Efficient Absorption of 1,2-dichloroethane by Ionic Liquids
-
摘要:
为解决传统吸收过程中存在的能耗高、溶剂挥发性损失大问题,提出离子液体高效吸收废气中1,2-二氯乙烷(DCE)技术,在预测型分子热力学理论的指导下,从分子尺度到过程尺度系统研究了其应用前景。首先采用COSMO-RS模型进行离子液体结构(阳离子骨架结构、羧酸盐阴离子链长及氟化)对分离性能(1,2-二氯乙烷与氮气的选择性及溶解度)的影响分析,并筛选出适宜的离子液体(1-丁基-3-甲基咪唑醋酸盐,[BMIM][Ac])。通过实验方法测定不同离子液体中DCE的饱和吸收容量,验证COSMO-RS模型的适用性;并进一步考察吸收温度和DCE初始含量对[BMIM][Ac]吸收性能的影响,结果表明在20 ℃、常压、进气DCE为饱和含量时[BMIM][Ac]对DCE的饱和吸收容量达到2 177 mg/g。在分子尺度,采用量子化学计算和波函数分析,探讨了离子液体吸收1,2-二氯乙烷的微观机理。结果表明吸收过程阴离子起主导作用,表现为强氢键作用和范德华(vdW)色散作用,阳离子与DCE间主要以C—H…Cl相互作用和vdW色散作用结合。最后在过程尺度,对离子液体吸收DCE的工艺进行了概念设计和流程优化,在给定条件下,离子液体对1,2-二氯乙烷的去除率达到99.88%。通过与传统有机溶剂进行对比,发现离子液体具有更低的产品损失、溶剂损失和能耗。表明采用离子液体吸收1,2-二氯乙烷是一种不错的策略,具有一定的工业应用潜力。
Abstract:The traditional organic solvent absorption process is characterized by high energy consumption and large solvent volatility lass. To solve this problem, this work proposes to use ionic liquids (ILs) for efficient absorption of 1,2-dichloroethane from waste gas, and guided by a predictive molecular thermodynamic model, this paper systematically investigated the practical application prospects from the molecular to system scales. The COSMO-RS model was used to screen 476 types of ILs. The effect of IL structure on the absorption of 1,2-dichloroethane was investigated from the cationic skeleton, the length of carboxylate anion carbon chain and the degree of fluorination. It was found that the nonaromatic non cyclic cations and the shorter carboxylate anion carbon chain length and the nonfluorinated anion structure were conducive to the better absorption of 1,2-dichloroethane by ILs. Finally, 1-butyl-3-methylimidazole acetate ([BMIM][Ac]) was determined as the appropriate absorbent. The optimization experiment of absorption conditions was conducted at different temperatures and partial pressures, and the results showed that the saturated absorption capacity of [BMIM][Ac] for 1,2-dichloroethane reached 2177 mg/g at 20℃ and atmospheric pressure. Through quantum chemistry calculation and wave function analysis, the microscopic mechanism of ionic liquid absorbing 1,2-dichloroethane was discussed. The reason for enhanced absorption is due to the strong HB effect and vdW dispersion effect, which are significantly contributed by anions. Cations are mainly combined with C—H…Cl interaction and vdW dispersion effect. Conceptual design and process simulation were conducted on the process of DCE absorption by ILs. An equilibrium stage model (EQ) was established for the absorption process, and COSMO-SAC was selected as the thermodynamic model. For the selected operating conditions, the removal rate of 1,2-dichloroethane by ILs reached 99.88%. Compared to traditional organic solvents, it was found that ILs have lower product gas loss and energy consumption. This indicates that using ILs to absorb 1,2-dichloroethane is a good strategy and has certain industrial potential.
-
近年来,随着经济和社会的发展,环境污染已然成为当今世界各国亟待解决的难题之一。大气中的挥发性有机化合物(volatile organic compounds, VOCs)是导致环境问题的一大类重要污染物,包括BTXs(benzene(苯)、toluene(甲苯)、xylene(二甲苯))、醛类、酮类和氯化烃类等,特别是含氯VOCs——排在欧共体公布的废气黑名单的首位。含氯VOCs主要包括烷烃类(二氯甲烷、氯甲烷、氯仿、四氯化碳、二氯乙烷等)、烯烃类(氯乙烯、三氯乙烯等)和芳烃类(氯苯、二氯甲苯)等,其在使用过程中通过挥发、泄露、排放等途径进入环境中,还会造成臭氧层破坏、光化学烟雾等,并且含氯VOCs难于生物降解,易于在生物体内积累,具有很强的致癌、致畸、致突变的“三致”作用。其中1,2-二氯乙烷(1,2-dichloroethane,DCE)是重要的有机合成原料,广泛应用于化工行业,国内二氯乙烷的年产能在2.00 Mt/a左右,年需求量约1.05 Mt[1],全球约有95%的DCE用于生产氯乙烯单体。但由于DCE的沸点较低,挥发性强,在使用过程中极易逃逸到环境中。且DCE在环境中降解周期较长,将带来持续的生态污染和人体健康损害,寻找一种合适的捕集DCE技术迫在眉睫。
VOCs处理技术大体上可以分为两大类[2]:一类是销毁技术[3],包括热破坏法(直接燃烧法、催化燃烧法和浓缩燃烧法)、生物法及光化学氧化法;一类是回收法,包括吸收法、冷凝法、吸附法、膜分离法。光催化降解虽然反应条件较温和,但降解效率很低。燃烧法需要高温环境而消耗大量的能量,同时会产生很多副产物,如二噁英、氮氧化物等,并且给环境污染治理带来很大的后续难题[4]。回收技术以吸附法和吸收法应用最为广泛。活性炭、活性炭纤维、树脂聚合物、金属有机框架(metal organic framework,MOFs)材料等常用的气体吸附剂,初期吸附效果好,但其再生不彻底,吸附能力衰减快;且一般吸附法仅适应用于大通量、低浓度(体积分数小于1%)的废气间歇回收处理过程[5-6]。相比较之下,吸收法工艺流程简单、操作稳定,被广泛应用于聚氯乙烯(polyvinyl chloride,PVC)行业氯乙烯尾气、有机硅生产过程尾气处理等含氯挥发性有机物(chlorinated volatile organic compound,CVOCs)回收过程[7]。吸收法能否高效回收CVOCs的关键是吸收剂,目前工业上常用的传统溶剂有三甘醇、聚乙二醇、矿物油等,由于沸点高、价格低等得到应用广泛。但溶剂再生过程存在能耗高、装置体积大的缺点,同时溶剂具有挥发损失,易造成二次污染[8-9]。因此为了克服上述问题,必须寻找高效节能、挥发性低、热稳定性高的新型吸收剂。
近几年来,离子液体(ionic liquids,ILs)由于极低的蒸汽压、广泛的电化学窗口、良好的热稳定性和化学稳定性、结构可调等特点被称为“可设计合成的绿色溶剂”[10-11],受到国内外学者的广泛关注,在气体分离、萃取分离、电化学催化、聚合材料的化学回收等方面具有良好应用[12-14]。到目前为止,离子液体在气体分离过程中发挥着重要作用,例如酸性气体捕获[15-17]、气体干燥[9, 18]和挥发性有机化合物[19-20]捕获。Wu等[21]基于COSMO-RS模型筛选出1-乙基哌啶醋酸盐(1-ethylpiperidine acetate,[C2Pip][C1COO])作为吸收二氯甲烷的最佳离子液体(亨利常数为3.29 kPa),通过工艺流程模拟与传统有机溶剂进行比较,发现所选离子液体年运行费用最低。Cheng等[22]提出离子液体可用作氯乙烯吸收的替代绿色溶剂,并且氯乙烯可在较高温度和真空条件下解吸。Gui等[23]采用1-乙基-3-甲基咪唑醋酸盐(1-ethyl-3-methylimidazole acetate,[EMIM][Ac])吸收二氯甲烷,实验结果表明在20 ℃和环境压力下,二氯甲烷的去除率达到91.82%。本课题组采用1-乙基-3-甲基咪唑四氟硼酸盐对氯苯类废气进行深度脱除,净化气中C6H5Cl(氯苯)/C6H4Cl2(邻二氯苯)的摩尔分数可降至13.6/(9.9×10-6)[24]。
上述研究表明离子液体高效捕集CVOCs技术是可行的,同时为更深入了解体系的作用机制,使用量子化学计算来进行分析。借助计算机的发展,量子化学已有了广泛的应用,它可以在不依赖实验数据的情况下,预测分子的相对稳定性、研究反应机理等[25]。其中密度泛函理论(density functional theory,DFT)即以电子密度函数的方法来描述分子的结构和性质。经过多年发展,DFT对离子液体的量化计算也引起很多关注。在Wang等[26]的研究中,通过DFT计算揭示了木质素在离子液体中溶解是阴离子和阳离子共同作用的结果。鉴于离子液体良好的工业应用前景,因此模拟其在工业规模上的操作条件是必不可少的。过程模拟主要用于单元过程所组成的化工过程系统的模拟。其中的生产装置设计、稳态模拟和优化功能,可以在依靠简单的物性数据的条件下,模拟出符合实际工艺所需的单元操作条件。而这大大节省了实验人员的时间和精力,因此在化工、石化、炼油等过程工业制造行业得到广泛应用[27]。
虽然研究人员对离子液体在CVOCs治理方面开展了很多的工作,但是目前对于DCE捕集方面的系统研究尚未见报道。本文在前期工作基础上提出采用离子液体高效吸收废气中DCE技术,并对其从以下几个方面展开系统研究:1)采用COSMO-RS模型进行离子液体结构(阳离子骨架结构、羧酸盐阴离子链长及氟化)对分离性能(DCE与氮气的选择性及溶解度)的影响分析,筛选出适宜的离子液体; 2)测定不同离子液体中DCE的饱和吸收容量,验证COSMO-RS模型的适用性,并进一步考察吸收温度和DCE初始含量对[BMIM][Ac]吸收性能的影响; 3)在分子尺度,采用量子化学计算和波函数分析,探讨离子液体吸收DCE的微观机理; 4)在过程尺度,对离子液体吸收DCE的工艺进行概念设计和流程优化,并与传统有机溶剂吸收进行比较。
1. 实验部分
1.1 材料
DCE(质量分数99%)购自上海阿拉丁生化科技股份有限公司,N2(质量分数99.9%)购自北京北氧氧源股份有限公司,离子液体(质量分数99%)均购自上海成捷化学有限公司,所有试剂均直接使用而无须预处理。
1.2 饱和吸收容量测量
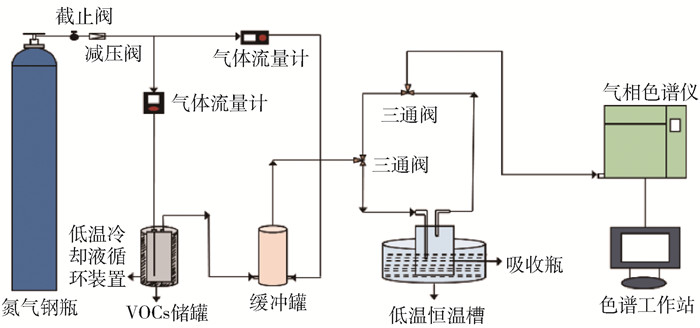
采用静态法测定离子液体中DCE的饱和吸收容量,实验装置示意图如图 1所示。将装有离子液体(每次用量约2 g)的高约17 cm、吸收口内径约3 mm的玻璃吸收瓶置于恒温水浴槽中(北京神泰伟业仪器设备有限公司,DFY-5/20),温控波动为±0.01 ℃。实验采用氮气作为载体,自钢瓶分为2股气路:一股氮气通入DCE储罐中采用鼓泡的方式获得饱和含量DCE气体,其中储罐温度控制在(20±0.01) ℃;另一股氮气作为稀释气通入缓冲罐中,与第一股气充分混合,通过调节2股气的比例从而获得不同DCE初始含量的原料气。在实验中,原料气以100 mL/min的气速由储罐进入吸收瓶,经由离子液体充分吸收后,净化气体进入气相色谱。采用气相色谱(山东鲁南瑞虹化工仪器有限公司,SP-6890型)中的FID检测器,每间隔5 min进行一次采样记录,测定原料气及吸收后尾气中DCE含量,60 min内稳定不变时,认为达到平衡状态。采用重量法确定饱和吸收容量(absorption capacity, AC, mg/g),具体计算式为
$$ \mathrm{AC}=\frac{m_2-m_1}{m_1-m_0} \times 1\;000 $$ (1) 式中:m0为吸收瓶质量,g;m1和m2分别为吸收前、后吸收瓶和IL的总质量,g,实验过程中采用电子天平进行称重,精度为±0.000 1 g。
2. 模型描述
2.1 COSMO-RS模型
COSMO-RS模型是Klamt等[28]开发的,作为一种不依靠实验数据的先验预测型分子热力学模型,在离子液体筛选及预测气体溶解度方面受到了广泛关注。本工作采用量子化学软件Gaussian 09(D.01)将所需的离子液体结构进行几何构型优化,随后将得到的COSMO文件导入COSMOthermX软件(19.0.4)预测DCE和氮气在离子液体中的亨利常数及选择性。
2.2 量子化学计算
在分子尺度,采用DFT方法Gaussian 09 (D.01) B3LYP/6-31+G (d, p)[29]基组对所有体系几何结构进行预优化,利用DFT-D3 (BJ)进行色散校正[30-31],同时进行振动频率分析,从而确定最稳定结构,用于分子弱相互作用的分析。之后将优化好的几何构型在B3LYP/6-311++G (d, p) 基组计算相互作用能[32],为消除基组叠加计算带来的能量误差,引用BSSE能量矫正,计算公式为
$$ \Delta E_{\mathrm{A}+\mathrm{B}}=E_{\mathrm{A}+\mathrm{B}}-E_{\mathrm{A}}-E_{\mathrm{B}}+E_{\mathrm{BSSE}} $$ (2) 式中EA、EB、EA+B和EBSSE分别代表组分A、组分B、A+B体系以及基组叠加误差项的能量,所有计算能量值均已经过零点校正。
最后通过Multiwfn (3.7)[33]软件对DCE-IL体系进行独立梯度模型(independent gradient model based on Hirshfeld partition,IGMH)[34]、静电势(electrostatic potential,ESP)[35]的弱相互作用分析。
2.3 流程模拟
在过程尺度,对优选离子液体吸收DCE的工艺进行了概念设计和流程优化,采用Aspen Plus (V12)软件构建吸收塔和闪蒸罐的平衡级数学模型,其中热力学模型选择COSMO-SAC模型,离子液体作为虚拟组分借助COSMOthermX软件进行创建。并与常用传统有机溶剂吸收剂(三甘醇,TEG)从吸收性能、吸收剂用量、能耗等方面进行比较,考察离子液体吸收DCE的工业应用前景。
3. 结果与讨论
3.1 适宜离子液体筛选及构效分析
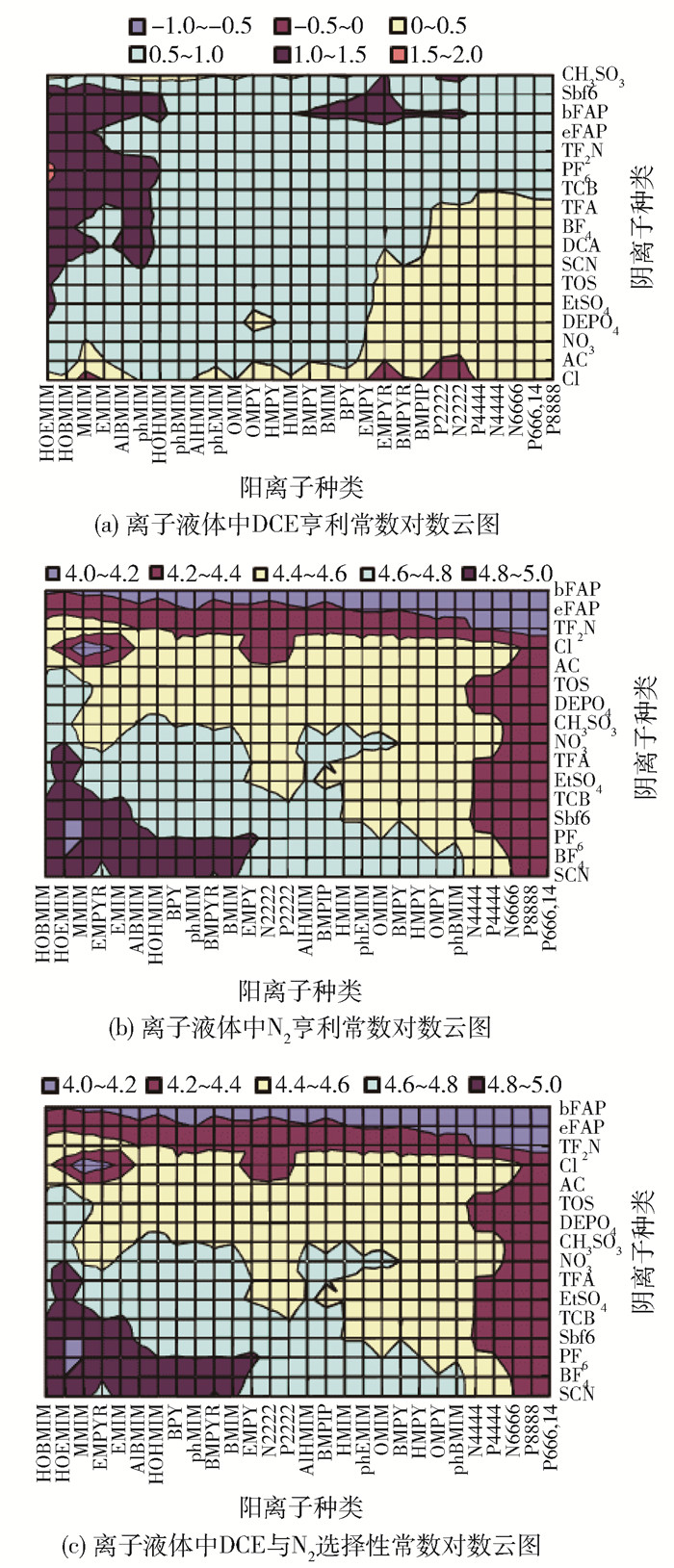
采用COSMO-RS模型的COSMOthermX软件预测了476种(28种阳离子和17种阴离子两两组合)常见离子液体中DCE和氮气的亨利常数和选择性,有关COSMO-RS模型计算过程详见 https://www.scm.com/doc/Tutorials/COSMO-RS/Ionic_Liquids.html。亨利常数可通过无限稀释活度系数获得,选择性定义为氮气与DCE的亨利常数之比,相关表达式为
$$ H_i=\lim\limits _{x_i \rightarrow 0}\left(\gamma_i p_i^{\mathrm{s}}\right)=\gamma_i^{\infty} p_i^{\mathrm{s}} $$ (3) $$ S_{\mathrm{DCEN}_2}=\frac{H_{\mathrm{N}_2}}{H_{\mathrm{DCE}}} $$ (4) 式中:Hi为组分i的亨利常数,kPa;γi和γ∞i分别表示在有限浓度(xi)和无限稀释时的活度系数;psi为给定温度下的饱和蒸汽压。
从图 2中可以看出,离子液体中DCE和氮气的溶解度(亨利常数)及选择性由阴阳离子共同主导。众所周知,溶解度越大则亨利常数越小。氮气的亨利常数(104~105 kPa)远大于DCE的亨利常数(10-1~102 kPa),根据式(4)定义的选择性可知,离子液体表现出非常高的DCE选择性(约104),因此后续离子液体筛选主要考虑DCE的溶解性能,并系统探讨离子液体结构(阳离子骨架、羧酸阴离子链长及氟化)对DCE亨利常数的影响。
3.1.1 阳离子骨架对DCE吸收影响
选取不同阴离子([Ac]-、[BF4]-、[EtSO4]-和[CH3SO3]-)考察阳离子骨架(非环状季铵盐[N4444]+和季膦盐[P4444]+、环状吡咯烷盐[BMPYR]+和哌啶盐[BMPIP]+、芳香族咪唑阳离子[BMIM]+和吡啶阳离子[BMPY]+)对DCE吸收的影响,结果如图 3所示。可见离子液体中DCE亨利常数从大到小依次为芳香族阳离子、非芳香环状阳离子、非环状非芳香族阳离子,这可能是由于非环状非芳香族阳离子的长链状结构使得其有更多的位点与其他物质结合,同时具有较大的自由体积。芳香族阳离子较其他2种骨架阳离子具有更大的空间位阻,与DCE结合形成氢键的能力较弱[36]。同时芳香族结构中咪唑阳离子的亨利常数整体要高于吡啶阳离子的亨利常数,这是因为咪唑阳离子具有的五元环结构体积要小于吡啶阳离子的六元环结构,使得吡啶阳离子承受了更多电子离域带来的环变形,与DCE之间形成更强的范德华力。
虽然非环状非芳香族阳离子表现出较低的亨利常数,但较其他阳离子具有的高黏度性质使得在实际工业中对吸收过程的传质不利,对管道运输的要求增大。除黏度外离子液体的热稳定性和价格也是需要衡量的因素,而咪唑阳离子具有的π电子特性使得其较其他阳离子具有更好的热稳定性[37]和更低的成本,因此接下来选择咪唑盐阳离子进一步探究阴离子结构的影响。
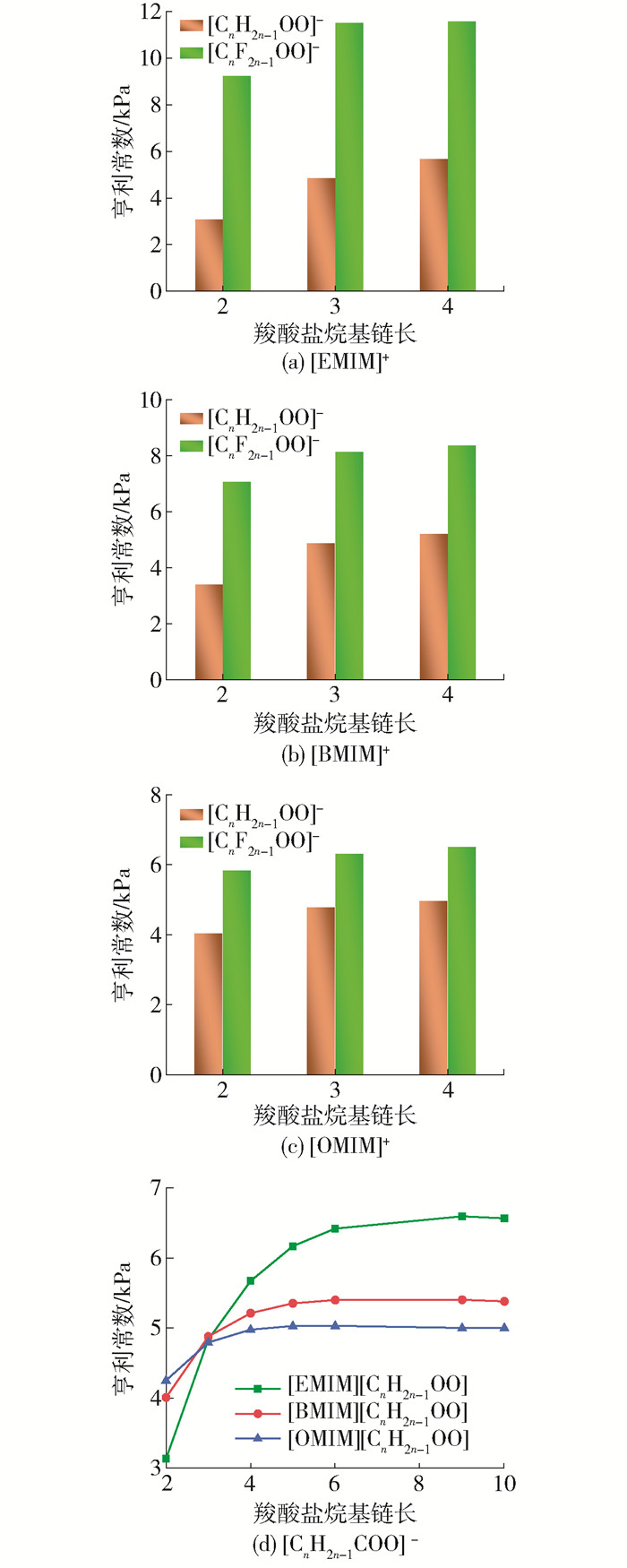
3.1.2 羧酸阴离子结构对DCE吸收影响
由图 2(a)可见醋酸阴离子基离子液体均表现出优良的DCE吸收性能(低亨利常数),因此,针对羧酸阴离子结构(氟化作用、烷基链长度)对吸收性能进一步进行研究。由图 4可见,对于相同的阳离子([EMIM]+、[BMIM]+、[OMIM]+),羧酸阴离子氟化后([CnF2n-1OO]-)比相同碳链长度未氟化的离子液体表现出更高的DCE亨利常数,即羧酸阴离子被氟化后,咪唑基离子液体对DCE的吸收性能变差。主要是因为氟化后离子液体的极性增强,与DCE间静电斥力增大。此外,对于氟化羧酸基离子液体,DCE亨利常数随着阴离子烷基链长(n在2~4范围内)的增大而增大,随阳离子烷基链长度增大而减小,同时可以看到氟化后的羧酸基离子液体均表现出比非氟化羧酸基离子液体更大的亨利常数,这表明阴离子氟化对吸收不利。
针对非氟化羧酸离子液体进一步考察了烷基链长度(C2~C10)对DCE溶解度的影响,可见,当阴离子碳链数大于5时,进一步增长碳链长度DCE亨利常数值增长减缓。说明当羧酸盐阴离子碳链数较小(小于5)时, 碳链的增加会显著降低离子液体的吸收性能;而当羧酸盐阴离子碳链数较大(大于5)时, 碳链的增长对离子液体的吸收性能影响较小。
3.2 饱和吸收容量实验结果
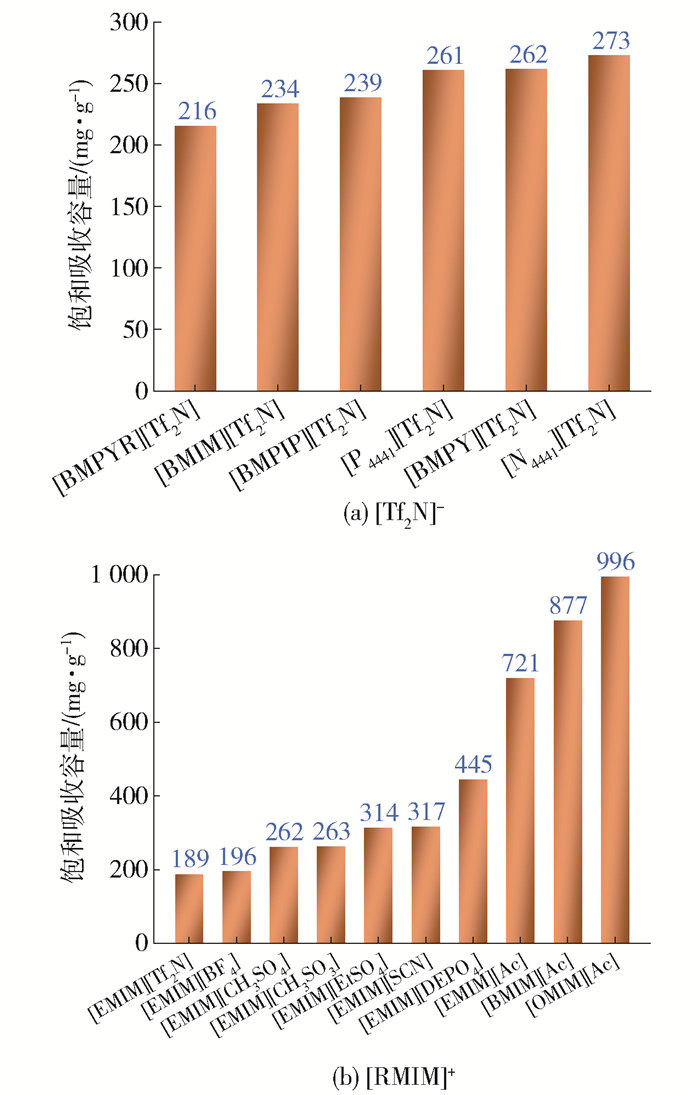
DCE in different ILs at 30 ℃在30 ℃、进气DCE为0.008 4 MPa(20 ℃下饱和蒸汽含量)时,进一步采用实验方法测定了阴阳离子结构对DCE饱和吸收容量的影响,实验过程气体流速为100 mL/min,实验结果如图 5所示。可见,当阴离子固定为[Tf2N]-时,所考察离子液体的饱和吸收容量都在200 mg/g以上,均表现出了DCE良好的吸收性能。同时可见,相比环状阳离子非芳香族非环状阳离子具有更高的吸收容量,与COSMO-RS预算的结果一致。但是阳离子结构对DCE饱和吸收容量的影响不大。
从图 5(b)中可以看出,当阳离子为[EMIM]+时,不同阴离子结构的离子液体中DCE饱和吸收容量差异很大。[EMIM][Tf2N]饱和吸收容量最小,为189 mg/g,[EMIM][Ac]具有最大的饱和吸收容量为721 mg/g。随后选择阴离子为[Ac]-,实验考察了咪唑阳离子烷基链长度对DCE饱和吸收容量的影响。结果表明随阳离子烷基链增长,DCE饱和吸收容量增大。其中,[OMIM][Ac]饱和吸收容量为996 mg/g,[BMIM][Ac]饱和吸收容量为877 mg/g。同时对比了其他关于使用离子液体吸收DCE的工作,Wang等[38]在313.15 K、常压下使用离子液体[BMIM][DCA]对DCE的吸收容量为370 mg/g。Song等[39]使用[EMIM][BF4]对DCE的吸收率为95.81%,本工作也选取了[EMIM][BF4]作为吸收剂,其在30 ℃下的饱和吸收容量为196 mg/g。但在吸收过程中,黏度、热分解温度以及成本也是决定适宜吸收剂选择的重要因素。表 1为测定的不同温度下[BMIM][Ac]和[OMIM][Ac]黏度,可以看到[BMIM][Ac]的黏度更小。综合考虑,本工作选取[BMIM][Ac](热分解温度:[BMIM][Ac]为216 ℃;[OMIM][Ac]为216 ℃)[11]为吸收剂进一步考察操作参数对吸收容量的影响。
表 1 离子液体在不同温度下的黏度Table 1. Viscosity of ionic liquids at different temperaturesPa·s 温度/℃ [BMIM][Ac] [OMIM][Ac] 20 432.33 970.26 25 300.64 720.63 30 215.07 553.71 35 157.85 391.68 40 118.78 285.51 3.3 温度和DCE初始含量对吸收容量的影响
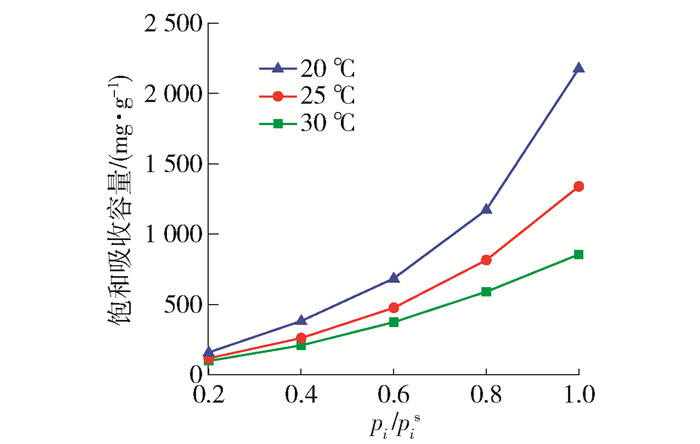
针对优选的[BMIM][Ac]离子液体进一步探讨了操作温度和进气中DCE含量(分压pi/psi,其中psi为DCE在20 ℃时饱和分压)对吸收的影响,如图 6所示。可见,DCE饱和吸收容量随温度的降低而逐渐增大,即低温有利于吸收;随进气中DCE分压的增大吸收容量显著提高,在低压时,饱和吸收容量与分压呈正相关,说明吸收过程为物理吸收,可通过提高温度或降低压力的手段实现吸收后离子液体的再生。
3.4 从分子水平探讨吸收机理
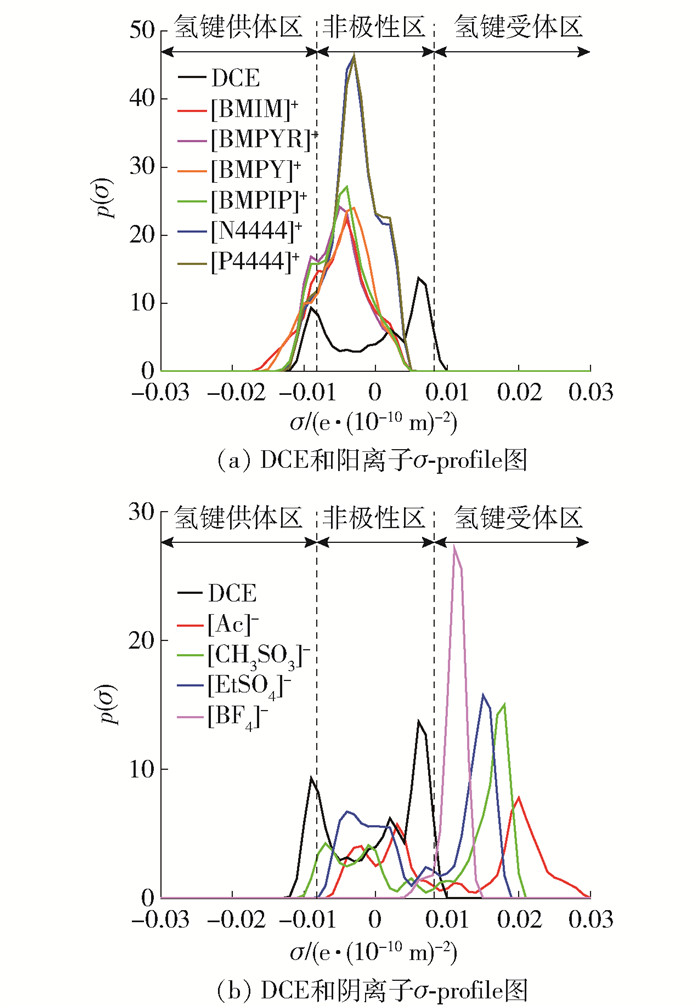
3.4.1 分子表面电荷密度分布(σ-profile)分析
σ-profile可以描述分子表面的局部极性并确定分子之间的相互作用能,被称为分子描述符。根据分子的σ-profiles曲线、分子的极性和非极性,可以得出不同官能团对电荷分布的影响以及分子表面上的有效屏蔽电荷信息。σ-profile分为3个区域:氢键供体区(σ < -0.008 2 e/(10-10 m)2)、非极性区(-0.008 2~0.008 2 e/(10-10 m)2)和氢键受体区(σ>0.008 2 e/(10-10 m)2),见图 7。DCE的σ-profile范围广(-0.012~0.009 e/(10-10 m)2),分别在-0.009 e/(10-10 m)2和0.006 e/(10-10 m)2位置出现一个强峰,在0.002 e/(10-10 m)2处呈现出一个弱峰,可见DCE主要表现为非极性及氢键供体能力。通过对不同骨架阳离子进行σ-profile分析,峰值均位于非极性区域,说明阳离子与DCE间作用以范德华力为主导。季铵盐和季膦盐阳离子的非极性区域峰值明显大于其他4种阳离子,与DCE间表现出更强的范德华力,这与离子液体中DCE饱和吸收容量的COSMO-RS预测值及实验结果一致。[BF4]-、[EtSO4]-、[CH3SO3]-和[Ac]-阴离子分别在0.011、0.015、0.018和0.020 m处呈现出强峰,表明其具有强氢键受体能力,在吸收DCE过程时可形成氢键作用。同时可见,阴离子与DCE间(氢键)相互作用显著高于阳离子(范德华力),说明离子液体吸收DCE为阴离子主导,与图 5实验结果一致。
3.4.2 结合能分析
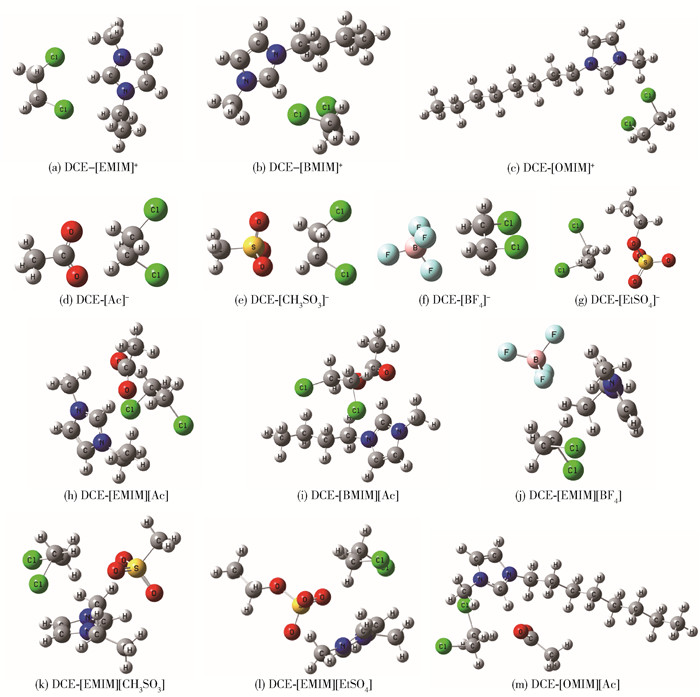
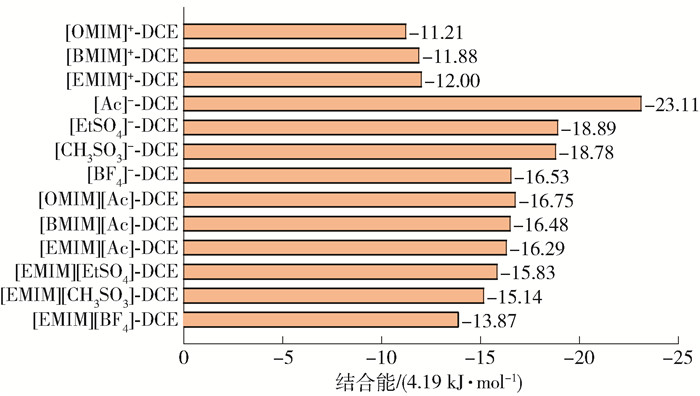
为了定量分析不同结构离子液体与DCE间相互作用,采用Gaussian 09对结合能进行了分析,DCE与阴/阳离子/离子液体整体优化几何结构如图 8所示,相互作用能结果如图 9所示。可见,阴离子与DCE间相互作用能远大于阳离子与DCE相互作用能,说明阴离子与DCE结合能力更强,印证了阴离子在吸收过程起主导作用。阳离子烷基碳链越长,相互作用能越小,主要由于烷基链的增长使得咪唑环上活泼氢的正电性减小,从而导致形成的氢键(C—H…Cl)减弱。阴离子与DCE相互作用能(绝对值)从大到小依次为[Ac]-、[EtSO4]-、[CH3SO3]-、[BF4]-,相互作用能越大表示两者相互作用越强,这与σ-profile分析及离子液体饱和吸收容量结果一致。离子液体与DCE间相互作用能介于阴/阳离子与DCE的相互作用能之间,主要是因为阴阳离子间亦存在静电力、氢键力及范德华力。离子液体与DCE间相互作用能大小遵循与阴离子一样的结果,这与饱和吸收容量实验结果一致,说明体系的相互作用能越大,吸收能力越强。
3.4.3 分子范德华表面静电势分析
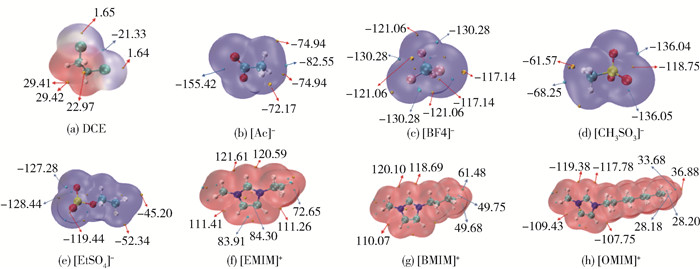
通过ESP可以快速捕捉分子间潜在的最佳结合位点,这是因为分子间更倾向以静电势互补的方式结合。图 10给出了DCE、阴离子、阳离子的静电势分布,可见,DCE静电势负值区域分布在2个氯原子中间,最小值为-21.33×4.19 kJ/mol,这是由于具有较强电负性的氯离子,将氢原子周围电子云吸引所致。由于氢原子周围的电荷密度降低,出现具有最大正值的红色区域,且离氯原子距离越远,ESP值越大。全局ESP最大值点为29.42×4.19 kJ/mol,可与其他分子负ESP位置具有强相互作用。
对于阴离子,由于其负离子特性,ESP均为负值。[Ac]-阴离子ESP最小值(-155.42×4.19 kJ/mol)位于2个氧原子中间,且比其他阴离子最小值都小,因此表现出与DCE最强的相互作用。对于[BF4]-阴离子,由于其四面体结构,全局出现了3个相同的最负ESP值点(-121.06×4.19 kJ/mol),且都是对称的。[CH3SO3]-和[EtSO4]-阴离子的最负ESP值点都是位于氧原子上方,更利于和DCE的正ESP处形成静电相互作用。
与阴离子相反,阳离子分子表面的静电势数值均为正值,咪唑环周围分布有2个非常大的ESP极大值点。正ESP值全局最大值点均出现在咪唑环上的酸性氢原子和甲基之间,其随着支链增长,正ESP值极大值减小,这是因为阳离子中的烷基链作为供电基团,它的增加使得咪唑环上的活泼氢原子的电子云密度增大。
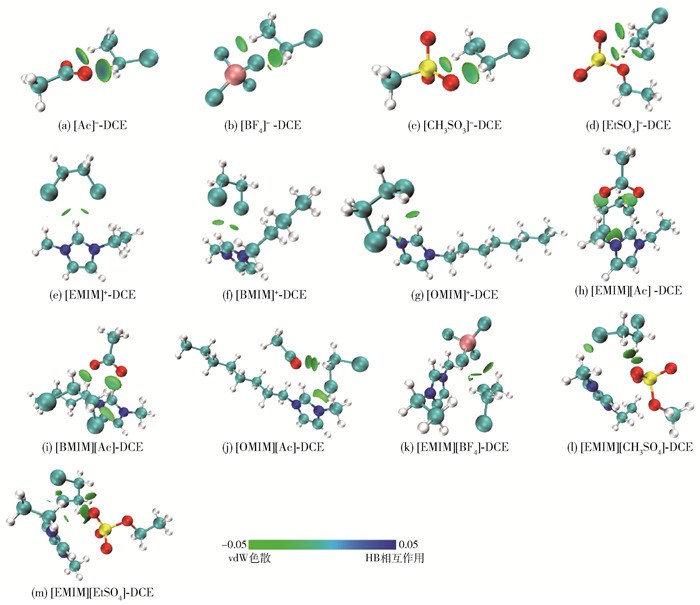
3.4.4 弱相互作用的可视化分析
IGMH分析作为分子间弱相互作用可视化分析的重要手段,可以通过对分子片段间等值面的大小及颜色分析得到分子间弱相互作用的强度和类型(氢键力、范德华力、静电作用力)。如图 11所示,[Ac]-阴离子氧原子与DCE分子中氢原子间形成2片明显的蓝色等值面,即形成C—H…O氢键。ESP分析中阴离子氧原子上方存在明显的静电势负值区域,DCE氢原子上方存在明显的静电势正值区域,因此可形成强氢键。其他阴离子与DCE分子间以范德华相互作用为主,同时存在弱氢键([BF4]-体系为C—H…F氢键、[CH3SO3]-/[EtSO4]-体系为C—H…S和C—H…O氢键)。
对于阳离子-DCE体系,DCE氯原子和阳离子咪唑环的酸性氢原子之间出现了大面积的绿色等值面,说明它们之间主要是以范德华(vdW)色散作用为主导。与阴离子-DCE体系相比,阳离子-DCE体系的蓝色等值面较小,基本可忽略,这意味着HB相互作用较小,这也就解释了阴离子与DCE体系的结合能要大于阳离子与DCE体系的原因。
在离子液体-DCE体系中,以代表vdW色散作用的绿色等值面居多,并且可以看到弱相互作用力的产生位点,与单独阴/阳离子-DCE作用力的产生位点接近,DCE与阴离子之间的弱相互作用等值面比DCE与阳离子之间的弱相互作用等值面更大。表明阴离子比阳离子对离子液体-DCE之间的相互作用贡献更大,这也符合之前COSMO-RS模型预测的结果。
3.5 流程概念设计与优化
3.5.1 工艺流程概念设计
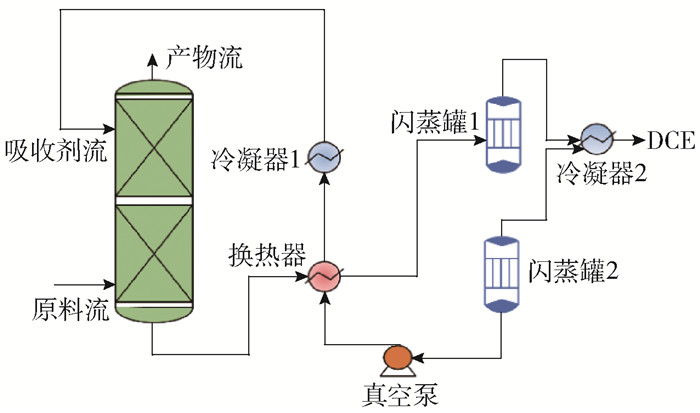
采用离子液体[BMIM][Ac]作为吸收剂捕集DCE进行流程概念设计,如图 12所示。原料气从吸收塔底部进入并与吸收剂逆流接触,脱除DCE之后的产物流从吸收塔顶部获得,塔底富DCE吸收剂经逐级闪蒸进行吸收剂再生。基于Aspen Plus建立吸收-解吸平衡级数学模型,其中热力学模型选择COSMO-SAC模型。在流程模拟与优化过程中,离子液体作为虚拟组分借助COSMOthermX软件进行创建并添加到Aspen数据库中,DCE、N2作为常规组分可直接从内置数据库中获得。
3.5.2 工艺流程优化
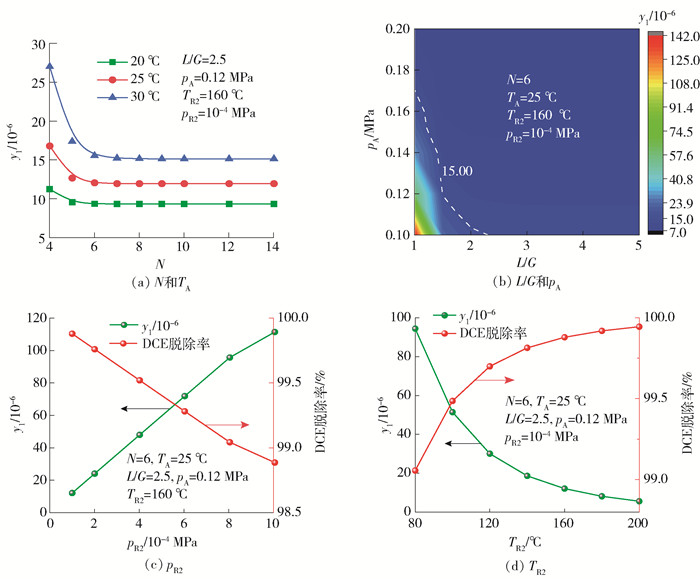
为满足真实的工业需要,模拟原料气选择体积分数为1%的DCE和99%的N2组成的混合气体,处理量为1 000 kg/h,要求吸收塔顶部产物气中DCE体积分数(y1)不大于1.5×10-5。本工艺富DCE离子液体采用逐级闪蒸进行解吸再生,其中一级闪蒸罐温度和压力分别设定为TR1=160 ℃和pR1=10-3 MPa,为满足特定的分离目标,需对以下设计和操作参数进行优化:吸收塔理论塔板数(N)、操作压力(pA,MPa)、温度(TA,℃)、吸收剂流量(液气质量比L/G)、二级闪蒸罐的操作温度(TR2,℃)和压力(pR2,MPa)。各参数对吸收塔顶产品DCE含量的影响如图 13所示。
由图 13(a)可见,随着吸收塔理论塔板数的增大,塔顶气体中DCE含量逐渐降低,但当塔板数高于6之后,DCE含量基本保持不变,因此综合考虑设备投资,适宜的理论塔板数选择为6块。吸收塔操作温度对塔顶产品气中DCE含量影响很大,低温有利于吸收。但温度降低也会增加离子液体的黏度,从而增加管道运输的成本,所以吸收塔的操作温度设定为25 ℃。随后考察了吸收塔操作压力(pA)和吸收剂流量(液气质量比L/G)对塔顶产品气DCE出口体积分数的影响,见图 13(b),白色虚线右上方是满足产品气含量要求的区域。增大吸收塔的操作压力和吸收剂用量都能降低产品气DCE的出口体积分数。随着L/G的增大,DCE的出口体积分数逐渐减小,但当比值达到2.5,即吸收剂流速达到2 500 kg/h时,进一步增大离子液体用量对出口体积分数的影响很微弱。并且塔板压力以0.02 MPa的恒增量提高时,净化气的出口体积分数都能达到分离任务。根据以上工艺优化,最终确定吸收塔最佳操作条件为:N=6,TA=25 ℃,pA=0.12 MPa,L/G=2.5。
众所周知,吸收剂中溶质的含量对吸收性能有直接影响,而再生溶剂中DCE的含量取决于二级闪蒸罐的操作条件(温度和压力),见图 13(c)(d)。随着闪蒸罐2压力降低(即真空度的增大),产品气DCE的出口体积分数显著下降。当闪蒸罐2的压力从10-3 MPa降低到10-4 MPa时,DCE的出口体积分数从1.11×10-4下降到1.2×10-5。随着闪蒸罐再生温度的提高,DCE的出口体积分数显著降低,当温度从80 ℃提高到200 ℃时,DCE脱除率提高到99.9%,当温度大于160 ℃时,脱除率增长开始变缓,说明此时温度的提高对DCE脱除率的影响逐渐减小。较高的闪蒸温度和较低的闪蒸压力有利于再生过程,但对设备的制造和操作要求会带来较高的能耗和成本。最终,再生的优化条件选为TR2=160 ℃、pR2=10-4 MPa。在此条件下,DCE的脱除率为99.88%,吸收塔顶产物中DCE体积分数为1.2×10-5。
3.5.3 与传统有机溶剂吸收工艺对比
接下来在优选操作条件下将离子液体吸收过程与常用传统有机吸收剂(三甘醇,TEG)从吸收性能、吸收剂用量、能耗等方面进行了比较,结果如表 2所示,其中三甘醇吸收DCE工艺流程与吸收甲苯类似,与离子液体吸收工艺不同之处在于TEG回收单元为蒸馏塔,具体流程参见Chen等[40]的研究。吸收操作条件与ILs捕集DCE工艺相同,再生蒸馏塔操作条件:塔板数NR=6、压力pR=1 MPa、塔顶回流比R=1。由表 2可见,实现相同的分离任务(y1 < 1.5×10-5),离子液体工艺相比TEG工艺表现出较低的能量消耗:总加热能耗为24.77 kW,总冷凝能耗为28.38 kW,换热器能耗为36.44 kW,相比TEG工艺分别节约了34.22%、11.15%和82.85%。本工作中对于离子液体吸收DCE的建设成本和投资成本未进行深入研究,但在Wu等[21]模拟离子液体吸收二氯甲烷的工作中表明,在经济核算时,传统溶剂二甲基亚砜具有最高的操作成本(349.493万美元),同时能量成本较离子液体[BMIM][SCN](1-丁基-3-甲基咪唑硫氰酸盐)和[C2Pip][C1COO] (1-乙基哌啶醋酸盐)分别高出59.88%和42.71%。这说明离子液体在成本可行性方面较传统溶剂有较大的优势。通过工艺模拟吸收DCE的过程可以得知,离子液体在吸收剂用量和节能降耗等方面都有较大的工业应用潜力。同时在其他CVOCs的吸收工作中也可以看到离子液体的广泛应用,但迄今为止,由于离子液体的高黏度特性导致管道运输成本增加和腐蚀仍是亟待解决的问题,限制了其在工业中的大规模实践和应用。因此在后续研发中,除了要考虑离子液体的吸收性能,黏度、热稳定性等物性也要评估,这也意味着对离子液体的开发和利用还有很长的路要走。
表 2 不同吸收剂捕集DCE的流程模拟结果及能耗比较Table 2. Process simulation results and energy consumption comparison of different absorbents to capture DCE名称及参数 吸收剂 [BMIM][Ac] TEG 温度/℃ 25 25 产物流 质量流速/(kg·h-1) 964.81 965.17 DCE体积分数 1.21×10-5 1.46×10-5 闪蒸罐1顶部物流 温度/℃ 160 35 质量流率/(kg·h-1) 32.85 0.09 闪蒸罐2顶部物流 温度/℃ 160 质量流率/(kg·h-1) 2.31 蒸馏塔顶部物流 温度/℃ 112 质量流率/(kg·h-1) 32.15 闪蒸罐1 能耗/kW 24.59 10.41 闪蒸罐2 能耗/kW 0.18 蒸馏塔 能耗/kW 26.97 总加热能耗/kW 24.77 37.38 热物流出口温度/℃ 45 45 换热器 冷物流进口温度/℃ 28 35 冷物流出口温度/℃ 145 166 能耗/kW 36.44 212.46 进口温度/℃ 45 45 冷凝器1 出口温度/℃ 25 25 能耗/kW -23.86 -28.08 进口温度/℃ 160 112 冷凝器2 出口温度/℃ 25 25 能耗/kW -4.52 -3.86 总冷凝能耗/kW -28.38 -31.94 真空泵能耗/kW 0.26 0.22 4. 结论
本文提出离子液体高效吸收DCE技术,在预测型分子热力学理论的指导下,从分子尺度到过程尺度系统研究了其应用前景。相关的研究结论总结如下:
1) 通过COSMO-RS模型对包括17种阴离子和28种阳离子组合成的ILs进行筛选,并从阳离子骨架结构、羧酸盐阴离子链长及氟化进行构效分析,探究对DCE分离性能的影响。发现非芳香族非环状阳离子表现出较好的性能,同时增加阴离子侧链烷基碳链长度及氟化阴离子会减弱ILs对DCE的吸收能力。
2) 以不同阳离子骨架、不同阴离子种类的离子液体为出发点,实验测定了系列离子液体对DCE的饱和吸收容量,表明非芳香族非环状结构的阳离子表现出最好的饱和吸收容量,在阴离子当中,[Ac]-具有最大的饱和吸收容量。DCE吸收容量主要由阴离子决定,同时考虑离子液体黏度等因素,最终确定1-丁基-3-甲基咪唑醋酸盐([BMIM][Ac])为适宜的吸收剂,并进一步考察温度和分压对DCE吸收的影响。结果表明低温和高压更有利于离子液体对DCE的吸收,在20 ℃、常压、进气DCE为20 ℃饱和含量(约0.008 4 MPa),[BMIM][Ac]对DCE饱和吸收容量达到2 177 mg/g。
3) 为了深刻理解吸收机理,对离子液体和DCE体系进行分子水平上的研究。σ-profile分析结果表明DCE可作为强氢键供体或以非极性特征与吸收剂结合;阳离子大部分分布在非极性区域,具有非极性相互作用;阴离子可作为氢键受体与DCE形成强氢键。在结合能分析中,阴离子与DCE体系的相互作用能要远大于阳离子与DCE体系的相互作用能,说明阴离子对吸收效果的影响起主导作用。ESP和IGMH分析揭示了阴离子与DCE主要是以强氢键作用和范德华色散作用结合,离子液体对DCE的吸收是一个物理过程。
4) 使用Aspen Plus对离子液体捕集DCE过程进行概念设计和流程优化,结果表明在优选条件下:吸收塔(N=6,TA=25 ℃,pA=1.2 MPa,L/G=2.5),二级闪蒸(TR1=160 ℃、pR1=10-3 MPa,TR2=160 ℃、pR2=10-4 MPa),DCE的脱除率为99.88%,气体出口DCE体积分数为1.2×10-5。与传统有机溶剂TEG进行比较时,发现当实现相同的分离任务时,IL工艺具有更低的能量消耗。
-
表 1 离子液体在不同温度下的黏度
Table 1 Viscosity of ionic liquids at different temperatures
Pa·s 温度/℃ [BMIM][Ac] [OMIM][Ac] 20 432.33 970.26 25 300.64 720.63 30 215.07 553.71 35 157.85 391.68 40 118.78 285.51 表 2 不同吸收剂捕集DCE的流程模拟结果及能耗比较
Table 2 Process simulation results and energy consumption comparison of different absorbents to capture DCE
名称及参数 吸收剂 [BMIM][Ac] TEG 温度/℃ 25 25 产物流 质量流速/(kg·h-1) 964.81 965.17 DCE体积分数 1.21×10-5 1.46×10-5 闪蒸罐1顶部物流 温度/℃ 160 35 质量流率/(kg·h-1) 32.85 0.09 闪蒸罐2顶部物流 温度/℃ 160 质量流率/(kg·h-1) 2.31 蒸馏塔顶部物流 温度/℃ 112 质量流率/(kg·h-1) 32.15 闪蒸罐1 能耗/kW 24.59 10.41 闪蒸罐2 能耗/kW 0.18 蒸馏塔 能耗/kW 26.97 总加热能耗/kW 24.77 37.38 热物流出口温度/℃ 45 45 换热器 冷物流进口温度/℃ 28 35 冷物流出口温度/℃ 145 166 能耗/kW 36.44 212.46 进口温度/℃ 45 45 冷凝器1 出口温度/℃ 25 25 能耗/kW -23.86 -28.08 进口温度/℃ 160 112 冷凝器2 出口温度/℃ 25 25 能耗/kW -4.52 -3.86 总冷凝能耗/kW -28.38 -31.94 真空泵能耗/kW 0.26 0.22 -
[1] 牛彦红. 新增二氯乙烷项目的分析及生产总结[J]. 齐鲁石油化工, 2020, 48(2): 128-131. NIU Y H. Analysis and production summary on the new dichloroethane project[J]. Qilu Petrochemical Technology, 2020, 48(2): 128-131. (in Chinese)
[2] 刘媛, 王鸯鸯, 杨威. 浅析挥发性有机废气治理技术[J]. 中国环保产业, 2012(11): 40-43. LIU Y, WANG Y Y, YANG W. Analysis of volatile organic waste gas treatment technology[J]. China Environmental Protection Industry, 2012(11): 40-43. (in Chinese)
[3] 李明广, 施政, 吴志平, 等. 挥发性有机废气治理技术进展[J]. 绿色环保建材, 2020(7): 38-39. LI M G, SHI Z, WU Z P, et al. Progress in volatile organic waste gas treatment technology[J]. Green and Environmentally Friendly Building Materials, 2020(7): 38-39. (in Chinese)
[4] LI K, LUO X Q. Research progress on catalytic combustion of volatile organic compounds in industrial waste gas[J]. Catalysts, 2023, 13(2): 268. doi: 10.3390/catal13020268
[5] LI T, LI H, LI C. A review and perspective of recent research in biological treatment applied in removal of chlorinated volatile organic compounds from waste air[J]. Chemosphere, 2020, 250: 126338. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.126338
[6] FU L P, ZUO J, LIAO K L, et al. Preparation of adsorption resin and itas application in VOCs adsorption[J]. Journal of Polymer Research, 2023, 30(5): 167. doi: 10.1007/s10965-023-03510-2
[7] LYU X P, CHEN N, GUO H, et al. Ambient volatile organic compounds and their effect on ozone production in Wuhan, central China[J]. Scinence of the Total Environment, 2016, 541: 200-209. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2015.09.093
[8] DARWISH N A, HILAL N. Sensitivity analysis and faults diagnosis using artificial neural networks in natural gas teg-dehydration plants[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2008, 137(2): 189-197. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2007.04.008
[9] GUI C M, ZHU R S, LI G X, et al. Natural gas dehydration with ionic-liquid-based mixed solvents[J]. Acs Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering, 2021, 9(17): 6033-6047.
[10] WANG B S, QIN L, MU T C, et al. Are ionic liquids chemically stable?[J]. Chemical Reviews, 2017, 117(10): 7113-7131. doi: 10.1021/acs.chemrev.6b00594
[11] CAO Y Y, MU T C. Comprehensive investigation on the thermal stability of 66 ionic liquids by thermogravimetric analysis[J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2014, 53(20): 8651-8664.
[12] VENTURA S P M, E SILVA F A, QUENTAL M V, et al. Ionic-liquid-mediated extraction and separation processes for bioactive compounds: past, present, and future trends[J]. Chemical Reviews, 2017, 117(10): 6984-7052.
[13] JIANG C H, CHENG H Y, QIN Z X, et al. COSMO-RS prediction and experimental verification of 1, 5-pentanediamine extraction from aqueous solution by ionic liquids[J]. Green Energy & Environment, 2021, 6(3): 422-431.
[14] HU X T, WANG J W, MEI M C, et al. Transformation of CO2 incorporated in adducts of N-heterocyclic carbene into dialkyl carbonates under ambient conditions: an experimental and mechanistic study[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2021, 413: 127469.
[15] WANG H M, ZHU J M, TAN L, et al. Encapsulated ionic liquids for CO2 capture[J]. Materials Chemistry and Physics, 2020, 251: 122982.
[16] WANG L Y, ZHANG Y J, LIU Y, et al. SO2 absorption in pure ionic liquids: solubility and functionalization[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2020, 392: 122504.
[17] ZHANG X M, XIONG W J, SHI M Z, et al. Task-specific ionic liquids as absorbents and catalysts for efficient capture and conversion of H2S into value-added mercaptan acids[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2021, 408: 127866.
[18] HAN J L, DAI C N, LEI Z G, et al. Gas drying with ionic liquids[J]. Aiche Journal, 2018, 64(2): 606-619.
[19] WANG W L, MA X L, GRIMES S, et al. Study on the absorbability, regeneration characteristics and thermal stability of ionic liquids for VOCs removal[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2017, 328: 353-359.
[20] XU R N, DAI C N, MU M L, et al. Highly efficient capture of odorous sulfur-based VOCs by ionic liquids[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2021, 402: 123507.
[21] WU Z X, SHI S S, ZHAN G X, et al. Ionic liquid screening for dichloromethane absorption by multi-scale simulations[J]. Separation and Purification Technology, 2021, 275: 119187.
[22] CHENG X, MU T, WANG X, et al. Low pressure solubilities of vinyl chloride in ionic liquids[J]. Journal of Chemical and Engineering Data, 2008, 53(12): 2807-2809.
[23] GUI C M, LI G X, ZHU R S, et al. Capturing VOCs in the pharmaceutical industry with ionic liquids[J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 2022, 252: 117504.
[24] MU M L, ZHANG X F, YU G Q, et al. Deep removal of chlorobenzene based volatile organic compounds from exhaust gas with ionic liquids[J]. Separation and Purification Technology, 2022, 298: 121610.
[25] SALAHUB D R, DE LA LANDE A, GOURSOT A, et al. Recent progress in density functional methodology for biomolecular modeling[M]//PUTZ M V, MINGOS D M P. Applications of density functional theory to biological and bioinorganic chemistry. Berlin: Springer, 2013: 1-64.
[26] WANG J, SHI X Q, DU X H, et al. A DFT investigation on interactions between lignin and ionic liquids[J]. Russian Journal of Physical Chemistry A, 2017, 91(8): 1468-1473.
[27] HUANG X, AI N, LI L, et al. Simulation of CO2 capture process in flue gas from oxy-fuel combustion plant and effects of properties of absorbent[J]. Separations, 2022, 9(4): 95.
[28] KLAMT A, ECKERT F. COSMO-RS: a novel and efficient method for the a priori prediction of thermophysical data of liquids[J]. Fluid Phase Equilibria, 2000, 172(1): 43-72.
[29] BLAUDEAU J P, MCGRATH M P, CURTISS L A, et al. Extension of gaussian-2 (G2) theory to molecules containing third-row atoms K and Ca[J]. Journal of Chemical Physics, 1997, 107(13): 5016-5021.
[30] GRIMME S, EHRLICH S, GOERIGK L. Effect of the damping function in dispersion corrected density functional theory[J]. Journal of Computational Chemistry, 2011, 32(7): 1456-1465.
[31] GRIMME S, ANTONY J, EHRLICH S, et al. A consistent and accurate ab initio parametrization of density functional dispersion correction (DFT-D) for the 94 elements H-Pu[J]. Journal of Chemical Physics, 2010, 132(15): 154104.
[32] ANDERSSON M P, UVDAL P. New scale factors for harmonic vibrational frequencies using the B3LYP density functional method with the triple-zeta basis set 6-311+G(d, p)[J]. Journal of Physical Chemistry A, 2005, 109(12): 2937-2941.
[33] LU T, CHEN F W. Multiwfn: a multifunctional wavefunction analyzer[J]. Journal of Computational Chemistry, 2012, 33(5): 580-592.
[34] LU T, CHEN Q X. Independent gradient model based on hirshfeld partition: a new method for visual study of interactions in chemical systems[J]. Journal of Computational Chemistry, 2022, 43(8): 539-555.
[35] LU T, CHEN F W. Quantitative analysis of molecular surface based on improved Marching Tetrahedra algorithm[J]. Journal of Molecular Graphics & Modelling, 2012, 38: 314-323.
[36] RASHID Z, WILFRED C D, GNANASUNDARAM N, et al. Screening of ionic liquids as green oilfield solvents for the potential removal of asphaltene from simulated oil: COSMO-RS model approach[J]. Journal of Molecular Liquids, 2018, 255: 492-503.
[37] TOKUDA H, HAYAMIZU K, ISHII K, et al. Physicochemical properties and structures of room temperature ionic liquids. 2. Variation of alkyl chain length in imidazolium cation[J]. Journal of Physical Chemistry B, 2005, 109(13): 6103-6110.
[38] WANG Z Q, WU Y D, CAO Z D, et al. Absorption of ethylene dichloride with imidazolium-based ionic liquids[J]. Journal of Molecular Liquids, 2023, 376: 121449.
[39] SONG M, GUI C, LEI Z. Experimental and simulation studies on the capture of chlorinated volatile organic compounds by ionic liquids[J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2023, 62(26): 10184-10194.
[40] CHEN M, DAI C N, YU G Q, et al. Highly efficient absorption of methyl tert-butyl ether with ionic liquids[J]. Separation and Purification Technology, 2022, 282: 120108.



 下载:
下载: