绪进行了不同维度的归类和基本情绪的探寻;二是对社会情绪产生因素及其作用探究。学界相关研究发现,社会情感氛围作为社会群体中客观存在的情感基调,既是社会情绪的基础,同时也是对公共政策的反馈[15],而积极的社会氛围能够有效助推发展。不仅如此,学界既有研究表明,社会情感氛围还能有效预测集体的行为和选择,从而实现危机预警的功能。
在此基础上,许多学者对社会情绪的治理策略开展了深入的讨论。其中社会情绪建模是学界常用的分析方法,通过该模型,有学者将社会情绪稳定性分为外部、内部和传播三个子系统。外部系统主要指社会、经济、政策等外部环境及其可能带来的影响;内部系统则指,认知、经验、情绪等个体自身因素;传播是连接内外部系统的一座桥梁,不同传播方式可能会导致不同的作用效果进而产生不同的社会情绪。这三个系统的有机结合可以为分析和预测典型情境突发事件下的社会情绪动力和稳定性趋势提供借鉴[16]。在这三个维度中,外部系统是多数学者研究的切入点,有学者认为,通过改变社会情感氛围的方式,能够营造和谐温馨的积极社会氛围,并借助这种情绪渲染调节公众的负面情绪、引起社会群体的积极情绪共鸣、增强公众的社会信任感和安全感,从而达到化解公众冲突、缓和社会矛盾等目的[17]。基于此,有部分学者进一步深入探讨了社会工作在社会情绪治理过程中的重要作用,认为社会工作通过信息沟通和开展理性疏导的方式,为社会群体凝聚共识、增强信心、消减负面情绪提供了前提和基础;同时,也以实际行动引导人们采取温和理性的方式去分析问题,舒缓情绪,将消极、悲观的负面情绪转化为积极、乐观的正面情绪,从而提高社会的支持水平[18]。
本研究在梳理社会情绪治理相关研究发现,近年来,学界对于社会情绪的关注点逐渐聚焦到互联网上,网络舆情作为社会情绪的聚集和表现形式,已经成为现代社会治理的重要内容。现有研究发现,网络的作用已经由最初的普通公众抒发情绪、表达意见的平台,逐渐发展为大众“利益求解的渠道”[19]。在这样的趋势下,网友若拥有相同情绪和观点的“志同道合”,则会更容易听到相同的声音和感受到相似的情绪,从而不断强化自己对相关信息的获取和交流,甚至出现“群体情绪极化”[20]的倾向,并形成相应的社会舆论。特别是在当下,能源结构调整、社会转型升级的背景下,快节奏的都市生活和愈发激烈的社会竞争使得公众处于高压的工作和生活环境,缺少自我放松和自我调节的时间精力,容易引发公众迷茫、失望、惶恐等负面情绪的产生。这些负面的、消极的情绪在现实的社会规则中,往往因个体的社会角色需求而被压抑且不能表达,所以公众亟需通过其他渠道,以卸掉自身的社会角色、宣泄内心的情感,而网络的虚拟性和自由性恰好满足了公众自我表达的需求。因此,网络生态戾气凸显、“键盘侠”层出不穷、负面情绪铺天盖地,正义名义下的民族主义、同情弱势群体的心理、仇富仇官心理,等等,往往成为网络群体情绪极化现象的引爆点。部分“别有用心”的力量借助网民这一心理特点,也在网络舆情上大做文章,特别是在三农、教育、扶贫、乡村振兴、共同富裕、疫情、房价、腐败等重要话题、敏感话题上,公众虽然看似人人具有平等的话语权,能够共同形成社会“公共舆论”,但实际上,某些“网络推手”往往趁机利用和操控公众的“非理性”特征和信息的不对称特征,制造“多数人的暴力”现象产生。因此,有学者探讨了社会情绪对政府形象的影响[21],同时,也有学者认为,政府应当关注、理解并接纳公众的情绪感受,除了理性解决现实问题之外,也应当更多考虑公众的情感需要[22],避免群体情绪极化的产生。
本研究通过理论梳理可以发现,深入研究社会情绪治理对于更好发挥当下舆情治理作用至关重要,但是学界现有研究大多数聚焦于常规热点事件下的公众情绪治理研究,对于突发公共卫生事件等危机情境下的研究还相对较少。本研究认为,危机情境下公众的情绪更敏感也更冲动,处理好危机情境下公众的情绪需求是风险社会中不可回避的治理问题,基于社会情绪需求的危机处理也更能够彰显以人为本的治理理念和政府现代化治理的能力。
三 理论假设
情绪地理是舆情治理中的重要研究内容,最初起源于教育学领域,探究的三个主要对象为——人、情绪与空间,主要聚焦于分析三者之间的关系及其相互影响作用。随着研究的深入,情绪地理逐渐被引入社会治理相关研究领域,主要的研究内容包括以下几个方面。一是对不同空间场所下个体情绪差异的研究,主要聚焦于不同场所特征差异及其背后的情感寓意;二是探究不同空间场所对个体的情绪差异影响;三是情绪地理的可测量和可视化研究。随着现代化信息技术的发展,学者所研究的“场域”逐渐由现实空间向互联网虚拟空间聚焦。社交媒体平台打破了传统个体交往的空间屏障和地域隔阂,使得不同个体之间能够瞬时开展“屏对屏”交流。这种信息的快速传播特性使得个体在社交媒体平台上所展现的情绪和经历更容易被发现和看见,也更容易获得具有相似经历个体的关注、共鸣和互动,进而形成一个小的情绪共享圈,并以滚雪球效应或串联效应的形式传递出去[23],形成社会认同。许多学者针对互联网这一虚拟空间上公众情绪的特征,也对其传播方式和治理路径展开了深入探讨,并且借助大数据分析软件等工具,对包括“推特”在内的社交媒体平台用户信息数据进行追踪和语义分析,并将结果运用于政策关注、社会运动等现代化治理问题实践中[24, 25]。
目前,聚焦到危机情景下的区域情绪差异研究,大部分学者主要关注地理位置对危机情境下公众的情绪影响,认为不同地区公众对突发公共卫生事件的情绪反应各不相同[26]。学界现有主流观点认为,这种区别主要来自于公众所在区域与突发公共卫生事件发生地之间的物理距离以及公众受突发公共卫生事件影响程度的大小[27]。基于此,有学者通过不同地区的公众情绪进行统计和划分,比较不同地区之间公众情绪状态的差异[28]。此外,也有部分学者将公众的地域信息与网络行为相联系,认为突发公共卫生情境下社交媒体用户发布的贴子数量与该用户到最近权威医院之间的物理距离存在明显的相关关系[29]。无论是现实公众情绪,还是网络公众情绪,学界现有研究均指向此研究结论——公众离危机源头越近时,就越有可能受到危机的影响,其风险感知水平也会越高[30],因此就越有可能对旨在保护他们的政策产生支持、拥护等积极情绪[31],反之亦然。然而,本研究通过文献梳理发现,学界现有关于突发公共卫生情境下公众情绪的地域差异研究,大多数聚焦于危机事件本身对不同地域公众的情绪影响及其反馈特征差异,少有研究关注危机事件中政府公共政策对不同地域公众情绪的作用。然而在特定突发公共卫生事件议题中,往往存在着许多不同的事件和主题,这使得研究很难区分危机事件中的公众情绪是对何种现象的反应。因此,本研究依据现有研究结论及现实实践经验,将危机情境下公众的情绪差异聚焦到“延迟开学”政策中,并提出假设。
H1:公众对突发公共卫生事件下公共政策的情绪反馈具有地域差异。
H1a:受疫情影响严重的区域公众对“延迟开学”政策的积极情绪更高。
H1b:受疫情影响较轻的区域公众对“延迟开学”政策的消极情绪更高。
三. 研究设计
一 样本选择
新浪微博是一个基于用户关系的社交媒体平台,平台用户可以通过各种移动终端进行信息即时共享和传播。本研究选择以新浪微博作为数据收集平台的原因,主要分为几点。一是该平台拥有较成熟的运营技术和较广泛的用户量。自2009年开放内测起,新浪微博已经陪伴中国公众走过10多个年头,成为公众日常表达自我、获取资讯、互动交流的一个重要平台。截至2019年底,新浪微博月活跃用户达5.16亿①,成为本研究提供数据量的保障。二是该平台能够实时汇聚当下社会热点事件。无论是娱乐圈吃瓜、还是社会热点事件评论,新浪微博热搜榜的排名,往往体现了当下社会公众的关注焦点,这一通道既是公众迅速了解社会热点的一个途径,也是他们参与相关热点事件评论、表达的一个窗口。通过这样一种形式,相应热点事件能够迅速在平台发酵并形成相关的讨论氛围,有利于本研究更全面获取公众对于“延迟开学”政策的情绪态度和反馈信息。三是该平台不同用户间具有信息交流共享的开放性。区别于微信、QQ等社交软件的熟人圈层,新浪微博平台为用户提供了一个无阻隔的社交沟通渠道,平台间用户的对话和交流基于彼此共同关注的事件展开,不受是否互为好友或是否互相关注等限制,使得话题的聚焦性更强,信息交流更迅速。
① 新浪科技,微博月活跃用户达5.16亿竞争壁垒依旧稳固。https://baijiahao.baidu.com/s?id=1659601919021773231&wfr=spider&for=pc。
基于以上原因,本研究以新浪微博平台作为数据采集的端口,以“延迟开学”词组(“延迟开学”“推迟开学”“开学延迟”等)作为关键词数据搜索,对2020年1月1日至2020年4月7日之间发布的微博贴子进行收集,同时对其发布用户的地理位置信息、关注量、粉丝量等相关信息进行采集。通过该方法,本研究共获得18 475个不同贴子及其相关发贴人信息,并将所有数据存储到同一个数据集中进行数据编码与赋值。
二 分析方法
情感分析是一种用于预测文本极性和主观性的方法[32]。就社交媒体而言,是捕捉人们对事件、产品、话题和角色的情感反应的常用手段[33],是识别公众网络情绪信息的重要方式,同时也是衡量网络舆情的主要途径[34]。我们借助情感分析工具,能够快速理解公众的心理状态,同时强化对网络舆情的识别、监控以及对潜在网络舆情危机的预警和处理[35]。因此,学界聚焦于网络主题词研究及其情绪分析工具的开发,其中的大多数研究将文本内容按照情绪极性分为正面和负面两种类型;也有部分研究将其分为积极、中性和消极三个层次;同时,还有少部分研究从非常积极到非常消极将其分为五个级别。这些研究的分类过程大多数应用了三种分析方式:一是机器学习方法,即使用训练算法来识别人工编码的极坐标文本,通过给定文本与手动编码文本之间的相似性来预测目标文本的情绪;二是基于词典的方法,其本质上是一种有监督的分类方法[32],先是形成一组词汇极性参考,然后通过在给定文本中搜索相同的词汇来对情感进行分类;三是语言分析,即使用上下文和语法结构来预测给定文本的情绪[36]。在实践中,这些方法通常被混合和改进以用于实现更准确的文本情感分类。在此基础上,一些学者开发了一系列情感分析工具。其中语言学研究与字数统计(Linguistic Inquiry and Word Count,简称LIWC)作为一种基于频率的未加权词汇工具[37],综合应用了这三种分析方法的优点,可以通过计算机程序自动识别并计算文本中表达积极和消极情绪的单词[38],成为目前被应用最广泛的情感分析方法之一,在社交媒体上的应用已相当成熟。为了进一步对获取的文本情绪值进行分析,本研究应用LIWC对每个文本样本中积极词汇和消极词汇进行提取和赋值,并结合人工检验确保赋值的正确;同时,结合Logit回归分析对变量之间的影响关系进行显著性检验分析。
三 变量赋值
本研究在数据分析前对后续研究中的各项相关参数进行梳理和编码,具体包括情绪编码和地域编码。
情绪编码分为文本情绪人工编码、文本情绪机器编码和提取赋值三个步骤。为了明确所收集文本中公众对于“延迟开学”政策的情绪态度,本研究将文本进行情绪编码,并将其归类为“积极”“消极”与“其他”。其中,“其他”类别为无法确定情绪倾向或内容无关文本。首先,本研究随机抽取1 000个数据样本作为训练集,用于后续编码训练。其次,从训练集中随机抽取100个数据样本,邀请三位志愿者独立开展情绪编码工作,该阶段三位志愿者的编码内部一致性信度系数为0.78。此后,为了提高数据集的一致性,我们进行了一轮讨论,并在讨论后对训练集中剩余的900个数据样本开展独立编码,该阶段编码内部一致性信度系数为0.87。在人工编码之后,本研究训练了四个监督学习分类器,并将所有数据样本与第二轮编码贴子分类为训练集(80%作为训练集,20%作为测试集),开展机器编码。最终结果显示,支持向量机(SVM)朴素贝叶斯分类器在所有分类器中性能最好,内部一致性信度系数为0.89。在此基础上,本研究应用LIWC工具提取所有样本中每个贴子的积极情绪和消极情绪词汇量,并对每个文本样本中的积极情绪值和消极情绪值进行整体情绪值计算,具体计算公式见式(1)。
$$ 整体情绪值 = \frac{{\# 积极情绪词汇量 + 1}}{{\# 消极情绪词汇量 + 1}} \;\;\;\;\;\;- 1 $$ (1) 文本地域类别编码。本研究对所收集文本数据所对应的用户进行地域信息编码,根据我国34个省级行政区设置,对用户所处的地理位置进行序列编码。同时,根据国家统计局对我国34个省级行政区的划分,本研究将数据文本所属用户所在区域进行归类并赋值,其中,东部=1;中部=2;西部=3。
四. 数据分析
一 总体样本描述
本研究所用研究数据分为三个部分。第一部分是公众对“延迟开学”政策的情绪反馈数据,该部分通过微博平台共收集18 475个与“延迟开学”主题相关的贴子及其相关发贴人信息,并对所收集数据根据发贴时间、用户的情绪值及其所属地域进行归类赋值;第二部分是疫情通报数据,该部分通过国家卫生健康委员会、湖北省卫生健康委员会等相关官方平台,共收集全国和湖北省98组每日新增确诊病例和每日新增死亡病例通报数据;第三部分是“延迟开学”政策文本数据,该部分通过教育部官网、地方政府官网等政府公开途径收集。
二 “延迟开学”政策与微博用户情绪的时间线梳理
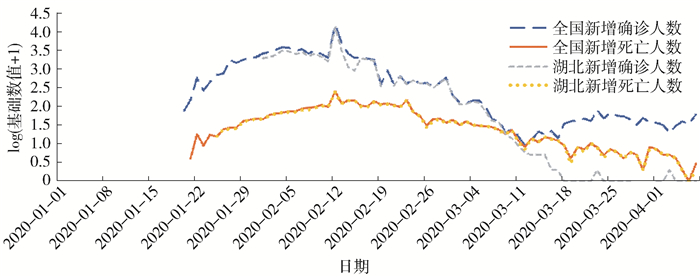
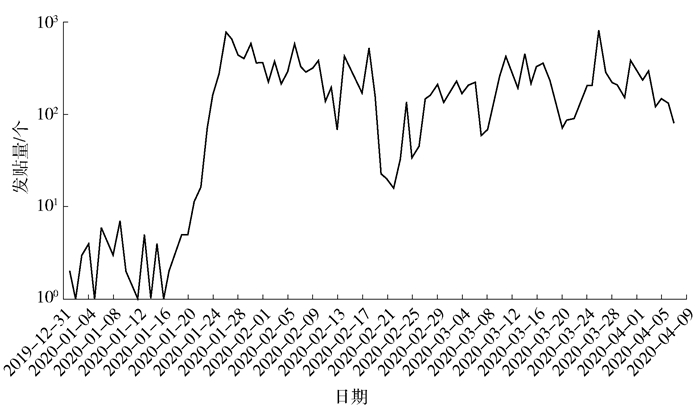
图 1展示了2020年1月1日至2020年4月7日之间,新浪微博平台上与“延迟开学”话题相关的贴子数量的变化情况。总体而言,新浪微博用户在该时间段对这一话题的关注程度较高,且在此期间,公众的关注度出现了几次较为明显的波动。这一关注度变化除了与“延迟开学”政策相关以外,也可能与当时全国的疫情走势相关。因此,本研究同时整理了国家卫生健康委员会发布的疫情每日通报信息(详见图 2),同时,根据时间线对于国内的疫情变化情况、“延迟开学”政策的出台和调整情况,以及新浪微博用户发贴数量变化情况进行简单的比较和梳理。
![]() 图 2 2020年1月1日至4月7日中国疫情情况数据来源:中华人民共和国国家卫生健康委员会,http://www.nhc.gov.cn/,湖北省卫生健康委员会,http://wjw.hubei.gov.cn/bmdt/ztzl/fkxxgzbdgrfyyq/。
图 2 2020年1月1日至4月7日中国疫情情况数据来源:中华人民共和国国家卫生健康委员会,http://www.nhc.gov.cn/,湖北省卫生健康委员会,http://wjw.hubei.gov.cn/bmdt/ztzl/fkxxgzbdgrfyyq/。根据国家卫生健康委员会每日疫情通报信息发现,自2020年1月中下旬开始,国内每日疫情新增确诊病例数量增速迅猛,从2020年1月20日的77例新增确诊病例,增加到2020年1月27日的1 771例新增确诊病例。在此背景下,春节假期之后是否开学、如何安排新学期学习计划等,一系列的相关问题成为了公众的重点关注,并且新浪微博平台上关于“延迟开学”相关的话题热度也逐渐显现出来。自2020年1月17日开始,新浪微博平台关于“延迟开学”相关话题的贴子数量迅速增长,并在2020年1月26日达到第一个高峰(765个)。2020年1月27日,教育部发文出台“延迟开学”相关政策①。在此后的20天里,我国疫情的每日新增确诊病例都在增加,新浪微博平台上关于“延迟开学”话题的热度也一直保持在较高水平。2020年2月12日,国家相关部门对于确诊病例的评判标准进行调整,使得当天国内疫情确诊病例数量大幅增加,达到15 152例。这一数据的公布使得公众更多地将注意力集中到疫情上,这可能是导致新浪微博平台上对于“延迟开学”关注度下降的原因。此后,全国每日确诊病例数量逐渐减少,2020年2月19日,全国新增确诊病例降至1 000以下,而新浪微博平台用户对于“延迟开学”政策的关注度,随着每日疫情新增确诊病例数量的变化而有所波动,并在2020年2月22日达到低谷。2020年2月28日,教育部对于“延迟开学”政策作出调整②,从全面延迟开学转为根据各地疫情实际情况安排高三学生有序开学。这一政策的调整再次引起了公众的关注和热议。2020年3月,我国疫情情况日趋向好,每日新增确诊病例以境外输入为主,本土新增确诊病例数量保持在两位数。我国对疫情的有效控制,使得公众对于“延迟开学”政策的关注度重新增强,并在2020年3月26日达到第二个发贴高峰,高达814个。2020年3月31日,教育部出台2020年高考推迟一个月开考的政策③,并再次在新浪微博平台上引起热烈关注。
① 中华人民共和国教育部,教育部关于2020年春季学期延期开学的通知。http://www.moe.gov.cn/jyb_xwfb/gzdt_gzdt/s5987/202001/t20200127_416672.html。
② 中华人民共和国教育部,中共教育部党组关于统筹做好教育系统新冠肺炎疫情防控和教育改革发展工作的通知。http://www.gov.cn/xinwen/2020-02/29/content_5485057.htm。
③ 中华人民共和国教育部,关于2020年全国高考时间安排的公告。http://www.moe.gov.cn/jyb_xwfb/xw_zt/moe_357/jyzt_2020n/2020_zt03/zydt/zydt_jyb/202003/t20200331_436662.html。
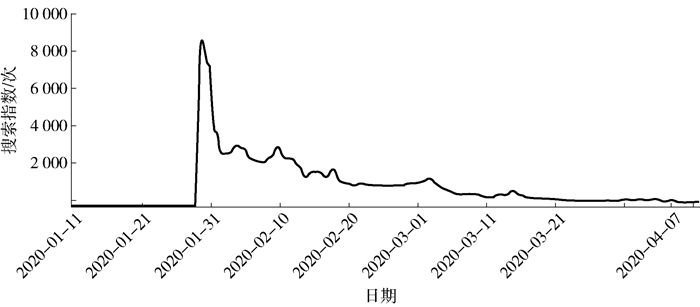
本研究为了更好印证公众对“延迟开学”政策的关注和反馈情况,同时在百度搜索引擎上获取了相应时间段关于“延迟开学”的百度搜索指数(详见图 3),并通过对比发现,新浪微博关于“延迟开学”话题的贴子数量,与百度指数中关于“延迟开学”话题的搜索量变化趋势相似,从而也进一步验证了公众对“延迟开学”的关注程度及其变化趋势。
本研究通过比较疫情情况、“延迟开学”政策发布时间线以及新浪微博用户对该话题的发贴数量发现,公众对于延迟开学事件的关注度与疫情的严重程度对“延迟开学”政策的出台密切相关。在全国疫情情况较为严峻的情况下,公众对于“延迟开学”相关话题的关注度较低,但当全国疫情情况趋于稳定向好时,公众对于“延迟开学”的关注度较高;同时,通过时间线梳理还发现,在每次“延迟开学”政策出台前夕,公众对于“延迟开学”相关话题的讨论都较为热烈,政策的出台往往在公众关注度的最高点出现。因此,“延迟开学”政策可能是政府在考虑疫情现实因素和公众情绪的基础上,对于公众担忧和压力的一种回应方式。
三 回归分析结果
在数据预处理阶段,本研究对所采集的新浪微博数据按照地域开展分类和赋值。在剔除地理位置缺漏信息项之后,本研究应用Stata SE15软件对剩余的13 132个数据根据自变量分类进行描述性统计分析,具体分析结果如表 1所示。由数据可以发现,本研究所采集的数据覆盖全国东、中、西部三个区域,其中东部地区用户发贴量最多,共7 651个,占总发贴量的58.26%;中部地区用户发贴量共3 045个,占23.19%;西部地区用户发贴量最少,共2 436个。
表 1 中国不同地区微博用户对“延续开学”政策情绪反馈回归分析的自变量描述性统计类别变量 观测值 百分比/% 累计百分比/% 地区 东部(=1) 7 651 58.26 58.26 中部(=2) 3 045 23.19 81.45 西部(=3) 2 436 18.55 100 合计 13 132 100 数据来源:新浪微博平台。 关于公众对“延迟开学”政策情绪值这一因变量,本研究根据LIWC方法的情感分类及其赋值公式对每个用户所发布贴子的文本情绪进行初步赋值。由于本研究需要先探究地域因素是否影响公众对“延迟开学”政策的情绪反馈,再根据结果进一步考虑是否探究地域因素的具体影响作用,因此,本研究根据整体情绪值的正负情况,将公众对“延迟开学”政策的整体情绪反馈进行二分类赋值以简化分析过程,二分类赋值结果为:1=积极情绪,0=消极情绪。
同时,学界既有研究表明,新浪微博等社交平台上用户的粉丝数量、关注用户数量及其发贴数量,与该用户贴子内容的价值取向及其情绪动态相关[39-40]。因此,本研究将关注量、粉丝量和发贴量三个用户特征指标作为控制变量加入到Logit回归分析中,具体分析结果如表 2所示。
表 2 中国不同地区微博用户对“延迟开学”政策情绪反馈的回归分析结果变量 (1) (1) (2) (2) 情绪 情绪
Exp(B)情绪 情绪
Exp(B)地区 0 1 (·) (·) 中部 0.097 8** 1.103** (0.052 7) (0.058 1) 西部 0.144** 1.155** (0.056 3) (0.065 0) 关注量 0.000 08*** 1.000*** 0.000 08*** 1.000*** (0.000 020 7) (0.000 020 7) (0.000 020 7) (0.000 020 7) 粉丝量 -1.09×10-8*** 1.000*** -9.96×10-9** 1.000** (3.97×10-9) (3.97×10-9) (3.97×10-9) (3.97×10-9) 发贴量 0.000 009*** 1.000*** 0.000 009*** 1.000*** (0.000 001 01) (0.000 001 01) (0.000 001 00) (0.000 001 01) N 9 680 9 680 9 680 9 680 pseudo R2 0.012 0.012 0.013 0.013 注:双尾检验统计显著度,*** p < 0.01, ** p < 0.05,*p < 0.1。
数据来源:新浪微博平台。本研究从结果可以发现,新浪微博用户的平台关注量、粉丝量和发贴量都显著影响其在平台上对“延迟开学”政策的情绪表达,这与前人的研究结果相一致。此外,东、中、西部的地域差异也显著影响公众的情绪表达,这与假设H1的预设结果相一致。相比于东部地区,中部地区公众对“延迟开学”政策的积极情绪反馈更显著,回归系数为0.097 8,其积极情绪反馈的概率比东部地区高10.3%(e0.0978-1=0.103,p < 0.05);西部地区公众对“延迟开学”政策的积极情绪反馈也更显著,回归系数为0.144,其积极情绪反馈的概率比东部地区高15.5%(e0.144-1=0.155,p < 0.05)。从整体情绪变化上看,区域差异显著影响公众对“延迟开学”政策的情绪反馈差异,且中、西部地区公众对“延迟开学”政策的总体情绪相比于东部地区公众而言相对较为积极。因此,本研究认为有必要对公众主观情绪反馈的区域差异再进行深入分析探讨。
四 文本分析结果
由Logit回归分析结果可以发现,区域差异对公众的情绪反馈有一定影响。因此,本节根据国家34个省级行政区的东中西部划分,对收集的数据进行过滤与筛选并开展区域统计分析,从区域维度上对公众的情绪反馈差异进行分析,在此基础上,再根据34个省级行政区的具体特征由表及里、由浅入深开展情绪值差异分析。
1.东、中、西部地区微博用户对“延迟开学”政策的情绪差异
东、中、西部地区微博用户对“延迟开学”政策的积极情绪值、消极情绪值和整体情绪值分析,结果如表 3所示。
表 3 中国东、中、西部地区微博用户情绪值统计分析区域 积极情绪值 消极情绪值 整体情绪值 涵盖省级行政区 东部 2.69 3.98 -0.32 上海、北京、天津、山东、广东、江苏、河北、浙江、海南、福建、辽宁 中部 2.64 3.79 -0.31 山西、吉林、安徽、江西、河南、湖北、湖南、黑龙江 西部 2.58 3.86 -0.31 云南、内蒙古、四川、宁夏、广西、新疆、甘肃、西藏、贵州、重庆、陕西、青海 本研究由数据分析结果可以发现,全国公众对“延迟开学”政策的总体情绪反馈都呈现较为消极的态度,这在疫情严重肆虐的2020年初,是一种较为正常的情绪反馈。从社会群体上看,“延迟开学”政策虽然是疫情防控过程中的一个应对措施,但是政策的出台实际上也是从官方的角度上证实了此次疫情的特殊性和严重性,因此公众对此呈现消极的情绪也是情理之中。从学生群体上看,“延迟开学”政策的实施意味着学生难以享受学校的教学资源,难以保持原有的学习模式和学习状态,对于大多数学生而言,“延迟开学”政策会打乱他们正常的学习计划,影响他们的学习效率甚至是学习成绩,特别是对于即将面临考研、高考、中考等重要考试的学生而言,这更是艰难的挑战。从教师群体上看,“延迟开学”政策的实施意味着教师需要将传统的线下授课模式向线上转移,改变原有的授课计划、学习线上教学软件的使用、引导学生适应线上教学方式等,无形中增大了教师群体的教学压力。从学校上看,教学模式从线下向线上的转变对学校的师资力量、教学方法和教学设备也带来了巨大的挑战,特别是对于经济相对不发达和教育水平相对落后的地区而言,如何保证线上教学的正常开展成为学校的一大难题。从家庭关系上看,在长期的居家隔离中,家庭矛盾和家庭冲突也不断激增,因此延迟开学给家长也带来了巨大的压力,特别是对于双职工家庭而言,家长复工后孩子的照料成了巨大的问题。因此,无论是学生、学校还是家长,新学期的正常开学都是他们的共同期盼。
本研究从东、中、西部的比较分析结果还发现,东、中、西部地区之间公众对“延迟开学”政策的情绪反馈虽有显著差异,但是具体的情绪值相差较小。从三个地区公众各自的情绪反馈上看,东部地区公众对于“延迟开学”政策的积极情绪值(2.69)和消极情绪值(3.98)都最高,但东部地区整体上仍呈现较为消极的情绪,其整体情绪也最为消极(-0.32),这可能与地区的经济发展水平相关。相比而言,东部地区的经济发展速度较快,区域网络普及度较高,公众对于国家政策的关注度和政治参与意识也较高,能够更好理解国家政策的用意和目的,因此积极情绪值较高。但与此同时,由于东部地区的经济发展体量大、人员密度高等特征,疫情对该地区的影响也相比于其他地区更显著,稍有不慎,则会引发更为严重的间接影响,而且“延迟开学”政策的出台也意味着停工停产等相似措施,也极有可能同步推进。这对于地区经济、社会发展等多方面的影响也是显而易见的,因此该地区公众对于疫情的担忧也更显著,消极情绪值也更高。相比之下,中部地区和西部地区公众的情绪反馈较不强烈。其中,中部地区公众(2.64)对于“延迟开学”政策的积极情绪值比西部地区(2.58)稍高,而中部地区公众(3.79)的消极情绪值比西部地区(3.86)稍低。这可能与区域的整体疫情情况相关联,相比于中部地区,西部地区的整体疫情情况较为平缓,多个省级行政区仅有零星几个感染病例,因此,西部地区公众可能对疫情的风险感知程度相对较低,对于“延迟开学”政策的必要性认知较为不足,所以对政策的消极情绪反馈也较明显。相反,中部地区受疫情影响,对政策的出台可能更为支持。
2. 34个省级行政区微博用户对“延迟开学”政策的情绪差异
为了进一步探究不同地区公众对“延迟开学”政策的情绪反馈,本研究对新浪微博平台上公众的积极情绪值、消极情绪值、整体情绪值和贴子数量进行了梳理并根据地域进行分类,具体如表 4所示。其中,数据剔除了平台用户位置未明确或不清楚的数据,同时,中国台湾、中国香港特别行政区、中国澳门特别行政区等作为“延迟开学”政策非直接目标群体,其数据也暂不列入统计分析范围。
表 4 中国34个省级行政区微博用户情绪值和微博贴子数统计分析省级行政区 积极情绪值 消极情绪值 整体情绪值 贴子数 西藏 1.940 5.720 -0.660 17 内蒙古 2.090 3.880 -0.460 146 上海 2.600 4.260 -0.390 595 江苏 2.560 4.140 -0.380 1 137 吉林 2.410 3.800 -0.370 163 甘肃 2.640 4.190 -0.370 138 重庆 2.770 4.420 -0.370 307 湖南 2.380 3.700 -0.360 551 北京 2.500 3.840 -0.350 1 354 天津 2.690 4.110 -0.340 203 广东 2.660 4.050 -0.340 1 250 广西 2.160 3.270 -0.340 258 山东 2.710 3.960 -0.320 999 新疆 2.680 3.950 -0.320 67 江西 2.530 3.730 -0.320 248 浙江 2.590 3.800 -0.320 830 湖北 2.690 3.970 -0.320 372 云南 2.560 3.690 -0.310 193 四川 2.720 3.960 -0.310 599 河北 2.830 4.110 -0.310 393 海南 2.680 3.910 -0.310 72 河南 2.680 3.810 -0.300 853 辽宁 2.750 3.890 -0.290 320 安徽 2.550 3.490 -0.270 473 陕西 2.680 3.680 -0.270 370 山西 2.810 3.790 -0.260 214 黑龙江 3.080 4.060 -0.240 171 福建 2.970 3.750 -0.210 498 青海 2.350 2.980 -0.210 26 宁夏 2.770 3.200 -0.130 42 贵州 3.640 3.390 0.070 273 总计 13 132 本研究通过数据发现,在“延迟开学”这一话题的讨论中,贵州(截至北京时间2020年4月7日24时,贵州累计报告本地确诊病例146例,境外输入病例1例,死亡病例2例)微博用户表达的积极情绪词汇数量的情绪平均值最高,即整体的积极情绪值最高,黑龙江(截至北京时间2020年4月7日24时,黑龙江累计报告本地确诊病例482例,境外输入确诊病例30例)和福建(截至北京时间2020年4月7日24时,福建累计报告确诊病例296例,境外输入确诊病例55例)的微博用户在讨论“延迟开学”政策时也表现出较高的积极情绪。从消极情绪上看,青海(截至北京时间2020年4月7日24:00,青海累计报告确诊病例18例)微博用户表达的消极情绪词汇数量的情绪平均值最低,即整体的消极情绪值最低。同时,来自宁夏(截至北京时间2020年4月7日24时,宁夏累计报告确诊病例75例,且已连续35天无新增确诊病例)、贵州和广西(截至北京时间2020年4月7日24时,广西累计报告确诊病例254例,死亡2例)的微博用户对于“延迟开学”这一政策也较少表达负面情绪。此外,结合两种情绪值可以发现,来自西藏(截至北京时间2020年4月7日24时,西藏累计报告确诊病例1例)的微博用户针对“延迟开学”话题表达的积极词汇数量最少,而消极词汇数量最多。
本研究考虑到公众的情绪通常复杂而多样,将积极情绪和消极情绪综合考量更能反映公众对“延迟开学”政策的整体情绪倾向,进一步计算了34个省份用户的综合情绪值。我国除了贵州(整体情绪值为0.070 0)以外,整体上呈现出较为消极的趋势。其中,西藏的微博用户对“延迟开学”政策的整体情绪最为消极(-0.600),其次是内蒙古(-0.460 0),综合来看,较为明显消极情绪的区域均属于受疫情影响较轻的地区。这些地区的公众可能对于尽快恢复正常的学习、工作生活抱有较高的期待,因此对“延迟开学”这一暂停日常学习活动的政策存在一定的不理解,对该政策的消极情绪也较高。这也是符合假设H1b的预设情况。
在整体数据中,本研究针对唯一整体情绪值呈正值的贵州、消极情绪值最为明显的西藏以及受疫情影响最为严重的湖北三个特殊省级行政区,展开进一步的探讨和解释。
在本次采集的样本中,贵州是34个省级行政区中唯一一个公众对“延迟开学”政策整体情绪值呈现正值的省级行政区,从数据分析结果上发现,其中有部分用户虽然对该政策持消极态度(平均消极情绪值=3.390),但更多的用户持积极态度(平均积极情绪值=3.64);同时,根据贵州省卫生健康委员会发布的疫情信息,截至北京时间2020年4月7日24时,贵州累计报告本地确诊病例146例,境外输入病例1例,死亡2例。因此,从疫情数据上看,贵州虽然遭受疫情冲击不太严重,但其城市运行也并非不受疫情的影响。
本研究除了疫情本身的影响之外,尝试从地理位置和教育资源两方面对这一现象进行分析。从地理位置上看,贵州素有“八山一水一分田”之说,全省覆盖高原、山地、丘陵、盆地等多种特殊地形,唯独平原稀缺;受地形地貌的影响,常年遭受自然灾害的侵扰,当地公众对灾害的风险感知较高,对灾害可能造成后果的严重性评估也较高。因此,在疫情发生后,贵州宁愿选择更加谨慎的延迟开学措施,而不愿因为开学等活动影响疫情防控。不仅如此,从每年高考的参加人数和录取分数可以发现,贵州教育资源水平在全国范围内相对较低,而“延迟开学”政策的实施倒逼全省乃至全国线上教学的发展,这也意味着,当地学生能够享受到更多的教学资源和更高层次的教学水平。因此,从地理位置和教学资源两个角度上分析,贵州公众对于“延迟开学”政策所产生的积极情绪是可以理解的。
与贵州相反的是,西藏公众对于“延迟开学”政策表达出较为明显的消极情绪,这可能是因为疫情对当地的影响较小。根据西藏卫生健康委员会公布的疫情信息,截至2020年4月7日,西藏只有1例确诊病例。因此,与全国其他地区相比,西藏的疫情防控压力相对较小,当地公众的安全感也相对较高,这可能也是当地公众认为“延迟开学”政策必要性不高的原因。此外,西藏公众对“延迟开学”政策呈现出的消极情绪,也可能与西藏新浪微博用户对该话题关注度不高有关。本研究数据仅采集到17个来自西藏地区关于“延迟开学”政策的数据,其数量远低于其他省级行政区。因此,这些用户能否代表整个地区公众的整体态度也是值得深入探讨的。
此外,湖北也是值得本研究重点关注的一个省份。作为2020年深受疫情影响的地区,湖北承受了全国大部分的抗击疫情重任。在数据采集时间段内,全国绝大多数确诊病例和死亡病例均来自湖北省。一般来说,在这样一个遭受疫情严重影响的地区,公众出于自身安全考虑,应该对“延迟开学”政策持积极态度。然而,本研究通过新浪微博用户反馈发现,当地公众对“延迟开学”这一话题并没有明显的情绪倾向,其积极情绪值和消极情绪值均在全国34个省级行政区数值的中位值。这一现象与假设H1a不相符,但可能与当地公众对疫情的担忧和战胜疫情的信心有关。
武汉作为2020年初全国受疫情影响最严重的地区,一方面,当地公众对于“延迟开学”政策的积极情绪并未显著,这可能与当地的疫情形势有关。因为在疫情形势较为严重的地区,公众的生命健康安全受到严重威胁,对于与疫情直接相关的信息关注度较高。根据马斯洛需求层次理论,生命健康需求是人类最底层的需求,当疫情严重影响公众生命健康时,教育、工作等较高层次的需求会暂被忽略。因此,在受疫情影响较为严重的地区,公众可能更倾向于关注与疫情直接相关的信息,比如,疫情走向、疫情治疗方法、新增病例流调轨迹,等等。与此同时,社会正常的开学和开工,是疫情形态转好的象征,“延迟开学”政策对于当地公众可能有超乎政策本身的特殊含义;“延迟开学”政策在春节期间的出台,意味着全国范围内的疫情仍处于较为严重的形态,这对于深受疫情影响的地区而言,意味着当地公众可能需要承受更多的生命威胁。因此,这可能是当地公众对“延迟开学”政策积极情绪不高的原因,另一方面,湖北公众对“延迟开学”政策的消极情绪也并没有十分显著,这可能与疫情的严重态势和国家前期的抗击疫情投入有关。从理性上看,“延迟开学”政策的出台,确实能够有效减少公众的人员流动和接触,从而有效降低病毒感染的风险,对于疫情较为严重的地区而言,有效遏制病毒的扩散和传染是极为重要的政策。因此,公众对该政策仍是持理解的态度,消极情绪并没有十分显著。不仅如此,自疫情发生以来,来自全国数以万计的医疗队伍、部队官兵迅速驰援湖北,当地数以万计的基层工作人员和社区志愿者夜以继日英勇奋战,“火神山”“雷神山”两座方舱医院迅速建成,在政府的正确指挥下和全民的共同努力下,湖北的疫情迅速得到了控制并逐步好转。因此,这些举措也极大振奋了湖北公众对于抗击疫情的信心,使得他们对国家的政策保持足够的信任。这也表明,对于受疫情影响严重的地区而言,公众虽然仍处于焦虑恐慌的状态,特别是“延迟开学”政策的出台,使得他们更加意识到疫情的严重性和危害性,对于自身的健康和安全也极为担忧,但同时,当地公众也理解该政策是有效遏制疫情传播的重要举措,相信政府的力量,相信政策出台有其必要性和重要性,所以公众呈现出一个既非十分积极,而非十分消极的态度。
五. 结论与讨论
一 结果讨论
基于研究假设的验证情况,本研究结合数据分析过程及其现实意义,探究不同地区公众对“延迟开学”政策的情绪差异,对假设呈现的可能性进行阐释,并将其从“延迟开学”政策向突发公共卫生事件中的应急政策进行延伸,希望通过寻求合理的解释能够为突发公共卫生事件中的政策出台提供实践经验和科学分析,最终得出两个方面的结论。
1.重大突发公共卫生事件背景下的公共政策制定,是政府基于事件危机评判后对公众作出的回应
本研究认为,政府政策出台的目的本就为了帮助公众解决急难愁盼的问题,而倾听民声、回应民意本就应当是政府政策制定的先行之举;通过比较疫情变化情况、新浪微博发贴数量和“延迟开学”政策发布情况,发现新浪微博平台上社交媒体用户的关注度与疫情情况和政策发布密切相关。在疫情紧张时,公众对于“延迟开学”这一话题的关注度相对较低;但当疫情稳定时,公众对此的关注度则明显增高,尤其在“延迟开学”政策出台和调整前夕,平台用户对于“延迟开学”这一话题都开展了较为激烈的讨论,话题热度往往达到阶段峰值。这表明,公共政策的制定具有社会属性的面向,政府通过政策出台以回应公众热切关心话题,不仅可以指引公众正确开展突发公共卫生事件中的应对举措,帮助大部分公众解决当下难题,还可以通过公众的反馈及时快速调整政策以达到最佳的执行效果;同时,通过应急政策出台的形式,还应向公众传递出政府对其生命健康的尊重和重视,缓解公众对于突发公共卫生事件的担忧和压力,避免社会舆情的滋生和传播。
2.在重大突发公共卫生事件中,政府基于公众总体需求的政策制定,会在不同地区出现公众情绪反馈上的差异
本研究从数据和现实实践中发现,公众对于应急政策的情绪反馈在地区之间具有一定差异,可能是受公众所处区域突发事件危害程度的影响。在突发公共卫生事件暴发的中心区域,公众往往更关注与事件直接相关和与生命健康直接相关的政策和信息,而对于受突发公共卫生事件影响比较不严重的区域,公众对于相关应急政策的关注度可能更高,并且其关注度因所处区域的经济发展水平、教育资源水平、地理位置等其他因素的影响,即在突发公共卫生事件影响的外围区域,公众对于应急政策的情绪反馈往往是公众基于其所处现状权衡政策利弊之后的情绪表达。
二 政策建议与未来展望
基于数据分析及现实讨论,本研究尝试从公众情绪回应和区域具体分析两个维度,结合现有研究成果及其相关学理分析,探寻可能有效提升突发公共卫生事件背景下公共政策出台科学性和执行高效性的因素,并为突发公共卫生事件背景下公共政策出台提供参考建议。
1.主动关注公众情绪性反馈,以人为本提升政策配合积极性
公众的情绪反馈是公众对于社会现实情境的感受和体会,也是其表达个人需求和期盼的方式和途径。在突发公共卫生事件背景下,政府往往面临着千头万绪的应急工作,借助公众的眼睛发现社会风险、寻求治理痛点、快速开展应急预案不失为有效之举。不仅如此,通过关注公众在危机情境下的情绪反馈,还可以帮助政府厘清何为公众所需、何为公众所急、何为公众所盼等问题,从而确保政府的应急政策更具人性化和精准化。因此,越是在危机关头,政府越应当主动关注公众的情绪表达和情绪需求。具体而言,政府可以通过畅通线上线下民意征集平台、组建现代化信息服务队伍、主动公开危机相关信息、尽快尽早回应公众情绪等方式释放政策信号,寻求公众理解与配合。
2.打破区域一统化政策模式,因地制宜提升靶向治理精准度
我国幅员辽阔,经济发展差异大、文化蕴意内涵丰富,不同地区之间都各具特色、各有千秋,具体受到突发公共卫生事件的影响也千差万别。因此地方政府在遵循国家统一应急方案的基础上,也可以结合地方实际情况,因地制宜调整政策目标,既不过分严苛,也不松懈怠慢,使政策能够真真正正适配当地应急需求、造福地方公众。具体而言,地方政策调试过程中可以考虑突发公共卫生事件整体的危害性与地区现实影响程度、地区政策执行条件与公众日常生活需求之间的平衡关系,根据城市特征和公众需求开展精细化管理和服务工作,以实现精准化和人性化治理。
总体而言,本研究基于疫情期间公众对“延迟开学”政策的情绪反馈及其影响因素开展研究,为探索突发公共卫生事件下公众的情绪影响因素提供了一种研究方法。但是更加具体的影响因素还需要结合更多危机事件响应政策和公众情绪数据进行多维度论证,包括但不限于结合线上和线下的公众情绪分析,细化地域经济发展水平、疫情防控政策等。此外,本研究仅从客观因素上探究了不同地区公众对于“延迟开学”政策的情绪反馈差异,但具体的影响机理尚未明确,这也是后续研究值得继续探讨的焦点。
-
图 2 2020年1月1日至4月7日中国疫情情况
数据来源:中华人民共和国国家卫生健康委员会,http://www.nhc.gov.cn/,湖北省卫生健康委员会,http://wjw.hubei.gov.cn/bmdt/ztzl/fkxxgzbdgrfyyq/。
表 1 中国不同地区微博用户对“延续开学”政策情绪反馈回归分析的自变量描述性统计
类别变量 观测值 百分比/% 累计百分比/% 地区 东部(=1) 7 651 58.26 58.26 中部(=2) 3 045 23.19 81.45 西部(=3) 2 436 18.55 100 合计 13 132 100 数据来源:新浪微博平台。 表 2 中国不同地区微博用户对“延迟开学”政策情绪反馈的回归分析结果
变量 (1) (1) (2) (2) 情绪 情绪
Exp(B)情绪 情绪
Exp(B)地区 0 1 (·) (·) 中部 0.097 8** 1.103** (0.052 7) (0.058 1) 西部 0.144** 1.155** (0.056 3) (0.065 0) 关注量 0.000 08*** 1.000*** 0.000 08*** 1.000*** (0.000 020 7) (0.000 020 7) (0.000 020 7) (0.000 020 7) 粉丝量 -1.09×10-8*** 1.000*** -9.96×10-9** 1.000** (3.97×10-9) (3.97×10-9) (3.97×10-9) (3.97×10-9) 发贴量 0.000 009*** 1.000*** 0.000 009*** 1.000*** (0.000 001 01) (0.000 001 01) (0.000 001 00) (0.000 001 01) N 9 680 9 680 9 680 9 680 pseudo R2 0.012 0.012 0.013 0.013 注:双尾检验统计显著度,*** p < 0.01, ** p < 0.05,*p < 0.1。
数据来源:新浪微博平台。表 3 中国东、中、西部地区微博用户情绪值统计分析
区域 积极情绪值 消极情绪值 整体情绪值 涵盖省级行政区 东部 2.69 3.98 -0.32 上海、北京、天津、山东、广东、江苏、河北、浙江、海南、福建、辽宁 中部 2.64 3.79 -0.31 山西、吉林、安徽、江西、河南、湖北、湖南、黑龙江 西部 2.58 3.86 -0.31 云南、内蒙古、四川、宁夏、广西、新疆、甘肃、西藏、贵州、重庆、陕西、青海 表 4 中国34个省级行政区微博用户情绪值和微博贴子数统计分析
省级行政区 积极情绪值 消极情绪值 整体情绪值 贴子数 西藏 1.940 5.720 -0.660 17 内蒙古 2.090 3.880 -0.460 146 上海 2.600 4.260 -0.390 595 江苏 2.560 4.140 -0.380 1 137 吉林 2.410 3.800 -0.370 163 甘肃 2.640 4.190 -0.370 138 重庆 2.770 4.420 -0.370 307 湖南 2.380 3.700 -0.360 551 北京 2.500 3.840 -0.350 1 354 天津 2.690 4.110 -0.340 203 广东 2.660 4.050 -0.340 1 250 广西 2.160 3.270 -0.340 258 山东 2.710 3.960 -0.320 999 新疆 2.680 3.950 -0.320 67 江西 2.530 3.730 -0.320 248 浙江 2.590 3.800 -0.320 830 湖北 2.690 3.970 -0.320 372 云南 2.560 3.690 -0.310 193 四川 2.720 3.960 -0.310 599 河北 2.830 4.110 -0.310 393 海南 2.680 3.910 -0.310 72 河南 2.680 3.810 -0.300 853 辽宁 2.750 3.890 -0.290 320 安徽 2.550 3.490 -0.270 473 陕西 2.680 3.680 -0.270 370 山西 2.810 3.790 -0.260 214 黑龙江 3.080 4.060 -0.240 171 福建 2.970 3.750 -0.210 498 青海 2.350 2.980 -0.210 26 宁夏 2.770 3.200 -0.130 42 贵州 3.640 3.390 0.070 273 总计 13 132 -
[1] 文宏. 危机情境中的人群"圈层阻隔"现象及形成逻辑——基于重大传染病事件的考察[J]. 政治学研究, 2021(4): 134-142. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-POLI202104014.htm [2] CAMPBELL A L. Policy makes mass politics[J]. Annual Review of Political Science, 2012, 15(1): 333-351. doi: 10.1146/annurev-polisci-012610-135202
[3] 朱春奎, 刘梦远, 徐菁媛. 气候政策态度研究进阶与拓展[J]. 南京社会科学, 2021(5): 71-81. doi: 10.15937/j.cnki.issn1001-8263.2021.05.009 [4] 王洪涛, 陈洪侠. 公众公共政策态度实证研究——以沈阳市为例[J]. 未来与发展, 2009, 30(3): 8-12. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-0166.2009.03.002 [5] 邱尔丽, 张竞, 王雨舟, 等. 基于网络舆情大数据的公共政策评价研究[J]. 领导科学, 2021(8): 118-121. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-2606.2021.08.034 [6] 魏传光. 现代人的生存焦虑及其排解[J]. 理论与现代化, 2010(5): 104-107. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-1502.2010.05.019 [7] 程同顺. 提高公共政策目标群体的能动性[J]. 群众, 2017(22): 51-52. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-QUNZ201722029.htm [8] KUCHARSKI A J, RUSSELL T W, DIAMOND C, et al. Early dynamics of transmission and control of COVID-19: a mathematical modelling study[J]. The Lancet Infectious Diseases, 2020, 20(5): 553-558. doi: 10.1016/S1473-3099(20)30144-4
[9] 戴维·迈尔斯. 社会心理学[M]. 侯玉波, 乐国安, 张智勇, 等, 译. 北京: 人民邮电出版社, 2016: 118-119. [10] PODGORSKI K V, KOCKELMAN K M. Public perceptions of toll roads: a survey of the Texas perspective[J]. Transportation Research Part A: Policy and Practice, 2006, 40(10): 888-902. doi: 10.1016/j.tra.2006.03.002
[11] TORRITI J, HASSAN M G, LEACH M. Demand response experience in Europe: policies, programmes and implementation[J]. Energy, 2010, 35(4): 1575-1583. doi: 10.1016/j.energy.2009.05.021
[12] BAIG S A, PEPPER J K, MORGAN J C, et al. Social identity and support for counteracting tobacco company marketing that targets vulnerable populations[J]. Social Science & Medicine, 2017, 182: 136-141.
[13] 马壮林, 崔姗姗, 胡大伟. 基于MIMIC模型的限行政策下城市居民低碳出行意向研究[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021: 1-10. [14] 张润泽, 杨华. 转型期乡村治理的社会情绪基础: 概念、类型及困境[J]. 湖南师范大学社会科学学报, 2006(4): 11-13. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HNSS200604001.htm [15] DE RIVERA J, PÁEZ D. Emotional climate, human security, and cultures of peace[J]. Journal of Social Issues, 2007, 63(2): 233-253. doi: 10.1111/j.1540-4560.2007.00506.x
[16] 李从东, 洪宇翔. 面向突发事件的社会情绪稳定性建模方法研究[J]. 情报杂志, 2014, 33(01): 146-151. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-QBZZ201401027.htm [17] BAR-TAL D, HALPERIN E, DE RIVERA J. Collective emotions in conflict situations: societal implications[J]. Journal of Social Issues, 2007, 63(2): 441-460.
[18] 杨铭, 向德平. 重大疫情中负面社会情绪的治理[J]. 社会工作, 2020(1): 16-19. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SHGO202001005.htm [19] 陈潭, 黄金. 群体性事件的网络舆情及其传播逻辑[J]. 理论探讨, 2011(4): 140-142. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LLTT201104034.htm [20] 叶宁玉, 王鑫. 从若干公共事件剖析网络群体极化现象[J]. 新闻记者, 2012(1): 46-51. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XWJZ201201010.htm [21] 易臣何, 李杉. 舆情危机事件中网民情绪生成及其对政府形象的影响分析[J]. 公共管理与政策评论, 2021, 10(4): 73-83. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GGZC202104010.htm [22] KIM. Bringing the emotion back in: an emotion-based interpretation of the communicative conflict between government and citizens[J]. The Korea Association for Policy Studies, 2011, 1(20): 83-110.
[23] 洪宇翔. 风险视角下网络空间社会情绪的形成和干预[J]. 浙江学刊, 2017(4): 135-139. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZJXK201704018.htm [24] WILKINSON E. The emotions least relevant to politics? queering autonomous activism[J]. Emotion, Space and Society, 2009, 2(1): 36-43.
[25] 蹇嘉, 甄峰, 席广亮, 等. 西方情绪地理学研究进展与启示[J]. 世界地理研究, 2016, 25(2): 123-136. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SJDJ201602013.htm [26] GRUEBNER O, LOWE S, SYKORA M, et al. Spatio-temporal distribution of negative emotions in new york city after a natural disaster as seen in social media[J]. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 2018, 15(10): 2275.
[27] HAN X, WANG J. Using social media to mine and analyze public sentiment during a disaster: a case study of the 2018 Shouguang city flood in China[J]. ISPRS International Journal of Geo-Information, 2019, 8(4): 185.
[28] HAN X, WANG J, ZHANG M, et al. Using social media to mine and analyze public opinion related to COVID-19 in China[J]. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 2020, 17(8): 2788.
[29] YU S, EISENMAN D, HAN Z. Temporal dynamics of public emotions during the COVID-19 pandemic at the epicenter of the outbreak: sentiment analysis of weibo posts from Wuhan[J]. Journal of Medical Internet Research, 2021, 23(3): e27078.
[30] DING Y, XU J, HUANG S, et al. Risk perception and depression in public health crises: evidence from the COVID-19 crisis in China[J]. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 2020, 17(16): 5728.
[31] SMITH N, LEISEROWITZ A. The role of emotion in global warming policy support and opposition[J]. Risk Analysis, 2014, 34(5): 937-948.
[32] TABOADA M, BROOKE J, TOFILOSK M, et al. Lexicon-based methods for sentiment analysis[J]. Computational Linguistics, 2011, 2(37): 267-307.
[33] PORIA S, CAMBRIA E, WINTERSTEIN G, et al. Sentic patterns: dependency-based rules for concept-level sentiment analysis[J]. Knowledge-based Systems, 2014, 69: 45-63.
[34] 曾润喜, 杜换霞, 王君泽. 网络舆情指标体系、方法与模型比较研究[J]. 情报杂志, 2014, 33(4): 96-101. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-QBZZ201404017.htm [35] 李光敏, 张行文, 张磊, 等. 面向网络舆情的评论文本情感分析研究[J]. 情报杂志, 2014, 33(5): 157-160. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-QBZZ201405029.htm [36] WILSON T, WIEBE J, HOFFMANN P. Recognizing contextual polarity: an exploration of features for phrase-level sentiment analysis[J]. Computational Linguistics - Association for Computational Linguistics, 2009, 35(3): 399-433.
[37] KRYVASHEYEU Y, CHEN H, OBRADOVICH N, et al. Rapid assessment of disaster damage using social media activity[J]. Science Advances, 2016, 2(3): e1500779.
[38] TAUSCZIK Y R, PENNEBAKER J W. The psychological meaning of words: LIWC and computerized text analysis methods[J]. Journal of Language and Social Psychology, 2010, 29(1): 24-54.
[39] BACAKSIZLAR N G, SHAIKH S, HADZIKADIC M. Anger in protest networks on twitter: ICT, Society and Human Beings 2019. Connected Smart Cities 2019 and Web Based Communities and Social Media 2019, Porto, Portugal, 2019[C].
[40] TAGO K, JIN Q. Influence analysis of emotional behaviors and user relationships based on Twitter data[J]. Tsinghua Science and Technology, 2018, 23(1): 104-113.
-
期刊类型引用(6)
1. 佘硕,林雅玲. 基于LDA主题模型的我国突发公共卫生事件应急管理主题热度与趋势分析. 中国应急管理科学. 2024(06): 66-85 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 苏欣宇,张海涛,张鑫蕊,刘伟利. 重大突发事件下应急管理部门政府回应性的组态归因研究. 情报学报. 2024(11): 1297-1309 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 李明德,寇杰. 铸牢中华民族共同体意识的网络具象化传播. 北京工业大学学报(社会科学版). 2023(05): 19-31 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 高光涵. 总体应急预案的府际差异与量化评价——基于29个省级预案文本的比较分析. 北京工业大学学报(社会科学版). 2023(06): 113-128 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 李晓,徐晓雨. 我国社交网络舆情研究的热点与趋势——基于CiteSpace的可视化分析. 电脑知识与技术. 2023(32): 4-7 .  百度学术
百度学术
6. 裴玲燕. 突发公共卫生事件背景下艺术类院校大学生心理状态调查分析——以新冠肺炎疫情为例. 心理月刊. 2022(24): 209-211+226 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(8)



 下载:
下载: