Forecasting Carbon Emission Reduction Potential of Four Major Transportation Sectors in China
-
摘要:
交通部门是我国碳排放的主要贡献部门。通过收集2000—2020年各省市的人口、经济、交通等相关资料, 结合各省市已颁布的规划政策预测了2021—2035年交通部门的活动水平, 并采用排放因子法和情景分析法, 估算了不同情景下东部、中部和西部地区不同交通部门的CO2排放量, 并对碳减排潜力进行了对比分析。结果表明, 我国交通部门在基准情景下的碳排放呈持续增长的趋势, 碳减排潜力最大的是调整运输结构情景, 2035年可降碳7.21亿t, 在该情景下, 公路部门的碳减排潜力最大, 减排效果从高到低依次为东部地区、西部地区、中部地区, 航空部门仅在中部地区具有减排潜力, 铁路、水路部门在该情景下的减排潜力均为负值。而铁路、航空和水路部门在优化能源结构情景下更具有减排潜力, 2035年将分别减排49.30%、20.53%和15.66%, 在该情景下, 铁路部门短期内在东部地区减排效果较好, 长期在中部地区的减排潜力更大, 航空部门的减排潜力在东部和西部地区更优, 水路部门的减排效果在东部地区更显著。
Abstract:The transportation sector is the main contributor of carbon emissions in China. The article predicted the activity level of the transportation sector from 2021 to 2035 by collecting relevant information on population, economy, and transportation in each province and city from 2000 to 2020, and forecasted the activity level of the transportation sector from 2021 to 2035 by incorporating with the planning policies that have been enacted in each province and city. The emission factor method and the scenario analysis method were adopted to estimate the CO2 emissions of different transport sectors in different scenarios for the eastern, central, and western regions, and a comparative carbon emission reduction potential was analyzed. Results show that the carbon emissions of China's transport sector under the baseline scenario exhibits a continuous growth trend, and the scenario with the greatest potential for carbon emission reduction is the scenario of adjusting the transport structure, which can reduce carbon by 721 million tonnes by 2035. Under this scenario, the road sector has a greatest potential for carbon emission reduction, the emission reduction effect from high to low is the eastern region, the western region, the central region, the aviation sector has the potential for emission reduction only in the central region, and the emission reduction potentials of the railways and the waterway sector are all negative under this scenario. The railroad, aviation and waterway sectors have greater emission reduction potential under the optimization of the energy structure scenario, which will reduce emissions by 49.30%, 20.53% and 15.66% in 2035, respectively. Under this scenario, the railway sector has superior emission reduction effects in the eastern region in the short term, and greater emission reduction potential in the central region in the long term, while the aviation sector's emission reduction potentials are better in the east and west, and the emission reduction effect of the waterway sector is more significant in the eastern region.
-
在我国的碳排放结构中,交通部门是第三大碳排放来源,也是导致CO2排放量快速增长的主要部门之一。2019年,我国交通领域CO2排放量为1.16×109 t,受客货运需求持续增长的影响,预计CO2排放将于2028年达峰,峰值为1.63×109 t,较2019年增加4.7×108 t[1]。根据发达国家过去的发展经验,交通部门的碳排放和能源消费将随着经济发展而增加,交通部门已成为实施节能减排的重点部门[2-4]。
近年来,国内外学者从不同角度采用不同方法对交通部门的CO2排放进行了研究。从研究方法来看,有学者采用排放因子法分析交通部门污染物排放现状,也有学者利用能源模型结合情景分析预测未来交通碳排放情况,如Liimatainen等[5]、Annadanam等[6]、Alam等[7]、Fu等[8]、Hong等[9]和Kakouei等[10]使用德尔菲法、改进的自上而下法、自下而上法和应用LEAP模型等分别对芬兰、印度、爱尔兰、韩国和伊朗等国家交通部门的碳排放情况及影响因素进行了分析。目前我国有较多关于交通部门碳排放的研究,大多采用“自上而下”或“自下而上”的方法核算我国交通部门的碳排放量,并设置不同情景预测我国未来交通碳排放情况,分析交通部门的空间分布和变化趋势[1, 11]。
部分学者针对单一交通部门如公路部门[12-16]、航空部门[17-19]、铁路部门[20-22]、水路部门[23]、城市交通[24-27]的碳排放进行了研究,研究者采用不同的研究方法如排放因子法、情景分析法等,运用不同模型如LEAP模型、ICAO模型、EDMS模型等,基于能源消耗等对各部门的碳排放进行分析研究,发现不同交通部门的碳排放特征存在很大的差异。也有部分学者从宏观层面对我国交通部门的CO2排放进行了分析,如冯相昭等[28]、贾璐宇等[29]、田佩宁[30]、Li等[31]基于LEAP模型构建情景,或基于面板数据采用不同的研究方法对我国各交通部门的碳排放进行计算分析,然而对全国层面尤其是区域层面的系统研究还缺少考量。
同时,部分学者针对我国单个区域交通部门的污染情况进行研究,如潘鹏飞等[32]、周健等[33]、黄莹等[34]、Fan等[35]和罗薇等[36]应用LEAP模型分别对我国河南省、厦门市、广州市、北京市和云南省交通部门的能源消耗、碳排放等情况进行了分析和预测,谭琦璐等[37]、郭秀锐等[38]、徐新华等[39]、范育洁等[40]和Liu等[41]分别以京津冀、江浙沪、西北五省和珠三角等区域为研究对象,对交通部门的碳排放和污染物排放进行了测算和分析,但缺乏对交通部门碳排放未来趋势的分析和预测。
因此,本研究通过收集整理我国2000—2020年各省市的人口、经济、交通周转量和汽车保有量等数据,应用SPSS软件结合回归分析法、增长率法预测了2021—2035年各省市交通部门的活动水平,采用排放因子法和情景分析法,对我国各省市交通部门的CO2排放量进行计算,对比分析我国不同地区不同运输部门在不同情景下的减排潜力,为我国交通部门制定节能减排政策提供更有针对性的建议。
1. 方法
1.1 计算方法
本研究中交通部门CO2排放量采用自上而下法计算,即根据交通运输燃料消耗数据计算CO2排放量[42],具体计算公式如下。
能源消费量是根据与交通部门相关的能源强度和活动水平计算得出,其计算公式为
$$ E_e=\sum\left(N_m L_m V_{m, e}\right)+\sum\left(Q_t R_{t, e}\right) $$ (1) 式中:e为柴油、汽油、燃料油等相应能源类型;t为公路、铁路、航空、水路的客运或货运;m为出租车、私家车、公交车、摩托车等交通工具;Ee为能源e的消费量,tce;Nm为交通工具m的保有量,辆;Lm为m的年运输距离,km;Vm, e为交通工具m的能源消费类型e的百公里综合能耗,tce/100km;Qt为交通类型t的客运或货运周转量,t·km或人·km;Rt, e为交通类型t的能源消费类型e的单位周转量综合能耗,tce/(t· km)或tce/(人·km)。
交通部门的碳排放可根据交通工具的能源消耗与各种能源的排放因子计算得到,其计算公式为
$$ \mathrm{CE}=\sum \mathrm{Ee}_{i t} \mathrm{EF}_{i t} $$ (2) 式中:CE为交通碳排放总量;Eeit表示交通类型t在分部门i中的能源需求量, tce;EFit表示为交通类型t在分部门部门i中的排放因子,以CO2计。
1.2 数据来源
本研究从国家和区域角度进行了分析,研究对象包括交通全运输行业(公路、铁路、航空和水路)。具体数据来源如下:交通周转量和汽车保有量来源于各省市统计年鉴、《中国能源统计年鉴》、《中国移动源环境管理年报(2021)》、《交通运输行业发展统计公报》、《中国交通年鉴》等;单位周转能耗根据《中国交通运输中长期节能问题研究》和文献[43]的研究结果;排放因子根据蔡博峰等[42]在排放因子部分的研究方法计算得到,参考《中国能源统计年鉴2008》和《2006年国家温室气体排放清单指南》,如表 1所示;年均行驶里程、百公里能耗等数据主要参考《道路机动车大气污染物排放清单编制技术指南》《城市交通碳排放监测评估研究与实践》及文献[44-45]等。为确保本文预测数据的科学性和合理性,研究将人口、国内生产总值(gross domestic product,GDP)、人均GDP、第一产业值、第二产业值、第三产业值、工业产值、居民消费及城镇居民消费9个因素作为驱动因素,在收集各省市2000—2020年的9个驱动因素及交通周转量和汽车保有量等相关数据的基础上,通过SPSS软件建立各省市不同交通部门的交通周转量、汽车保有量与驱动因素的回归关系模型,得到交通周转量和汽车保有量与各驱动因素的相关系数,并对2021—2035年的交通周转量、汽车保有量进行预测,驱动因素的预测主要参考《2030年的中国》《国家人口发展规划(2016—2030年)》《中国2060年前碳中和研究报告》及各省市自治区的发展规划等。交通周转量和汽车保有量的预测主要参考各省市交通发展规划、学术机构的调查研究报告以及部分预测结果等。情景设置时主要参考《新能源汽车产业发展规划2021—2035年》《推进多式联运发展优化调整运输结构工作方案(2021—2025年)》及各省市交通部门已颁布的规划政策等。
表 1 各类能源的CO2排放因子Table 1. CO2 emission factors of various energy sourceskg/kg 交通类型 油品类型 碳排放因子 道路交通 汽油 2.98 柴油 3.16 铁路运输 柴油 3.12 水路运输 燃料油 3.24 航空运输 煤油 3.10 注: 1.汽油的排放因子采用蔡博峰等[42]的研究结果。
2.柴油、燃料油和煤油的排放因子根据1中的方法进行计算得到。2. 情景设置
为了探讨不同节能减排政策与发展路径对我国交通部门二氧化碳减排效果的影响,本文在充分分析我国交通部门能源结构优化及运输结构调整政策的基础上,设置了基准情景、能源结构优化情景、运输结构调整情景和综合情景。
2.1 基准情景
本研究假定2020年后交通部门将继续延续我国各省市目前现有的政策规划、减排措施以及可预见的技术路线等,预测未来交通部门的CO2排放情况[46]。基准情景(business as usual scenario,BAU)采用2000—2020年的数据,应用SPSS软件结合回归分析法、增长率法对各省市各部门的交通周转量和汽车保有量进行合理预测,从而估算出未来交通部门的CO2排放量。基准情景可看作与其他政策情景形成对比的一种参考情景。
2.2 政策情景
政策情景包括2类单一措施情景(能源结构优化情景和运输结构调整情景)及综合情景。
1. 能源结构优化情景(energy structure optimization,ESO)
《2030年前碳达峰行动方案》中提出要加大对新能源汽车的推广,提高城市内公共交通电动化的比例,在新车产销中逐步降低传统燃油汽车的占比,增加电力和清洁能源在重型货运车辆中的使用。同时,《“十四五”现代综合交通运输体系发展规划》中也对我国公路、铁路、航空和水路部门电力、新能源及清洁能源的使用提出了要求。根据《节能与新能源汽车技术路线图 2.0》新能源车销售占比2025年达到20%,2030年达到40%,2035年达到50%。
2. 运输结构调整情景(transport structural adjustment,TSA)
根据《推进多式联运发展优化调整运输结构工作方案(2021—2025年)》中的工作目标,到2025年,提高我国交通运输业多式联运发展水平,基本形成以铁路、水路为主的大宗货物和集装箱中长途运输的发展模式,大力推进“公转铁”和“公转水”的运输比例;与2020年相比,国内铁路货运量将增长约10%,水路货运量将增长约12%。
3. 综合情景(comprehensive scenario,CP)
综合情景是能源结构优化情景和运输结构调整情景中的所有减排措施同时实施的情景。该情景下,各省市的交通部门在提升铁路和水路货物运输量的基础上大力推广电力、生物燃油、生物航煤燃料等新能源。综合情景旨在分析在多种措施的共同作用下,各省市交通部门的最大减排潜力。
本文根据各省市已颁布的相关规划政策文件,对各省市分别进行情景设置,将我国分为三大地区(东部、中部和西部地区)进行研究。表 2是对各情景的具体描述,在情景描述部分仅对各部门的整体设置情况及个别省份的特殊设置进行了介绍。
表 2 各政策情景的具体描述Table 2. Detailed description of each policy scenario情景 情景设置 情景描述 参考依据 基准情景(BAU) 假定2020年后交通部门将不再采取新措施来干预其发展,延续我国各省市目前现有的政策规划、减排措施以及可预见的技术路线等 公路、铁路、航空和水路的交通周转量占比与2020年保持一致,公共汽车、私人汽车等的保有量延续历史趋势,交通用能结构与2020年保持一致 《中国能源统计年鉴》《交通运输行业发展统计公报》《中国铁道年鉴》《民航行业发展统计公报》及各省市的统计年鉴等 调整运输结构情景(TSA) 在基准情景基础上,增加铁路运输占比,大力发展铁路货运、水路货运交通,同时,进一步发展城市公共交通出行比例 在2020年基础上,2025年铁路货运增长率为10%~45%,水路货运的增长率为12%~35%;河北省铁路、水路货运量占比85%,陕西省、山西省、内蒙古自治区货运量占比90%,辽宁省铁路货运量占比达到80%等,同时增大城内公共交通分担率 《推进多式联运发展优化调整运输结构工作方案(2021—2025年)》《国家综合立体交通网规划纲要》等 优化能源结构情景(ESO) 综合考虑“十四五”及碳达峰期间已颁布的各种政策措施,在不改变能源效率的基础上,增大交通部门清洁能源(电力、天然气、生物燃料、氢能等)占比 2025年,公路客运和货运新能源占比7%,铁路客货运电力占比50%,航空生物燃油占比6%,水运生物燃油占比4%;2035年,公路客货运新能源占比18%,铁路客货运电力占比62%,航空部门生物燃油占比18%,水路部门生物燃油占比15%。2025年新能源公交车辆占比72%,2035年公交车和出租车全部新能源化的省市自治区有:北京市、陕西省、山西省、河南省、湖南省、广东市、广西省、海南省、重庆市、内蒙古自治区、西藏自治区。2025年、2030年、2035年私家车新能源汽车占比分别为23%、33%、50% 《新能源汽车产业发展规划(2021—2035年)》《能源转型展望》《2030年前碳达峰行动方案》《绿色交通“十四五”发展规划》《节能与新能源汽车技术路线图 2.0》《北京碳达峰实施方案》《天津市绿色交通“十四五”发展规划》《上海市交通发展白皮书》等 综合情景(CP) 大力推进“公转铁”“公转水”,增大公共交通出行比例的基础上大力推广电力、生物燃油、生物航煤燃料等新能源 该情景是TSA和ESO两个单一政策情景的综合,如在2025年,铁路货运增长率为10%~45%的同时,铁路客货运中电力占比为50%;水运水路货运的增长率为12%~35%的同时,水运生物燃油占比为4%等。各省市的情景综合相关规划政策文件进行设置,此处省略 《推进多式联运发展优化调整运输结构工作方案(2021—2025)》《新能源汽车产业发展规划(2021—2035)》《绿色交通“十四五”发展规划》等 3. 结果与讨论
3.1 中国四大交通部门的碳排放现状
3.1.1 各省市交通部门的碳排放现状
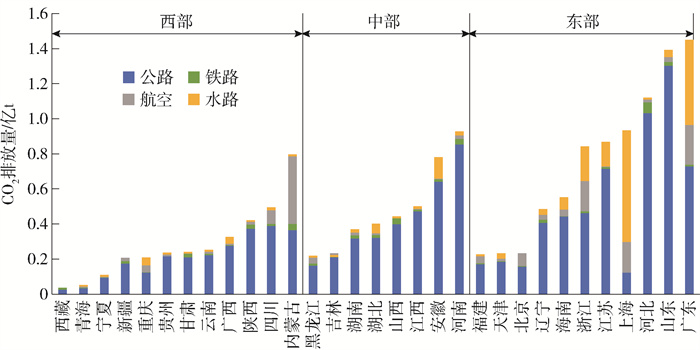
根据式(1)和(2),可计算出我国各省市自治区交通部门的CO2排放量(受数据来源的限制,本研究不考虑台湾省、澳门特别行政区和香港特别行政区)。通过计算可知,2020年我国交通部门的CO2排放量为15.46亿t,与严刚等[1]计算结果相比偏高,主要是因为核算范围不同,本文将交通部门分为四大部门进行研究,并将未纳入统计年鉴的非营运车辆计算在内,且私人汽车碳排放贡献度较大,不可忽视。研究发现各省市自治区交通部门的CO2排放水平相差较大,2020年我国交通碳排放最高的前5位分别是广东、山东、河北、上海和河南,最少的后5位分别是黑龙江、新疆、宁夏、青海、西藏,这与Guo等[47]、黄甫兰[48]的2019年研究结果大致相同,个别省份有差异是由于2020年受疫情等因素影响,交通运输结构出现了改变,且本文将西藏自治区列入了研究范围。其中广东省交通部门的CO2排放量最高,为1.45亿t,占总碳排放的9.4%,是碳排放量最低的西藏自治区的56倍。从整体来看,中、东部地区交通部门的CO2排放量高于西部地区。
从区域角度对我国交通碳排放进行分析,考虑到我国经济发展水平和地理位置,本文将我国划分为3个地区进行研究,如图 1所示。2020年我国三大地区中各省市交通部门的CO2排放量,由高至低依次为:东部地区、中部地区、西部地区,分别占我国交通碳排放总量的53.85%、24.75%、21.40%,这是由于东部地区沿海,贸易往来频繁,经济较发达,交通运输量增长较快,故其交通碳排放量较高,这与黄甫兰等[48]、蔡博峰等[42]、杜菲[49]的研究结果一致。在东部地区中,广东省的碳排放量最高,占东部地区交通总碳排放的17.42%,福建省、天津市、北京市的碳排放量较低,占比分别为2.60%、2.79%、2.79%;中部地区的河南省碳排放量较高,占中部地区交通碳排放的24.25%,黑龙江省和吉林省的碳排放量相对较低,占比分别为5.45%和5.81%;在西部地区中,碳排放水平相对较高的是内蒙古自治区,占西部地区交通碳排放的23.80%,较低的是西藏自治区,占比为0.78%。
3.1.2 不同交通部门的碳排放
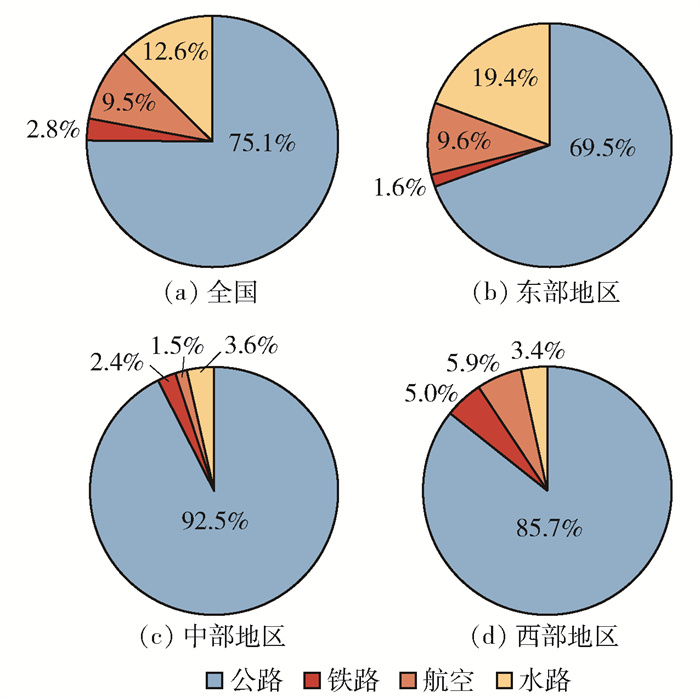
如图 2所示,2020年在四大交通部门中公路部门是CO2排放的主要来源部门,占交通部门碳排放总量的75.1%,其次是水路、航空和铁路部门,占比分别为12.6%、9.5%、2.8%。公路部门的碳排放是铁路部门碳排放的27倍、航空部门的8倍、水路运输的6倍。这与田佩宁等[30]2019年的研究结果大致相同,不同之处主要是由于2020年受疫情等因素影响,我国水路部门运输周转量显著上升,故水路部门的碳排放量较大。
不同省市自治区各交通部门碳排放占交通部门总碳排放的比例也不尽相同。公路部门碳排放占交通部门排放比例最高的是西藏自治区,达到了97.7%,最低的是上海市,仅为13.2%;铁路部门中碳排放比例最高的是青海省,达到了9.15%,最低的是上海市,仅为0.07%;航空部门碳排放占比最高的是内蒙古自治区,达到了49.13%;而水路部门碳排放比例最高的是上海市,达到了68.11%。
对比各交通部门在不同地区的碳排放情况发现:公路部门的碳排放主要发生在中部地区,铁路部门的碳排放主要发生在西部地区,航空部门和水路部门的碳排放主要发生在东部地区。分地区来看,东部地区的公路部门是其碳排放的主要来源,占总交通碳排放的69.5%,其次是水路部门、航空部门和铁路部门,占比分别为19.4%、9.6%和1.6%,其中水路部门的碳排放远超全国平均水平,这与我国东部大部分省份临海水路运输发达有关;在中部地区,公路部门的碳排放量最高,为5.5亿t,占比为92.5%,其次是水路部门、铁路部门和航空部门,占比分别为3.6%、2.4%和1.5%,这是由于我国中部地区人口稠密,私家车保有量大,故个人交通碳排放量较高,导致公路部门的碳排放远超全国平均水平;在西部地区,公路部门的碳排放量最高,为2.5亿t,占比为85.7%,其次是航空部门、铁路部门和水路部门,占比分别为5.9%、5.0%和3.4%,这是由于西部地区山地众多,铁路运输发展相对缓慢,目前仍以道路运输和航运为主。
3.2 中国四大交通部门的CO2排放量预测
3.2.1 不同情景下分地区交通部门CO2排放量预测
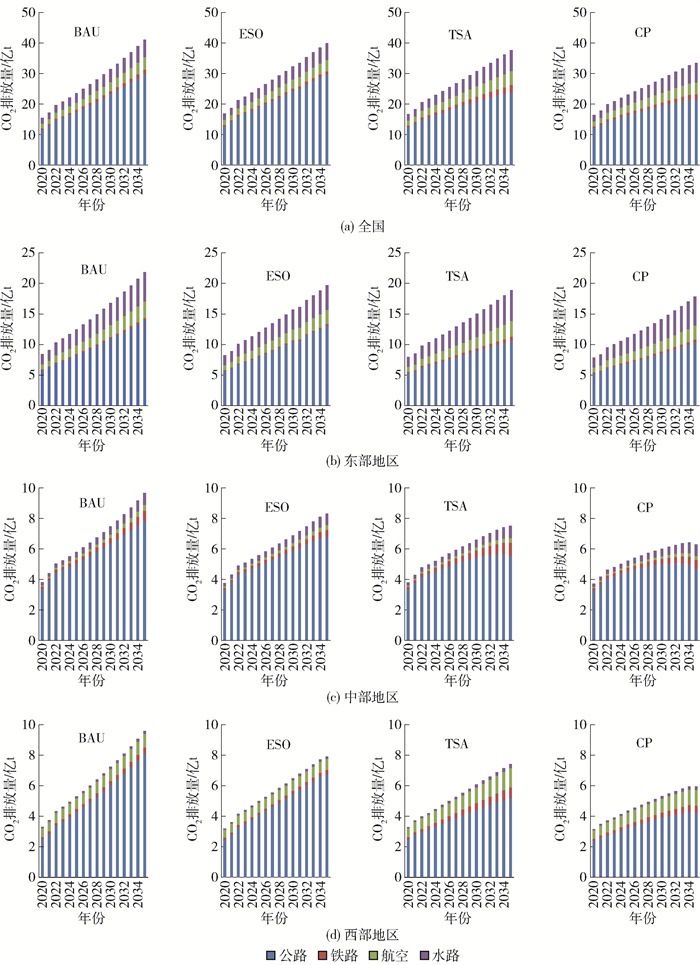
假设在某种交通运输方式下,不改变其能源消耗的平均排放因子,应用式(1)和(2)可进一步计算不同情景下我国交通部门2021—2035年的碳排放量,如图 3所示。由图 3(a)可以看出,2021—2035年我国交通部门的CO2排放仍呈持续增长的态势,不同情景下交通部门的CO2排放年均增长率由高到低分别为:基准情景、能源结构优化情景、运输结构调整情景、综合情景,增长率分别为7.16%、6.20%、5.77%、4.93%。
在基准情景下,我国交通运输部门CO2排放量由2020年的15.46亿t增长到2035年的41.09亿t。其中,增长最快的是铁路部门,从0.43亿t增长到1.46亿t,增长率为235.52%,增长相对较慢的是公路部门,从11.71亿t增长到29.88亿t,增长率为155.25%,水路部门碳排放的年均增长率保持在13%左右;在能源结构优化情景下,CO2排放在基准情景的基础上下降14.20%,其中铁路部门的降碳效果最好,为49.30%,其次是航空、公路和水路部门;在运输结构调整情景下,交通部门的CO2排放在能源结构优化情景的基础上又有所下降,其减排率为21.29%,其中公路部门的降碳效果最好,为203.60%,而铁路、航空和水路部门碳排放不减反增;4种情景中,综合情景的减排效果最好,在该情景下,2035年交通部门的CO2排放量为基准情景的73.25%,其中公路部门降碳效果最好,为277.89%,对水路部门减排效果不明显。本文各情景的减排率与贾璐宇等[29]情景设置后的减排率相近且减排效果相同。
基准情景下,2025年我国四大交通部门的CO2总排放量为23.59亿t,占“十四五”总碳排放目标的22.47%,能源结构优化和运输结构调整下交通部门的CO2排放量分别为22.65亿t和21.85亿t,与基准情景相比分别下降3.98%和7.38%,2030年分别下降7.54%和11.99%,2035年分别下降12.48%和17.55%。到2030年,在能源结构优化情景、运输结构调整情景和综合情景下的CO2排放较基准情景均有所下降,分别降碳8.16%、13.63%和23.48%,但在4种情景下我国交通部门的CO2排放均无法实现达峰,因此,为达到目标值,相关部门仍需采取更加有效的措施,如加大现有措施的实施力度、突破现有技术难关、提高能源效率等。
不同地区交通碳排放情况也不相同,由图 3(b)(c)(d)可以看出,基准情景下,我国东、中、西三大地区交通部门的CO2排放呈显著上升趋势,增长速度由快到慢依次为西部地区、东部地区、中部地区,年均增长率分别为7.39%、6.58%、6.48%,因此,应针对我国西部地区交通部门CO2排放增长迅速的特点采取有效的措施降低碳排放的增长速度;从碳排放总量来看,到2035年各地区交通部门的CO2排放量由高到低依次为东部地区、中部地区、西部地区,排放量分别为21.85亿、9.66亿、9.58亿t,因此,降低东部地区交通部门的CO2排放对整个交通部门的碳减排具有重要意义。
三类政策情景实施后我国三大地区交通部门的CO2排放量均有下降,但不同地区采取不同措施达到的效果不同。到2035年,东部地区的交通部门在三大政策情景(能源结构优化情景、运输结构调整情景和综合情景)下,其CO2排放量较2020年分别减排10.69%、15.42%、22.44%,采取综合措施更具有减排效果;中部地区的交通部门在三大政策情景下CO2分别减排16.21%、28.51%、53.40%,其中,在综合情景下有望于2034年达到峰值,峰值为6.42亿t,无法满足2030年前碳达峰目标;西部地区的交通部门在三大政策情景下CO2分别减排21.12%、28.94%、60.8%,在综合情景下西部地区有望于2034年达到峰值,峰值为5.96亿t,仍无法满足2030年前碳达峰的目标。综合来看,优化能源结构在西部地区的碳减排效果更佳,调整运输结构在中、西部地区的碳减排效果相差不大,在综合情景下我国三大地区交通部门的CO2排放均有较大幅度的下降。在碳达峰目标下,三大地区的交通部门均无法按时达峰,预计中部地区的公路部门在运输结构调整下的达峰时间为2033年,在综合情景下的达峰时间为2032年,西部地区的公路部门在综合情景下的达峰时间为2034年,东部地区的交通部门均无法达峰。在4种情景下,我国三大地区交通部门的CO2排放均不能满足2030年前达峰的政策目标。
3.2.2 四大交通部门CO2排放量预测与对比分析
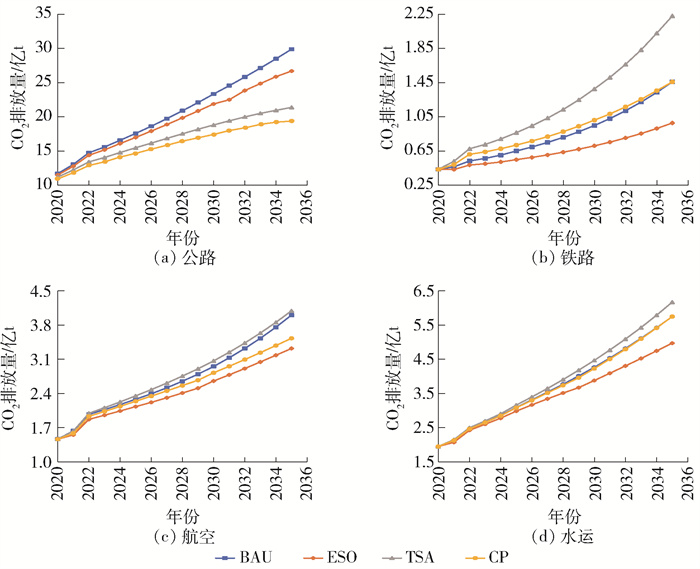
如图 4所示,三类政策情景对我国公路部门的碳排放均有减排效果,不同情景下的减排效果从大到小依次为:综合情景、运输结构调整情景和能源结构优化情景,其年均增长率分别为-2.67%、-1.22%、5.06%,均小于基准情景的7.01%。对于公路部门,长期更适合采取调整运输结构措施,其次是优化能源结构措施;对于铁路部门,长期采取优化能源结构措施的降碳效果更显著,综合措施在2035年之后也能起到降碳的效果,相反,在调整运输结构下,铁路部门受“公转铁”等运输结构调整政策的影响,周转量逐渐上升,其碳排放量也随之增加;对于航空部门,长期采取优化能源结构措施的降碳效果更显著,采取运输结构调整措施仅在短期内具有降碳效果;对于水路部门,长期采取优化能源结构措施的减排效果最佳,而仅采取运输结构调整措施的碳排放量不减反增。在四大交通部门中,仅公路部门有望在运输结构调整情景和综合情景下分别于2025年和2024年达峰,峰值分别为6.18亿和5.52亿t,这是由于“十四五”时期国家大力调整交通运输结构,使得公路部门的周转量减少,碳排放量也随之降低。
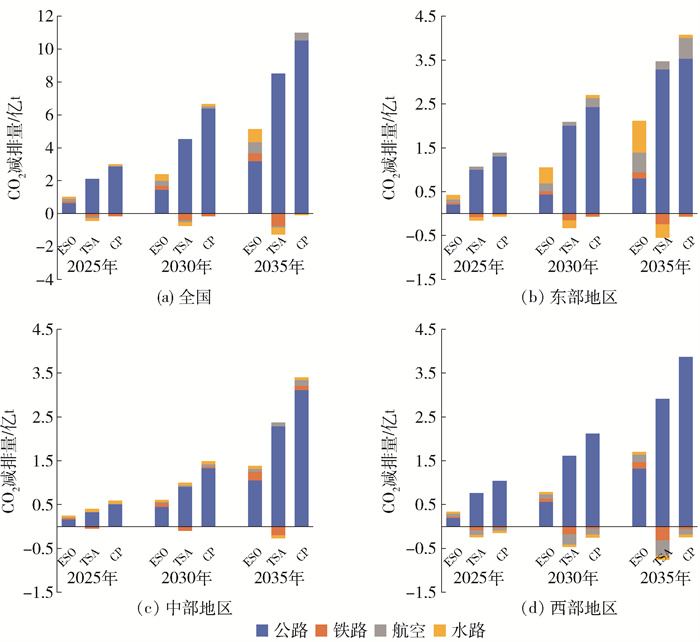
3.3 不同地区交通部门的碳减排潜力
本文的碳排放潜力是指在某一政策情景下未来的CO2排放量与同一年基准情景下的CO2排放量的差值,正值表示有减排潜力,负值表示实施该项措施与不实施该项措施相比CO2排放量会增加[46]。图 5展示了我国三大地区不同年份四大交通部门的碳减排潜力。总体上看,在单一政策情景中,我国交通部门通过调整运输结构的减排潜力更大,在2025年、2030年和2035年分别降碳1.74亿、3.78亿和7.21亿t,但在该情景下个别交通部门如铁路、航空和水路部门的减排潜力为负,这是由于受运输结构调整的影响,其货运量逐渐增大,故碳排放量也随之增加,为达到目标需配合其他措施进行减排。
各省采取不同措施的减排潜力也不同,在能源结构优化情景下,广东省、河北省、浙江省和山东省具有非常大的减排潜力,海南省、贵州省、西藏自治区和青海省的减排潜力较小;在运输结构调整情景下,河北省、河南省、辽宁省和陕西省的减排潜力更大,内蒙古自治区、湖北省、四川省和青海省的减排潜力较小,有些甚至为负值;在综合情景下,最有减排效果的省份有河北省、辽宁省、河南省和浙江省,海南省、青海省、西藏自治区和重庆市的减排潜力较小。
不同地区的碳减排潜力也不同,整体上看,我国东部地区交通部门的碳减排潜力最大,其次是西部地区和中部地区。2035年,在能源结构优化情景下,我国东、西、中三大地区的减排潜力分别为2.11亿、1.67亿、1.35亿t;在运输结构调整情景下,减排潜力分别为2.92亿、2.15亿、2.14亿t;在综合情景下,减排潜力分别为4.00亿、3.63亿、3.36亿t。
不同交通部门在不同地区的碳减排潜力也不同,从整体上看,公路部门具有巨大的碳减排潜力。对于公路部门,长期采取调整运输结构措施的减排潜力最大,其在三大地区的减排效果从高到低依次为东部地区、西部地区、中部地区,到2035年,公路部门在东部地区采取调整运输结构措施下可减排3.29亿t左右的碳,其减排潜力是中部地区的1.43倍,是西部地区的1.13倍。对于铁路部门,更适合采取优化能源结构措施,短期内东部地区的碳减排潜力略高于中、西部地区,但从中长期来看,中部地区的减排潜力最大,2035年可降碳0.19亿t。对于航空部门,在东、中部地区的两类单一政策情景下均具有减排效果,但东部地区采取优化能源结构措施的减排潜力更优,中部地区采取调整运输结构措施的减排量更多,而西部地区更适合采取优化能源结构的措施,采取调整运输结构反而会增大航空部门的碳排放量。水路部门在优化能源结构的措施下,在东部地区的碳减排潜力比在其他地区更明显,但在运输结构调整下东部地区的减排潜力为负数,这与水路运输周转量的增加有关。
4. 结论与建议
本文预测了不同地区不同情景下交通部门(公路、铁路、航空和水路)2021—2035年的CO2排放状况,并对比分析了东部、中部和西部三大地区各部门的减排潜力,主要得到以下几个结论:
1) 基准情景下,我国交通部门的CO2排放量稳步增长,预计2030年东部地区、中部地区和西部地区的排放量将分别较2020年增长99.46%、95.15%和118.87%,较2035年分别增长159.52%、152.48%和189.67%。其中,铁路部门的碳排放增长速度较快,增长率为235.52%。综合情景下交通部门CO2排放均会呈现较大幅度的下降,中、西部地区交通部门的CO2排放量有望在2034年达到峰值。
2) 对比分析不同政策情景下交通部门的CO2排放趋势可以发现,调整运输结构措施会产生最佳的碳减排效果,2035年东部、中部和西部地区将分别减排15.42%、28.51%和28.94%。而铁路、航空和水路部门采取优化能源结构措施的减排效果较好,2035年将分别减排49.30%、20.53%和15.66%,公路部门采取调整运输结构措施的减排效果更佳,2035年将减排203.60%。
3) 不同地区不同交通部门的减排潜力存在差异。在运输结构调整情景下,公路部门的减排效果从高到低依次为东部地区、西部地区、中部地区,航空部门仅在中部地区具有减排潜力,而铁路、水路部门在该情景下的减排潜力均为负值。在优化能源结构情景下,铁路部门短期内在东部地区的碳减排效果较好,长期在中部地区的减排潜力更大,航空部门的减排潜力在东部和西部地区更优,水路部门的减排效果在东部地区更显著。
通过本研究结果表明,优化能源结构和调整运输结构两类单一措施对我国交通部门的CO2排放均能起到减排效果,但综合措施下仍无法达到我国2030年碳达峰的目标要求,因此,我国交通部门应积极采取减排措施,政府等相关部门应根据不同地区、不同交通部门的碳排放特征制定更有针对性的政策,如在我国东部地区采取运输结构调整措施的同时需加大铁路、航空和水路部门清洁能源的使用,对于我国中、西部地区,优化交通结构和新政策的提出日益迫切,燃油经济性政策不应与东部地区相同。
-
表 1 各类能源的CO2排放因子
Table 1 CO2 emission factors of various energy sources
kg/kg 交通类型 油品类型 碳排放因子 道路交通 汽油 2.98 柴油 3.16 铁路运输 柴油 3.12 水路运输 燃料油 3.24 航空运输 煤油 3.10 注: 1.汽油的排放因子采用蔡博峰等[42]的研究结果。
2.柴油、燃料油和煤油的排放因子根据1中的方法进行计算得到。表 2 各政策情景的具体描述
Table 2 Detailed description of each policy scenario
情景 情景设置 情景描述 参考依据 基准情景(BAU) 假定2020年后交通部门将不再采取新措施来干预其发展,延续我国各省市目前现有的政策规划、减排措施以及可预见的技术路线等 公路、铁路、航空和水路的交通周转量占比与2020年保持一致,公共汽车、私人汽车等的保有量延续历史趋势,交通用能结构与2020年保持一致 《中国能源统计年鉴》《交通运输行业发展统计公报》《中国铁道年鉴》《民航行业发展统计公报》及各省市的统计年鉴等 调整运输结构情景(TSA) 在基准情景基础上,增加铁路运输占比,大力发展铁路货运、水路货运交通,同时,进一步发展城市公共交通出行比例 在2020年基础上,2025年铁路货运增长率为10%~45%,水路货运的增长率为12%~35%;河北省铁路、水路货运量占比85%,陕西省、山西省、内蒙古自治区货运量占比90%,辽宁省铁路货运量占比达到80%等,同时增大城内公共交通分担率 《推进多式联运发展优化调整运输结构工作方案(2021—2025年)》《国家综合立体交通网规划纲要》等 优化能源结构情景(ESO) 综合考虑“十四五”及碳达峰期间已颁布的各种政策措施,在不改变能源效率的基础上,增大交通部门清洁能源(电力、天然气、生物燃料、氢能等)占比 2025年,公路客运和货运新能源占比7%,铁路客货运电力占比50%,航空生物燃油占比6%,水运生物燃油占比4%;2035年,公路客货运新能源占比18%,铁路客货运电力占比62%,航空部门生物燃油占比18%,水路部门生物燃油占比15%。2025年新能源公交车辆占比72%,2035年公交车和出租车全部新能源化的省市自治区有:北京市、陕西省、山西省、河南省、湖南省、广东市、广西省、海南省、重庆市、内蒙古自治区、西藏自治区。2025年、2030年、2035年私家车新能源汽车占比分别为23%、33%、50% 《新能源汽车产业发展规划(2021—2035年)》《能源转型展望》《2030年前碳达峰行动方案》《绿色交通“十四五”发展规划》《节能与新能源汽车技术路线图 2.0》《北京碳达峰实施方案》《天津市绿色交通“十四五”发展规划》《上海市交通发展白皮书》等 综合情景(CP) 大力推进“公转铁”“公转水”,增大公共交通出行比例的基础上大力推广电力、生物燃油、生物航煤燃料等新能源 该情景是TSA和ESO两个单一政策情景的综合,如在2025年,铁路货运增长率为10%~45%的同时,铁路客货运中电力占比为50%;水运水路货运的增长率为12%~35%的同时,水运生物燃油占比为4%等。各省市的情景综合相关规划政策文件进行设置,此处省略 《推进多式联运发展优化调整运输结构工作方案(2021—2025)》《新能源汽车产业发展规划(2021—2035)》《绿色交通“十四五”发展规划》等 -
[1] 严刚, 郑逸璇, 王雪松, 等. 基于重点行业/领域的我国碳排放达峰路径研究[J]. 环境科学研究, 2022, 35(2): 309-319. YAN G, ZHENG Y X, WANG X S, et al. Pathway for carbon dioxide peaking in China based on sectoral analysis[J]. Research of Environmental Sciences, 2022, 35(2): 309-319. (in Chinese)
[2] KIM S. Decomposition analysis of greenhouse gas emissions in Korea's transportation sector[J]. Sustainability, 2019, 11(7): 1986. doi: 10.3390/su11071986
[3] 唐杰, 温照傑, 王东, 等. OECD国家碳排放达峰过程及对我国的借鉴意义[J]. 深圳社会科学, 2021, 4(4): 28-37. TANG J, WEN Z J, WANG D, et al. The process of carbon emission peak in OECD and the reference significance to China [J]. Social Sciences in Shenzhen, 2021, 4(4): 28-37. (in Chinese)
[4] 李艳红, 王安宇, 杨东. 基于LMDI与国际类比组合法的我国交通运输行业碳排放驱动因素及减排潜力[J]. 交通运输研究, 2022, 8(4): 36-45. LI Y H, WANG A Y, YANG D. Driving factors and carbon emission reduction potention of China's transportation industry based on the combination of LMDI and international analogies [J]. Transport Research, 2022, 8(4): 36-45. (in Chinese)
[5] LIIMATAINEN H, KALLIONPÄÄ E, PÖLLÄNEN M, et al. Decarbonizing road freight in the future—detailed scenarios of the carbon emissions of Finnish Road freight transport in 2030 using a Delphi method approach [J]. Technological Forecasting and Social Change, 2014, 81: 177-191. doi: 10.1016/j.techfore.2013.03.001
[6] ANNADANAM S K, KOTA S H. Emission of greenhouse gases and criteria pollutants from railways in India estimated using a modified top-down approach [J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2019, 213: 610-617. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2018.12.206
[7] ALAM M S, DUFFY P, HYDE B, et al. Improvement in the estimation and back-extrapolation of CO2 emissions from the Irish road transport sector using a bottom-up data modelling approach [J]. Transportation Research Part D: Transport and Environment, 2017, 56: 18-32. doi: 10.1016/j.trd.2017.07.011
[8] FU M, KELLY J A, CLINCH J P. Estimating annual average daily traffic and transport emissions for a national road network: a bottom-up methodology for both nationally-aggregated and spatially-disaggregated results [J]. Journal of Transport Geography, 2017, 58: 186-195. doi: 10.1016/j.jtrangeo.2016.12.002
[9] HONG S, CHUNG Y, KIM J, et al. Analysis on the level of contribution to the national greenhouse gas reduction target in Korean transportation sector using LEAP model [J]. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 2016, 60: 549-559. doi: 10.1016/j.rser.2015.12.164
[10] KAKOUEI A, VATANI A, IDRIS A K B. An estimation of traffic related CO2 emissions from motor vehicles in the capital city of Iran [J]. Iranian Journal of Environmental Health Science & Engineering, 2012, 9(1): 13. http://core.ac.uk/download/pdf/81854401.pdf
[11] 孙彦明, 刘士显. "双碳"目标下中国交通运输碳排放达峰预测[J]. 生态经济, 2023(11): 48-61. SUN Y M, LIU S X. Prediction of Chinese transportation carbon emissions peaking under the "Double Carbon" goal[J]. Ecological Economy, 2023(11): 48-61. (in Chinese)
[12] WANG C, CAI W J, LU X D, et al. CO2 mitigation scenarios in China's road transport sector [J]. Energy Conversion and Management, 2007, 48(7): 2110-2118. doi: 10.1016/j.enconman.2006.12.022
[13] 吕晨, 李艳霞, 杨楠, 等. 道路机动车温室气体排放评估与情景分析: 以北京市为例[J]. 环境工程, 2020, 38(11): 25-32. LÜ C, LI Y X, YANG N, et al. Assessment and scenario analysis of on-road vehicle greenhouse gases emission: a case study of Beijing[J]. Environmental Engineering, 2020, 38(11): 25-32. (in Chinese)
[14] 庞可, 张芊, 马彩云, 等. 基于LEAP模型的兰州市道路交通温室气体与污染物协同减排情景模拟[J]. 环境科学, 2022, 43(7): 3386-3395. PANG K, ZHANG Q, MA C Y, et al. Forecasting of emission co-reduction of greenhouse gases and pollutants for the road transport sector in Lanzhou based on the LEAP model [J]. Environmental Science, 2022, 43(7): 3386-3395. (in Chinese)
[15] 黄志辉, 纪亮, 尹洁, 等. 中国道路交通二氧化碳排放达峰路径研究[J]. 环境科学研究, 2022, 35(2): 385-393. HUANG Z H, JI L, YIN J, et al. Peak pathway of China's road traffic carbon emissions[J]. Research of Environmental Sciences, 2022, 35(2): 385-393. (in Chinese)
[16] 蔡博峰, 曹东, 刘兰翠, 等. 中国道路交通二氧化碳排放研究[J]. 中国能源, 2011, 33(4): 26-30. CAI B F, CAO D, LIU L C, et al. Study on CO2 emissions from road transport in China[J]. Energy of China, 2011, 33(4): 26-30. (in Chinese)
[17] SONG S K, SHON Z H. Emissions of greenhouse gases and air pollutants from commercial aircraft at international airports in Korea [J]. Atmospheric Environment, 2012, 61: 148-158. doi: 10.1016/j.atmosenv.2012.07.035
[18] 朱佳琳, 胡荣, 张军峰, 等. 机场碳排放测算与时间演化特征研究[J]. 武汉理工大学学报(交通科学与工程版), 2019, 43(1): 102-107. ZHU J L, HU R, ZHANG J F, et al. Research on the calculation and time evolution characteristics of airport carbon emissions[J]. Journal of Wuhan University of Technology (Transportation Science & Engineering), 2019, 43(1): 102-107. (in Chinese)
[19] 卢志想, 刘永红, 徐伟嘉, 等. 基于ICAO的航空碳排放计算与低碳对策探讨[J]. 资源节约与环保, 2014(9): 129-130. LU Z X, LIU Y H, XU W J, et al. ICAO based calculation of aviation carbon emissions and exploration of low-carbon strategies[J]. Resources Economization & Environmental Protection, 2014(9): 129-130. (in Chinese)
[20] 张永闯, 严凌. 基于铁路零碳排放的量化研究[J]. 物流科技, 2017, 40(8): 14-17. ZHANG Y C, YAN L. Quantitative study based on railway zero carbon emissions [J]. Logistics Sci-Tech, 2017, 40(8): 14-17. (in Chinese)
[21] 谢汉生, 周新军, 黄茵, 等. 铁路运营碳排放测算及低碳效应评价研究[J]. 铁道工程学报, 2014, 31(3): 117-122. XIE H S, ZHOU X J, HUANG Y, et al. Research on the measurement of carbon emission from railway operation and evaluation of low-carbon effect [J]. Journal of Railway Engineering Society, 2014, 31(3): 117-122. (in Chinese)
[22] 汪莹, 高佳钰, 雷雨轩. 我国铁路运营碳排放影响因素研究[J]. 铁道学报, 2020, 42(4): 7-16. WANG Y, GAO J Y, LEI Y X, et al. A research of influence factors on carbon emission of railway in China[J]. Journal of the China Railway Society, 2020, 42(4): 7-16. (in Chinese)
[23] 尹佩玲, 黄争超, 郑丹楠, 等. 宁波-舟山港船舶排放清单及时空分布特征[J]. 中国环境科学, 2017, 37(1): 27-37. YIN P L, HUANG Z C, ZHENG D N, et al. Marine vessel emission and its temporal and spatial distribution characteristics in Ningbo-Zhoushan Port [J]. China Environmental Science, 2017, 37(1): 27-37. (in Chinese)
[24] JIAO J D, HUANG Y, LIAO C P, et al. Sustainable development path research on urban transportation based on synergistic and cost-effective analysis: a case of Guangzhou [J]. Sustainable Cities and Society, 2021, 71: 102950. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S2210670721002353
[25] 张秀媛, 杨新苗, 闫琰. 城市交通能耗和碳排放统计测算方法研究[J]. 中国软科学, 2014(6): 142-150. ZHANG X Y, YANG X M, YAN Y. Statistical estimation method for energy consumption and carbon emissions by urban transport [J]. China Soft Science, 2014(6): 142-150. (in Chinese)
[26] 史丹, 叶云岭. 城市交通碳排放趋势与减排对策研究——以上海市为例[J]. 现代管理科学, 2022(4): 3-14. SHI D, YE Y L. Research on the trends and countermeasures of carbon emissions from urban transportation: a case study of Shanghai City[J]. Modern Management Science, 2022(4): 3-14. (in Chinese)
[27] 金昱, 苏红娟. 城市客运交通规划的碳排放估算方法[J]. 交通运输研究, 2022, 8(3): 42-48. JIN Y, SU H J. Carbon emissions estimation method of urban passenger transportation planning [J]. Transport Research, 2022, 8(3): 42-48. (in Chinese)
[28] 冯相昭, 赵梦雪, 王敏, 等. 中国交通部门污染物与温室气体协同控制模拟研究[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2021, 17(3): 279-288. FENG X Z, ZHAO M X, WANG M, et al. Simulation research on co-controlling pollutants and greenhouse gases emission in China's transportation sector [J]. Climate Change Research, 2021, 17(3): 279-288. (in Chinese)
[29] 贾璐宇, 王克. 碳中和背景下中国交通部门低碳发展转型路径[J]. 中国环境科学, 2023, 43(6): 3231-3243. JIA L Y, WANG K. Low-carbon transition pathways for China's transportation sector under the background of carbon neutrality [J]. China Environmental Science, 2023, 43(6): 3231-3243. (in Chinese)
[30] 田佩宁, 毛保华, 童瑞咏, 等. 我国交通运输行业及不同运输方式的碳排放水平和强度分析[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2023, 19(3): 347-356. TIAN P N, MAO B H, TONG R Y, et al. Analysis of carbon emission level and intensity of China's transportation industry and different transportation modes [J]. Climate Change Research, 2023, 19(3): 347-356. (in Chinese)
[31] LI W, LI H, ZHANG H, et al. The analysis of CO2 emissions and reduction potential in China's transport sector[J]. Mathematical Problems in Engineering, 2016, 2016: 1043717.
[32] 潘鹏飞, 王平, 李伟, 等. 基于LEAP的河南省交通运输节能减排潜力分析[J]. 河南农业大学学报, 2014, 48(3): 370-375. PAN P F, WANG P, LI W, et al. Analysis of the energy-saving and emission-reduction potential for transportation in Henan province based on LEAP [J]. Journal of Henan Agricultural University, 2014, 48(3): 370-375. (in Chinese)
[33] 周健, 崔胜辉, 林剑艺, 等. 基于LEAP模型的厦门交通能耗及大气污染物排放分析[J]. 环境科学与技术, 2011, 34(11): 164-170. ZHOU J, CUI S H, LIN J Y, et al. LEAP based analysis of transport energy consumption and air pollutants emission in Xiamen City[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2011, 34(11): 164-170. (in Chinese)
[34] 黄莹, 焦建东, 郭洪旭, 等. 交通领域二氧化碳和污染物协同控制效应研究[J]. 环境科学与技术, 2021, 44(7): 20-29. HUANG Y, JIAO J D, GUO H X, et al. Assessment of co-control effects for CO2 and air pollutants in transport sector [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2021, 44(7): 20-29. (in Chinese)
[35] FAN J L, WANG J X, LI F Y, et al. Energy demand and greenhouse gas emissions of urban passenger transport in the Internet era: a case study of Beijing [J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2017, 165: 177-189.
[36] 罗薇. 基于LEAP模型的云南省交通运输业能源消费及环境排放趋势研究[D]. 昆明: 云南大学, 2019. LUO W. Analysis of the energy-consume and mission-reduction trend for transportaion in Yunnan Province based on LEAP[D]. Kunming: Yunnan University, 2019. (in Chinese)
[37] 谭琦璐, 杨宏伟. 京津冀交通控制温室气体和污染物的协同效应分析[J]. 中国能源, 2017, 39(4): 25-31. TAN Q L, YANG H W. Synergistic effect analysis of greenhouse gases and pollutants in Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei traffic control [J]. Energy of China, 2017, 39(4): 25-31. (in Chinese)
[38] 郭秀锐, 刘芳熙, 符立伟, 等. 基于LEAP模型的京津冀地区道路交通节能减排情景预测[J]. 北京工业大学学报, 2017, 43(11): 1743-1749. GUO X R, LIU F X, FU L W, et al. Scenarios prediction of energy saving and emission reduction in the road transport sector of Beijing-Tianjin-Heibei region [J]. Journal of Beijing University of Technology, 2017, 43(11): 1743-1749. (in Chinese)
[39] 徐新华, 姜虹, 汪大辉. 江浙沪地区交通部门温室气体排放研究及减排措施[J]. 江苏环境科技, 1997(2): 41-44. XU X H, JIANG H, WANG D H. Research on greenhouse gas emissions and emission reduction measures of transportation departments in the Jiangsu-Zhejiang-Shanghai region[J]. Environmental Science and Technology, 1997(2): 41-44. (in Chinese)
[40] 范育洁, 曲建升, 张洪芬, 等. 西北五省区交通碳排放现状及影响因素研究[J]. 生态经济, 2019, 35(9): 32-37. FAN Y J, QU J S, ZHANG H F, et al. Study on the current situation and influence factors of transportation carbon emissions in five northwest provinces[J]. Ecological Economy, 2019, 35(9): 32-37. (in Chinese)
[41] LIU Y H, LIAO W Y, LIN X F, et al. Assessment of co-benefits of vehicle emission reduction measures for 2015—2020 in the Pearl River Delta region, China [J]. Environmental Pollution, 2017, 223: 62-72.
[42] 蔡博峰, 曹东, 刘兰翠, 等. 中国交通二氧化碳排放研究[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2011, 7(3): 197-203. CAI B F, CAO D, LIU L C, et al. China transport CO2 emission study [J]. Climate Change Research, 2011, 7(3): 197-203. (in Chinese)
[43] 董蕾. 基于LEAP模型的四川省交通运输业能源消费趋势研究[D]. 成都: 四川省社会科学院, 2016. DONG L. Research on energy consumption trends of Sichuan Province's transportation industry based on LEAP model[D]. Chengdu: Sichuan Academy of Social Sciences, 2016. (in Chinese)
[44] 王毅萌. 城市交通温室气体核算与减排潜力研究[D]. 邯郸: 河北工程大学, 2020. WANG Y M. Research on greenhouse gas accounting and emission reduction potential of urban transport[D]. Handan: Hebei University of Engineering Environmental Engineering, 2020. (in Chinese)
[45] 徐倩. 基于城市交通特征的中国机动车排放清单建立[D]. 广州: 暨南大学, 2020. XU Q. The establishment of China's vehicle emission inventory based on urban traffic characteristics[D]. Guangzhou: Jinan University, 2020. (in Chinese)
[46] 龚晓倩. 京津冀四大交通部门二氧化碳与污染物协同减排预测研究[D]. 北京: 北京工业大学, 2022. GONG X Q. Prediction of coordinated emission reduction of carbon dioxide and pollutants in the four major transportation sectors of Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei [D]. Beijing: Beijing University of Technology, 2022. (in Chinese)
[47] GUO B, GENG Y, FRANKE B, et al. Uncovering China's transport CO2 emission patterns at the regional level [J]. Energy Policy, 2014, 74: 134-146.
[48] 黄甫兰. 中国省域交通碳排放量的时空演变特征[J]. 物流科技, 2023, 46(11): 49-52. HUANG F L. The temporal and spatial characteristics of traffic carbon emissions in China [J]. Logistics Sci-Tech, 2023, 46(11): 49-52. (in Chinese)
[49] 杜菲. 碳达峰背景下中国交通运输碳排放现状及其减排路径研究[D]. 西安: 长安大学, 2022. DU F. Research on current situation of China's transportation carbon emission and its emission reduction path under the background of carbon peak[D]. Xi'an: Chang'an University, 2022. (in Chinese)



 下载:
下载: