Classification of Temporal Lobe Epilepsy Based on Radiomic Features of Hippocampal Subregions
-
摘要:
研究海马亚区的放射组学特征是否可以作为诊断颞叶癫痫(temporal lobe epilepsy, TLE)患者的生物学标志物,并探索某些放射组学特征在分类中的重要性. 实验纳入23例TLE患者和30例健康对照(healthy controls, HCs),对所有受试者进行结构磁共振成像(structural magnetic resonance imaging, sMRI)扫描,利用Freesurfer 7.2软件自动分割出海马亚区,3D slicer软件提取出每个亚区的放射组学特征,经过特征选择后采用支持向量机(support vector machine,SVM)对TLE组和HCs组进行分类. 左侧海马体部齿状回颗粒细胞层(GC_ML_DG-body)的分类准确度最高,为79.25%;右侧海马头部的分子层(Molecular_layer_HP-head)的分类准确度最高,为79.25%. 影响分类结果的重要特征中,二阶特征居多,其次是一阶特征和形状特征. 海马亚区的放射组学特征有望作为生物学标志物识别颞叶癫痫,其中二阶特征是用于颞叶癫痫分类的重要特征.
-
关键词:
- 颞叶癫痫(TLE) /
- 结构磁共振成像(sMRI) /
- 海马亚区 /
- 放射组学 /
- 支持向量机(SVM) /
- 分类
Abstract:To investigate whether radiomic features of hippocampal subregion can be used as biomarkers for the diagnosis of temporal lobe epilepsy (TLE) patients, and to explore the importance of some radiomics features in classification, structural magnetic resonance imaging (sMRI) was performed on 23 TLE patients and 30 healthy controls (HCs) subjects. Freesurfer 7.2 software was used for segmentation of hippocampal subregions. Radiomics features of hippocampal subregion were extracted by using 3D slicer software. After feature selection, support vector machine (SVM) was employed for the classification between TLE patients and HCs.The granule cell layer of dentate gyrus in the body of left hippocampus (GC_ML_DG-body) reached highest accuracy of 79.25%. The molecular_layer_HP in the head of right hippocampus (Molecular_layer_HP-head) has the highest classification accuracy of 79.25%. The majority of features related to classification results were second-order features, followed by first-order features and shape features. The radiomics features of hippocampal subregions can be used as a biomarker to identify TLE. The second-order features are the most important features for the classification of TLE.
-
医学图像所包含的信息比人眼所能识别出的有效信息要丰富得多,人们通常将视觉图像信息转化为深层特征进行定量研究. 作为定量图像分析的一个新兴领域,放射组学的概念被提出来[1],并应用于多种肿瘤和非肿瘤疾病,包括解码癌症的表型[2]、肿瘤的分级和诊断[3-4]以及肺结节的预测[5]. 随着医学图像处理的发展,放射组学在神经退行性疾病的诊断与预测中逐渐成为了研究的热点,如阿尔茨海默病[6]、帕金森病[7]、精神分裂症[8]等,通过对大量影像特征进行分析,并结合统计和机器学习方法来选择最有价值的影像特征,以便准确诊断和治疗疾病.
研究发现,在大多数颞叶癫痫(temporal lobe epilepsy, TLE)病例中,核磁共振影像(magnetic resonance imaging,MRI)通常在T1加权像中显示海马萎缩[9],海马体是内侧颞叶中最大的结构,被认为是导致幻觉和认知障碍病理生理学的主要大脑结构,这2种症状也是TLE的常见症状[10]. 另外,TLE伴海马硬化是成人最常见的局灶性癫痫之一[11],药物治疗往往难以治愈,针对这一类患者,手术切除癫痫病灶是控制癫痫发作的一种可行的治疗选择,而无创成像在精确识别致痫区方面起着重要作用[12]. 因此,对海马体的神经成像在TLE中仍然具有研究意义.
研究表明,海马结构的解剖亚区在神经系统疾病中受到了不同的影响[13]. 利用MRI对这些亚区的结构和功能进行分析,有助于深入了解神经疾病,比如Peixoto-Santos等[14]研究了下托、CA1、合并CA2-3、CA4、齿状回颗粒细胞层(GC_ML_DG)和整个海马的体积以区分海马硬化类型,进而确定了亚区特异性病理模式. Long等[15]研究了TLE双侧海马亚区体积与运动记忆的关系,包括伞部、CA1、合并CA2-3、合并CA4-齿状回、下托和前下托,结果发现海马亚区CA2-3体积与TLE患者的运动序列学习相关. 另外,海马不同的亚区参与了不同的记忆功能或病理过程,比如齿状回有助于处理空间和非空间信息[16-17],CA3有助于模式完成和空间记忆的快速灵活获取[18-19],CA1有助于所有感觉和记忆输入的整合[20],下托、旁下托和前下托有助于自我生成运动信息的整合等[21]. 也有证据表明,海马亚区的不同参与可能影响癫痫的控制或复发[22-23],因此,对海马亚区的深入研究仍值得被重视.
从MRI提取海马亚区的放射组学特征已被前人成功探索过,比如,Park等[8]将海马分为3个亚区: 亚区域复合体、合并CA1-3和合并CA4-齿状回,并且以82.1%的准确率识别出精神分裂症患者,发现海马亚区的显微组织特征可能会提高对精神分裂症的客观诊断,另外Park等[24]还发现双侧海马MRI放射组学特征能够鉴别TLE患者. Cheong等[25]进一步的研究发现,双侧海马放射组学特征有望识别MRI阴性TLE患者的病灶侧别,Feng等[26-27]发现阿尔茨海默病、轻度认知障碍与对照组相比,海马体的放射组学特征在多个亚区存在着显著差异,能够有助于检测阿尔茨海默病患者早期认知功能下降. 据了解,迄今为止还没有研究利用聚焦于海马亚区的放射组学特征来识别TLE患者.
本研究是基于MRI获取海马亚区的放射组学特征,深入探索不同海马亚区在TLE中的诊断价值,并对某些重要亚区及重要的放射组学特征进行统计分析,从而进一步确定诊断TLE患者的生物学标志物.
1. 实验对象与方法
1.1 实验对象
选取2017年10月—2018年10月就诊于北京天坛医院神经内科的TLE患者23例(男性15例,女性8例),所有患者均完成影像学数据及临床资料(年龄、病程、首发年龄等)的采集. 纳入标准:诊断符合国际抗癫痫联盟关于TLE的诊断标准,脑电图(electroencephalogram, EEG)检查显示病灶位于或起源于颞叶. 排除标准:药物滥用者、精神疾病者、患有影响智力的其他疾病患者、无法配合完成实验者以及检查不合格者. 同时招募30例(男性19例,女性11例)年龄、性别与患者组差异无统计学意义的无精神及神经系统疾病史、无脑血管病危险因素,且脑影像图像未见明显病变及变异的健康受试者作为对照组,具体的人口统计学如表 1所示,所有受试者均签署了知情同意书且实验获得北京天坛医院伦理委员会批准.
表 1 人口统计学数据Table 1. Data of demography参数 TLE组 NC组 P值 年龄 31.3±11.38 27.5±5.75 0.294 性别(男/女) 15/8 19/11 0.698 发病年龄 16.20±12.071 1.2 实验方法
1.2.1 数据采集
采用Siemens Trio 3.0T磁共振成像系统对所有受试者进行扫描,T1加权结构图像扫描参数为:重复时间(repetition time, TR)=2 300ms,回波时间(echo time, TE)=2.32 ms,反转恢复时间(inversion time, TI)=900ms,扫描野(field of view, FOV)=240mm×240mm,矩阵=256×256,层数=192,层厚=0.9mm,无间距扫描. 所有图像均经目测评价以确保成像质量.
1.2.2 数据处理
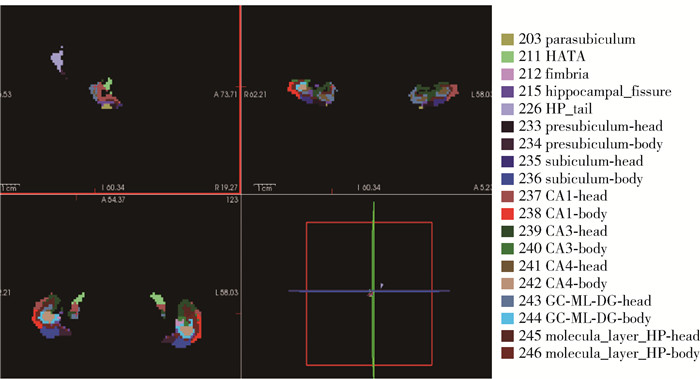
本研究的数据预处理及海马分割工作采用了FreeSurfer软件(在线下载 http://www.freesurfer.net/fswiki/DownloadAndInstall/). 预处理过程包括重采样、运动校正和确认、非均匀强度标准化、Talairach变换计算、强度标准化、皮质下白质和灰质结构的分割等[28-29]. 预处理结束后,进一步进行海马亚区的分割. Freesurfer中采用超高分辨率离体MRI数据(约0.1mm各向同性)构建的概率图谱来表示海马亚区[30],研究证明,基于FreeSurfer软件的海马亚区分割具有良好的可靠性和有效性[31]. 在该研究中,海马被分割为2组不同层次的亚区[32]:头部、体部和尾部;CA1、CA3(包含CA2)、CA4、齿状回颗粒细胞层(GC_ML_DG)、分子层(molecular_layer_HP)、下托(subiculum)、前下托(presubiculum)、旁下托(parasubiculum)、伞部(fimbria)、海马裂(hippocampal_fissure)和海马杏仁核过渡带(hippocampal amygdalar transition area, HATA),对每个参与者的亚区进行目测检查,以检测分割错误. 左右海马分别19个亚区的分割结果如图 1所示,具体名称如表 2所示.
表 2 所有海马亚区列表Table 2. List of all the hippocampal subregions部位 中文名称 英文名称 部位 中文名称 英文名称 前下托-头部 presubiculum-head 前下托-体部 presubiculum-body 下托-体部 subiculum-body 下托-头部 subiculum-head CA1-体部 CA1-body 海马 CA1-头部 CA1-head CA3-体部 CA3-body CA4-体部 CA4-body 头部 CA3-头部 CA3-head 海马 齿状回颗粒细胞层-体部 GC-ML-DG-body 体部 分子层-体部 molecular_layer_HP-body CA4-头部 CA4-head 旁下托 parasubiculum 海马杏仁核过渡带 HATA 齿状回颗粒细胞层-头部 GC_ML_DG-head 伞部 fimbria 海马裂 hippocampal_fissure 分子层-头部 molecular_layer_HP-head 海马尾 HP_tail 1.2.3 海马亚区放射组学提取
本研究使用3D Slicer软件进行可视化(在线下载https://download.slicer.org/),如图 2~4所示,输入2个图像,一个是带有海马19个标签的mask图像,一个是标准空间下的全脑影像. 图 2为左海马亚区放射组学特征的提取界面;图 3为右海马亚区放射组学特征的提取界面;图 4为功能框选择. 通过一个基于Python的开源模块(PyRadiomics, version 2.0) [33]自动计算左右海马每个标签亚区的放射组学特征: 18个一阶特征,14个形状特征,75个二阶特征(包括灰度共生矩阵、灰度游程矩阵、灰度大小区域矩阵、相邻灰度差矩阵),共提取2920个放射组学特征(107个特征×19个感兴趣区[左海马和右海马]).
1.2.4 特征选择与分类
所有放射组学特征均采用z评分标准化,然后采用2步特征选择策略进行特征选择,即双样本T检验(P<0.05)和最小绝对值收敛和选择算子(least absolute shrinkage and selection operator,LASSO),找到最佳特征子集并降低过度拟合的风险. T检验通过评估2组样本之间的差异性来选择特征[34]. LASSO是在回归过程中选择预测特征[35]. 在本研究中,首先通过双样本T检验方法确定了2组之间差异较大的特征集,然后利用LASSO算法选择最优特征子集,进一步提高分类性能. 支持向量机(support vector machine,SVM)是一种有监督的多元分类方法,用于识别最大边缘的最优超平面[36],核心思想是将样本映射到高维特征空间,使样本线性可分,其中核函数决定了映射形式. 径向基函数(radial basis function,RBF)作为SVM最常用的核函数,在小样本数据上,具有一定的稳定性并且性能表现较好[37]. 因此,使用Python中scikit-learn(https://scikit-learn.org/stable/)的SVM分类器和RBF进行后续分类.
$$ k\left(x_1, x_2\right)=\exp \left(-\frac{\left\|x_1-x_2\right\|^2}{2 \sigma^2}\right) $$ 式中:x1和x2为特征向量;σ为高斯核的宽度. 通过网格搜索选择最优的惩罚系数C和σ,最终得到最优的SVM模型.
海马每个亚区提取的107个特征组成特征向量,目标类别分别为0和1,其中0表示HCs受试者,1表示TLE患者,然后进行自动分类. 考虑到参与者人数较少在分类过程中采用留一交叉验证(Leave-one-out cross validation,LOOCV)算法[38],从而得到具有鲁棒性的结果,避免假高精度. 具体而言,在n个样本的每个LOOCV试验中,选择n-1个样本作为训练集,1个样本作为测试集. 另外,通过准确度、敏感度、特异性、F1分数和受试者工作特征(receiver operation characteristic,ROC)曲线和对应的ROC曲线下面积(area under curve,AUC)评估分类结果.
2. 结果
2.1 左海马19个亚区的放射组学特征分类结果
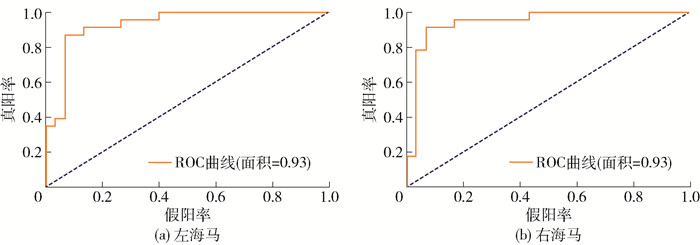
以AUC作为颞叶癫痫诊断能力的讨论标准,将0.8~1.0归为诊断能力好,0.7~0.8归为诊断能力较好,小于0.7归为诊断能力一般,如表 3所示,左海马19个亚区中,有7个亚区具有较好的诊断能力. 其中齿状回颗粒细胞层-体部(GC_ML_DG-body)准确度最高,为79.25%, 其次为CA4-头部(CA4-head),CA1-体部(CA1-body)和前下托-头部(presubiculum-head),准确度为75.47%. 结合左海马19个亚区的放射组学特征进行分类的准确度为84.91%,敏感度为69.57%,特异性为96.67%,F1分数为0.80,AUC为0.93,ROC曲线如图 5(a)所示.
表 3 左海马19个亚区的分类结果Table 3. Classification results of 19 subregions of left hippocampus亚区 准确度/% 敏感度/% 特异性/% F1分数 AUC parasubiculum 66.04 47.83 80.00 0.55 0.68 HATA 69.81 65.22 73.33 0.65 0.78 fimbria 66.04 65.22 66.67 0.63 0.71 hippocampal_fissure 67.92 69.57 66.67 0.65 0.68 HP_tail 64.15 47.83 76.67 0.54 0.72 presubiculum-head 75.47 52.17 93.33 0.65 0.75 presubiculum-body 54.72 39.3 66.67 0.43 0.66 subiculum-head 71.70 43.48 93.33 0.57 0.60 subiculum-body 60.08 47.83 70.00 0.51 0.65 CA1-head 66.04 47.83 80.00 0.55 0.65 CA1-body 75.47 69.57 80.00 0.71 0.73 CA3-head 64.15 56.52 70.00 0.58 0.65 CA3-body 64.15 34.78 86.67 0.46 0.66 CA4-head 75.47 65.22 83.33 0.70 0.70 CA4-body 67.92 43.48 86.67 0.54 0.61 GC-ML-DG-head 67.92 56.52 76.67 0.60 0.68 GC-ML-DG-body 79.25 65.22 90.00 0.73 0.75 molecular_layer_HP-head 64.15 43.48 80.00 0.51 0.59 molecular_layer_HP-body 67.92 56.52 76.67 0.60 0.67 left hippocampus 84.91 69.57 96.67 0.80 0.93 2.2 右海马19个亚区的放射组学特征分类结果
与左海马19个亚区类似,对右海马19个亚区进行了TLE组与HCs组的自动分类,结果如表 4所示. 通过观察结果发现,在右海马19个亚区中,13个亚区都具有较好的诊断能力,与左海马相比,亚区数量多了将近一倍,这可能意味着在TLE组与HCs组之间,右海马要比左海马的放射组学特征存在更多的异质性.分子层-头部(Molecular_layer_HP-head)达到了最高的准确度,为79.25%,其次为CA4-体部(CA4-body)、下托-头部(subiculum-head)、海马尾(HP_tail)、下托-体部(subiculum-body)、齿状回颗粒细胞层-体部(GC_ML_DG-body)和齿状回颗粒细胞层-头部(GC_ML_DG-head)等. 另外,右海马19个亚区的放射组学特征进行分类的准确度达到了88.68%,ROC曲线如图 5(b)所示. 与左海马比较,右海马的分类准确度更高,这可能意味着TLE患者中的右海马结构比左海马结构更具有识别价值.
表 4 右海马19个亚区的分类结果Table 4. Classification results of 19 subregions of right hippocampus亚区 准确度/% 敏感度/% 特异性/% F1分数 AUC parasubiculum 58.49 34.78 76.67 0.42 0.53 HATA 67.92 56.52 76.67 0.60 0.69 fimbria 58.49 43.48 70.00 0.48 0.61 hippocampal_fissure 69.81 43.48 90.00 0.56 0.71 HP_tail 73.58 56.52 86.67 0.65 0.73 presubiculum-head 64.15 56.52 70.00 0.58 0.69 presubiculum-body 66.04 30.43 93.33 0.44 0.60 subiculum-head 73.58 78.26 70.00 0.72 0.75 subiculum-body 71.70 60.87 80.00 0.65 0.71 CA1-head 66.04 52.17 76.67 0.57 0.70 CA1-body 66.04 34.78 90.00 0.47 0.71 CA3-head 58.49 34.78 76.67 0.42 0.60 CA3-body 69.81 34.48 96.67 0.50 0.73 CA4-head 69.81 39.13 93.33 0.53 0.74 CA4-body 75.47 43.48 100.00 0.61 0.76 GC-ML-DG-head 71.70 39.13 96.67 0.55 0.70 GC-ML-DG-body 71.70 47.83 90.00 0.59 0.73 molecular_layer_HP-head 79.25 60.87 93.33 0.72 0.90 molecular_layer_HP-body 58.49 30.43 80.00 0.39 0.75 right hippocampus 88.68 86.96 90.00 0.87 0.94 2.3 区分TLE组与HCs组的重要放射组学特征
经过双样本T检验保留了TLE组和HCs组具有显著差异性(P<0.05)的放射组学特征,进一步通过LASSO回归去除了回归系数为0的放射组学特征,最终确定了区分TLE组与HCs组的最优特征集. 如表 5所示,在左海马19个亚区中,确定了20个放射组学特征,其中有5个形状特征、4个一阶特征、11个二阶特征(3个灰度相关矩阵特征、3个灰度共生矩阵特征、3个灰度游程矩阵特征、1个相邻灰度差矩阵特征、1个灰度大小区域矩阵特征). 如表 6所示,右海马19个亚区中,确定了21个放射组学特征,其中有7个形状特征、6个一阶特征、8个二阶特征(4个灰度大小区域矩阵、3个灰度游程矩阵特征、1个灰度区域矩阵特征). 由此推断,二阶特征有可能是所有放射组学特征中最重要的特征,其次为形状特征,最后是一阶特征.
表 5 左海马19个亚区中区分TLE组与HCs组的重要放射组学特征列表Table 5. List of significant radiomic features to differentiate TLE from HCs in 19 subregions of left hippocampus亚区 特征类别 特征名称 英文名称 HATA 形状特征 最大长径 major axis length HATA 灰度依赖矩阵 小依赖性高灰度级强调 small dependence high gray level emphasis HATA 一阶特征 灰度范围 range fimbria 形状特征 最大长径 minor axis length fimbria 灰度依赖矩阵 依赖性熵 dependence entropy fimbria 灰度共生矩阵 自相关 autocorrelation fimbria 一阶特征 最小灰度 minimum hippocampal_fissure 一阶特征 最小灰度 minimum HP_tail 形状特征 体素体积 voxel volume HP_tail 形状特征 最大二维直径(柱) maximum 2D diameter column HP_tail 灰度依赖矩阵 依赖性非一致性 dependence non uniformity presubiculum-head 一阶特征 稳健平均绝对偏差 robust mean absolute deviation presubiculum-body 灰度大小区域矩阵 小面积强调 small area emphasis subiculum-head 灰度共生矩阵 相关性的信息测量2 imc2 subiculum-body 灰度游程矩阵 游程熵 run entropy CA3-head 灰度共生矩阵 集群突出 cluster prominence CA4-head 灰度游程矩阵 灰度级不均匀性归一化 gray level non uniformity normalized CA4-head 相邻灰度差矩阵 复杂性 complexity CA4-body 形状特征 最小长径 minor axis length CA4-body 灰度游程矩阵 灰度级不均匀性 gray level non uniformity 表 6 右海马19个亚区中区分TLE组与HCs组的重要放射组学特征列表Table 6. List of significant radiomic features to differentiate TLE from HCs in 19 subregions of right hippocampus右海马亚区 特征类别 特征名称 英文名称 parasubiculum 一阶特征 平均绝对偏差 mean absolute deviation HATA 形状特征 最大二维直径(切片) maximum 2D diameter slice HATA 灰度大小区域矩阵 灰度级偏差 gray level variance HP_tail 灰度游程矩阵 短游程低灰度级强调 short run low gray level emphasis presubiculum-head 灰度游程矩阵 游程熵 run entropy presubiculumbody 一阶特征 协方差 variance CA1-head 一阶特征 偏度 skewness CA1-body 形状特征 最大二维直径(切片) maximum 2D diameter slice CA1-body 一阶特征 偏度 skewness CA3-body 形状特征 最大三维直径 maximum 3D diameter CA3-body 灰度共生矩阵 相关性的信息测量1 imc1 CA3-body 灰度游程矩阵 低灰度级游程强调 low gray level run emphasis CA4-head 形状特征 表面积体积比 surface volume ratio CA4-head 灰度大小区域矩阵 小面积低灰度级强调 small area low gray level emphasis CA4-body 灰度大小区域矩阵 区域百分比 zone percentage GC-ML-DG-body 形状特征 最大二维直径(行) maximum 2D diameter row molecular_layer_HP-head 形状特征 最小长径 least axis length molecular_layer_HP-head 形状特征 平整度 flatness molecular_layer_HP-head 一阶特征 平均绝对偏差 mean absolute deviation molecular_layer_HP-head 灰度大小区域矩阵 区域熵 zone entropy molecular_layer_HP-body 一阶特征 四分位距 interquartile range 3. 讨论
由于海马不同亚区有着不同的发育模式[39],因此在以往的研究中,估计整个海马的放射组学特征可能掩盖区域发育差异,而该研究基于这个问题,探索利用海马亚区的放射组学特征进行TLE的自动分类. 发现不同的亚区有着不同的诊断能力,在左海马亚区中,齿状回颗粒细胞层-体部(GC-ML-DG-body)的分类准确度最高,在右海马亚区中,分子层-头部(molecular_layer_HP-head)的分类准确度最高, CA4、CA1、海马尾(HP_tail)在海马左右侧分类准确度都较好,结合右海马所有亚区的分类准确度要高于左海马所有亚区的分类准确度. 这与前人研究一致,在一项诊断TLE研究中发现,仅对海马的体积测定可能无法充分识别某些确诊癫痫病例,结合海马亚区更能够区分TLE组和HCs组,包括齿状回颗粒细胞层(GC-ML-DG)、分子层(molecular_layer_HP)、HP_tail、CA4和CA1等[40]. 在一项基于海马亚区放射组学特征区分精神分裂症患者与健康对照组的分类研究中,结果发现右海马亚区的放射组学特征被选择的数量更多[8],并且根据TLE疾病的进展,右侧海马比左侧海马更容易与对侧海马沟通[41],因此推断TLE作为精神疾病之一,右海马的组织结构异常可能要比左海马更多. 亚区的损伤与TLE患者的功能障碍也有一定的联系,比如齿状回萎缩与TLE患者在记忆编码任务中的表现不足相关,CA1萎缩与识别和回忆任务中的表现不足相关[42],齿状回和CA4中的细胞缺失导致陈述性记忆受损[43]. 此外,组织病理学评估显示的海马亚区的变化与手术后记忆功能的改善或恶化也有关[44]. 在该研究中,海马亚区的放射组学特征可以作为反映疾病神经学病理过程的神经影像生物标记物,辅助TLE的诊断,给未来关于TLE患者海马亚区更深层次的研究提供参考.
在本研究中,提取了放射组学特征中的3类特征,分别是形状特征、一阶特征和二阶特征. 形态特征主要反映体素的边界和整个区域,一阶特征可反映所测体素的对称性、均匀性以及局部强度分布变化,二阶特征描述了体素空间分布强度等级的特征. 这些放射组学特征可以将人眼观察不到的医学影像中的量化,增大了临床决策的成功率[45]. 在TLE的MRI检查中,T1弛豫时间是组织特征的直接反映,而二阶特征能够捕获T1信号强度的空间变化[46],这可能是二阶特征在分类过程中重要性占最高的原因. 在以往研究中,熵是海马二阶特征中最常选择的特征,熵反映图像中强度的均匀性或随机性[25],同样地,在本研究中,依赖性熵、游程熵、区域熵被选择出来,这可能提示TLE患者与HCs体素水平异质性显著不同. 据报道,海马形状异常[47]和二阶特征[48]与个体记忆表现相关,大脑结构的形状可以提供量化患有精神疾病的人群认知能力改变时的额外维度,在该研究中,形状特征和二阶特征也是区分TLE组与HCs组重要的放射组学特征,因此,放射组学利用高通量组学特征为颞叶癫痫的分类和预测提供了更准确的信息.
由于放射组学最终的目标是分类和预测,在自动分类识别模型中,特征选择作为最重要的一环,对分类结果十分重要. 在该研究中,采用双样本T检验与LASSO算法2步特征选择法,不仅避免了由于样本量较小而特征数量太多产生的过拟合,而且尽可能地选择出TLE组与HCs组之间最有分辨度的特征. 另外,研究表明神经影像学和机器学习的结合在癫痫诊断和预后方面越来越重要[49],支持向量机作为机器学习领域中一种可靠、高效的分类方法,在疾病诊断方面能够取得稳定且高精度的结果[50]. 在本研究中,利用海马亚区的放射组学特征结合支持向量机实现了的智能判别,对于机器学习技术应用于癫痫影像自动诊断中作出了有效尝试.
综上,海马亚区的放射组学特征可以作为潜在的生物学标记物帮助TLE的诊断. 然而,本研究也存在一些有待解决的问题. 第一,海马亚区的自动分割与真实大脑结构可能存在一定的差异,关于海马亚区自动分割的精确度还需更深入的研究. 第二,对于每个海马亚区,提取的放射组学特征数量比较多,经过特征选择后,具有鉴别意义的特征比较少,因此关于特征选择的研究有待深入. 第三,由于参与实验的被试量比较少,为了得到更客观的评估结果,需使用更多的临床数据进一步研究.
4. 结论
1) 海马作为TLE常见的病灶结构之一,利用放射组学特征能够有效区分TLE和HCs,提示放射组学特征可以作为MRI影像生物学标志物,反映TLE疾病的病理机制.
2) 在TLE自动分类中,二阶特征作为重要的MRI影像生物学标志物,能够有效表征出TLE与HCs之间的影像学差异.
3) 基于海马不同的亚区结构的放射组学特征进行TLE的自动分类,能够更加深入了解不同海马亚区结构的异常程度.
-
表 1 人口统计学数据
Table 1 Data of demography
参数 TLE组 NC组 P值 年龄 31.3±11.38 27.5±5.75 0.294 性别(男/女) 15/8 19/11 0.698 发病年龄 16.20±12.071 表 2 所有海马亚区列表
Table 2 List of all the hippocampal subregions
部位 中文名称 英文名称 部位 中文名称 英文名称 前下托-头部 presubiculum-head 前下托-体部 presubiculum-body 下托-体部 subiculum-body 下托-头部 subiculum-head CA1-体部 CA1-body 海马 CA1-头部 CA1-head CA3-体部 CA3-body CA4-体部 CA4-body 头部 CA3-头部 CA3-head 海马 齿状回颗粒细胞层-体部 GC-ML-DG-body 体部 分子层-体部 molecular_layer_HP-body CA4-头部 CA4-head 旁下托 parasubiculum 海马杏仁核过渡带 HATA 齿状回颗粒细胞层-头部 GC_ML_DG-head 伞部 fimbria 海马裂 hippocampal_fissure 分子层-头部 molecular_layer_HP-head 海马尾 HP_tail 表 3 左海马19个亚区的分类结果
Table 3 Classification results of 19 subregions of left hippocampus
亚区 准确度/% 敏感度/% 特异性/% F1分数 AUC parasubiculum 66.04 47.83 80.00 0.55 0.68 HATA 69.81 65.22 73.33 0.65 0.78 fimbria 66.04 65.22 66.67 0.63 0.71 hippocampal_fissure 67.92 69.57 66.67 0.65 0.68 HP_tail 64.15 47.83 76.67 0.54 0.72 presubiculum-head 75.47 52.17 93.33 0.65 0.75 presubiculum-body 54.72 39.3 66.67 0.43 0.66 subiculum-head 71.70 43.48 93.33 0.57 0.60 subiculum-body 60.08 47.83 70.00 0.51 0.65 CA1-head 66.04 47.83 80.00 0.55 0.65 CA1-body 75.47 69.57 80.00 0.71 0.73 CA3-head 64.15 56.52 70.00 0.58 0.65 CA3-body 64.15 34.78 86.67 0.46 0.66 CA4-head 75.47 65.22 83.33 0.70 0.70 CA4-body 67.92 43.48 86.67 0.54 0.61 GC-ML-DG-head 67.92 56.52 76.67 0.60 0.68 GC-ML-DG-body 79.25 65.22 90.00 0.73 0.75 molecular_layer_HP-head 64.15 43.48 80.00 0.51 0.59 molecular_layer_HP-body 67.92 56.52 76.67 0.60 0.67 left hippocampus 84.91 69.57 96.67 0.80 0.93 表 4 右海马19个亚区的分类结果
Table 4 Classification results of 19 subregions of right hippocampus
亚区 准确度/% 敏感度/% 特异性/% F1分数 AUC parasubiculum 58.49 34.78 76.67 0.42 0.53 HATA 67.92 56.52 76.67 0.60 0.69 fimbria 58.49 43.48 70.00 0.48 0.61 hippocampal_fissure 69.81 43.48 90.00 0.56 0.71 HP_tail 73.58 56.52 86.67 0.65 0.73 presubiculum-head 64.15 56.52 70.00 0.58 0.69 presubiculum-body 66.04 30.43 93.33 0.44 0.60 subiculum-head 73.58 78.26 70.00 0.72 0.75 subiculum-body 71.70 60.87 80.00 0.65 0.71 CA1-head 66.04 52.17 76.67 0.57 0.70 CA1-body 66.04 34.78 90.00 0.47 0.71 CA3-head 58.49 34.78 76.67 0.42 0.60 CA3-body 69.81 34.48 96.67 0.50 0.73 CA4-head 69.81 39.13 93.33 0.53 0.74 CA4-body 75.47 43.48 100.00 0.61 0.76 GC-ML-DG-head 71.70 39.13 96.67 0.55 0.70 GC-ML-DG-body 71.70 47.83 90.00 0.59 0.73 molecular_layer_HP-head 79.25 60.87 93.33 0.72 0.90 molecular_layer_HP-body 58.49 30.43 80.00 0.39 0.75 right hippocampus 88.68 86.96 90.00 0.87 0.94 表 5 左海马19个亚区中区分TLE组与HCs组的重要放射组学特征列表
Table 5 List of significant radiomic features to differentiate TLE from HCs in 19 subregions of left hippocampus
亚区 特征类别 特征名称 英文名称 HATA 形状特征 最大长径 major axis length HATA 灰度依赖矩阵 小依赖性高灰度级强调 small dependence high gray level emphasis HATA 一阶特征 灰度范围 range fimbria 形状特征 最大长径 minor axis length fimbria 灰度依赖矩阵 依赖性熵 dependence entropy fimbria 灰度共生矩阵 自相关 autocorrelation fimbria 一阶特征 最小灰度 minimum hippocampal_fissure 一阶特征 最小灰度 minimum HP_tail 形状特征 体素体积 voxel volume HP_tail 形状特征 最大二维直径(柱) maximum 2D diameter column HP_tail 灰度依赖矩阵 依赖性非一致性 dependence non uniformity presubiculum-head 一阶特征 稳健平均绝对偏差 robust mean absolute deviation presubiculum-body 灰度大小区域矩阵 小面积强调 small area emphasis subiculum-head 灰度共生矩阵 相关性的信息测量2 imc2 subiculum-body 灰度游程矩阵 游程熵 run entropy CA3-head 灰度共生矩阵 集群突出 cluster prominence CA4-head 灰度游程矩阵 灰度级不均匀性归一化 gray level non uniformity normalized CA4-head 相邻灰度差矩阵 复杂性 complexity CA4-body 形状特征 最小长径 minor axis length CA4-body 灰度游程矩阵 灰度级不均匀性 gray level non uniformity 表 6 右海马19个亚区中区分TLE组与HCs组的重要放射组学特征列表
Table 6 List of significant radiomic features to differentiate TLE from HCs in 19 subregions of right hippocampus
右海马亚区 特征类别 特征名称 英文名称 parasubiculum 一阶特征 平均绝对偏差 mean absolute deviation HATA 形状特征 最大二维直径(切片) maximum 2D diameter slice HATA 灰度大小区域矩阵 灰度级偏差 gray level variance HP_tail 灰度游程矩阵 短游程低灰度级强调 short run low gray level emphasis presubiculum-head 灰度游程矩阵 游程熵 run entropy presubiculumbody 一阶特征 协方差 variance CA1-head 一阶特征 偏度 skewness CA1-body 形状特征 最大二维直径(切片) maximum 2D diameter slice CA1-body 一阶特征 偏度 skewness CA3-body 形状特征 最大三维直径 maximum 3D diameter CA3-body 灰度共生矩阵 相关性的信息测量1 imc1 CA3-body 灰度游程矩阵 低灰度级游程强调 low gray level run emphasis CA4-head 形状特征 表面积体积比 surface volume ratio CA4-head 灰度大小区域矩阵 小面积低灰度级强调 small area low gray level emphasis CA4-body 灰度大小区域矩阵 区域百分比 zone percentage GC-ML-DG-body 形状特征 最大二维直径(行) maximum 2D diameter row molecular_layer_HP-head 形状特征 最小长径 least axis length molecular_layer_HP-head 形状特征 平整度 flatness molecular_layer_HP-head 一阶特征 平均绝对偏差 mean absolute deviation molecular_layer_HP-head 灰度大小区域矩阵 区域熵 zone entropy molecular_layer_HP-body 一阶特征 四分位距 interquartile range -
[1] LAMBIN P, RIOS V E, LEIJENAAR R, et al. Radiomics: extracting more information from medical images using advanced feature analysis[J]. European Journal of Cancer, 2012, 48(4): 441-446. doi: 10.1016/j.ejca.2011.11.036
[2] AERTS H J, VELAZQUEZ E R, LEIJWNAAR R T, et al. Decoding tumour phenotype by noninvasive imaging using a quantitative radiomics approach. [J]. Nature Communications, 2014, 5(1): 4004-4006. doi: 10.1038/ncomms5004
[3] PARK Y, CHOI Y S, AHN S S, et al. Radiomics MRI phenotyping with machine learning to predict the grade of lower-grade gliomas: a study focused on nonenhancing tumors[J]. Korean Journal of Radiology, 2019, 20(9): 1381-1389. doi: 10.3348/kjr.2018.0814
[4] PHILIPP L, ANNA-KATHARINA M, MARTIN K, et al. Feature-based PET/MRI radiomics in patients with brain tumors[J]. Neuro-Oncology Advances, 2021, 2(Suppl 4): iv15-iv21.
[5] 张莹, 王正通, 蓝天成, 等. CT影像组学在肺结节诊断中的研究进展[J]. 现代肿瘤医学, 2021, 29(19): 3503-3506. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SXZL202119040.htm ZHANG Y, WANG Z T, LAN T C, et al. Advances of radiomics research based on computed tomography in pulmonary nodules diagnosis[J]. Modern Oncology, 2021, 29(19): 3503-3506. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SXZL202119040.htm
[6] QI F, CHEN Y, LIAO Z, et al. Corpus callosum radiomics-based classification model in Alzheimer's disease: a case-control study[J]. Frontiers in Neurology, 2018, 9: 618-625. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2018.00618
[7] RAHMIM A, HUANG P, SHENKOV N, et al. Improved prediction of outcome in Parkinson's disease using radiomics analysis of longitudinal DAT SPECT images[J]. Neuroimage Clinical, 2017, 16(C): 539-544.
[8] PARK Y W, CHOI D, LEE J, et al. Differentiating patients with schizophrenia from healthy controls by hippocampal subfields using radiomics[J]. Schizophrenia Research, 2020, 223: 337-344. doi: 10.1016/j.schres.2020.09.009
[9] PAESSCHEN W V. Qualitative and quantitative imaging of the hippocampus in mesial temporal lobe epilepsy with hippocampal sclerosis[J]. Neuroimaging Clinics of North America, 2004, 14(3): 373-400. doi: 10.1016/j.nic.2004.04.004
[10] SOICHIRO N, MEGUMI A, HIROYUKI I, et al. Hippocampal pathophysiology: commonality shared by temporal lobe epilepsy and psychiatric disorders[J]. Neuroscience Journal, 2018, 2018: 1-9.
[11] BLUMCKE I, SPREAFICO R, HAAKER G, et al. Histopathological findings in brain tissue obtained during epilepsy surgery [J]. New England Journal of Medicine, 2017, 377(17): 1648-1656. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1703784
[12] LOWE A J, DAVID E, KILPATRICK C J, et al. Epilepsy surgery for pathologically proven hippocampal sclerosis provides long-term seizure control and improved quality of life[J]. Epilepsia, 2004, 45(3): 237-242. doi: 10.1111/j.0013-9580.2004.35903.x
[13] RODDY D W, CHLOE F, KELLY D, et al. The hippocampus in depression: more than the sum of its parts? advanced hippocampal substructure segmentation in depression[J]. Biological Psychiatry, 2019, 85(6): 487-497. doi: 10.1016/j.biopsych.2018.08.021
[14] PEIXOTO-SANTOS J E, CARVALHO L E D D, KANDRATAVICIUS L, et al. Manual hippocampal subfield segmentation using high-field MRI: impact of different subfields in hippocampal volume loss of temporal lobe epilepsy patients[J]. Frontiers in Neurology, 2018, 9: 927-933. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2018.00927
[15] LONG J, FENG Y, LIAO H P, et al. Motor sequence learning is associated with hippocampal subfield volume in humans with medial temporal lobe epilepsy[J]. Frontiers in Human Neuroscience, 2018, 12: 367-372. doi: 10.3389/fnhum.2018.00367
[16] BAKKER A, KIRWAN C B, MILLER M, et al. Pattern separation in the human hippocampal CA3 and dentate gyrus [J]. Science, 2008, 319(5870): 1640-1642. doi: 10.1126/science.1152882
[17] KESNER R P. A behavioral analysis of dentate gyrus function [J]. Progress in Brain Research, 2007, 163(163): 567-576.
[18] NAKAZAWA K. Requirement for hippocampal CA3 NMDA receptors in associative memory recall[J]. Science, 2002, 297(5579): 211-218. doi: 10.1126/science.1071795
[19] ROLLS E T, KESNER R P. A computational theory of hippocampal function, and empirical tests of the theory[J]. Progress in Neurobiology, 2006, 79(1): 1-48. doi: 10.1016/j.pneurobio.2006.04.005
[20] REMONDES M, SCHUMAN E. Role for a cortical input to hippocampal area CA1 in the consolidation of a long-term memory[J]. Nature, 2004, 431(7009): 699-703. doi: 10.1038/nature02965
[21] ROLLS E T. Neurophysiological and computational analyses of the primate presubiculum, subiculum and related areas[J]. Behavioural Brain Research, 2006, 174(2): 289-303. doi: 10.1016/j.bbr.2006.06.015
[22] BLUMCKE I, THOM M, ARONICA E, et al. International consensus classification of hippocampal sclerosis in temporal lobe epilepsy[J]. Epilepsia, 2013, 54(7): 1315-1329. doi: 10.1111/epi.12220
[23] KM A, HMH B, PM A, et al. Validation of automatic MRI hippocampal subfield segmentation by histopathological evaluation in patients with temporal lobe epilepsy[J]. Seizure, 2021, 87: 94-102. doi: 10.1016/j.seizure.2021.03.007
[24] PARK Y W, YUN S C, SONG E K, et al. Radiomics features of hippocampal regions in magnetic resonance imaging can differentiate medial temporal lobe epilepsy patients from healthy controls[J]. Scientific Reports, 2020, 10(1): 19567-19571. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-76283-z
[25] CHEONG E N, PARK J E, JUNG D E, et al. Extrahippocampal radiomics analysis can potentially identify laterality in patients with MRI-negative temporal lobe epilepsy[J]. Front Neurol, 2021, 12: 706576-706580. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2021.706576
[26] FENG Q, DING Z. MRI radiomics classification and prediction in Alzheimer's disease and mild cognitive impairment: a review[J]. Current Alzheimer Research, 2020, 17(3): 297-309. doi: 10.2174/1567205017666200303105016
[27] FENG Q, SONG Q, WANG M, et al. Hippocampus radiomic biomarkers for the diagnosis of amnestic mild cognitive impairment: a machine learning method[J]. Frontiers in Aging Neuroscience, 2019, 11: 323-328. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2019.00323
[28] FISCHL B, SALAT D H, VANDERKOUWE A J, et al. Sequence-independent segmentation of magnetic resonance images[J]. NeuroImage, 2004, 23: S69-S84. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2004.07.016
[29] SEGONNE F, DALE A M, BUSA E, et al. A hybrid approach to the skull stripping problem in MRI[J]. NeuroImage, 2004, 22(3): 1060-1075. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2004.03.032
[30] IGLESIAS J E, AUGUSTINACK J C, NGUYEN K, et al. A computational atlas of the hippocampal formation using ex vivo, ultra-high resolution MRI: application to adaptive segmentation of in vivo MRI[J]. NeuroImage, 2015, 115(1): 117-137.
[31] SMANN P G, IGLESIAS J E, GUTMAN B, et al. Free surfer-based segmentation of hippocampal subfields: a review of methods and applications, with a novel quality control procedure for ENIGMA studies and other collaborative efforts[J]. Human Brain Mapping, 2022, 43(1), 207-233. doi: 10.1002/hbm.25326
[32] ZHANG L, LU L, BU X, et al. Alterations in hippocampal subfield and amygdala subregion volumes in posttraumatic subjects with and without posttraumatic stress disorder[J]. Human Brain Mapping, 2021, 42(7): 2147-2158. doi: 10.1002/hbm.25356
[33] GRIETHUYSEN J, FEDOROV A, PARMAR C, et al. Computational radiomics system to decode the radiographic phenotype[J]. Cancer Research, 2017, 77(21): e104-e107. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-17-0339
[34] WANG X, REN Y S, ZHANG W S, et al. Classification of temporal lobe epilepsy with and without hippocampal sclerosis via two-level feature selection[C]//2017 International Conference on Computer Science and Technology. Lancaster: DEStech Publications, 2017.
[35] ROBERT T. Regression shrinkage and selection via the lasso: a retrospective[J]. Journal of the Royal Statistical Society: Series B (Statistical Methodology), 2011, 73(3): 267-288.
[36] CORTES C, VAPNIK V. Support-vector networks[J]. Machine Learning, 1995, 20(3): 273-297.
[37] ABBASNEJAD M E, RAMACHANDRAM D, MANDAVA R. A survey of the state of the art in learning the kernels[J]. Knowledge & Information Systems, 2012, 31(2): 193-221.
[38] WONG T T. Performance evaluation of classification algorithms by k-fold and leave-one-out cross validation[J]. Pattern Recognition, 2015, 48(9): 2839-2846. doi: 10.1016/j.patcog.2015.03.009
[39] TAMNES C K, BOS M, VAN D, et al. Longitudinal development of hippocampal subregions from childhood to adulthood[J]. Dev Cogn Neurosci, 2018, 30: 212-222. doi: 10.1016/j.dcn.2018.03.009
[40] PRINCICH J P, DONNELLY-KEHOE P A, DELEGLISE A, et al. Diagnostic performance of MRI volumetry in epilepsy patients with hippocampal sclerosis supported through a random forest automatic classification algorithm[J]. Frontiers in Neurology, 2021, 12: 613967-613971. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2021.613967
[41] MEMARIAN N, MADSEN S K, MACEY P M, et al. Ictal depth EEG and MRI structural evidence for two different epileptogenic networks in mesial temporal lobe epilepsy[J]. Plos One, 2015, 10(4): e0123588. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0123588
[42] MUELLER S G, LAXER K D, SCANLON C, et al. Different structural correlates for verbal memory impairment in temporal lobe epilepsy with and without mesial temporal lobe sclerosis[J]. Human Brain Mapping, 2012, 33(2): 489-499. doi: 10.1002/hbm.21226
[43] ROLAND C, ELISABETH P, LI J, et al. Differential influence of hippocampal subfields to memory formation: insights from patients with temporal lobe epilepsy[J]. Brain, 2014, 137(Pt 7): 1945-1957.
[44] JARDIM A P, LIU J, BABER J, et al. Characterising subtypes of hippocampal sclerosis and reorganization: correlation with pre and postoperative memory deficit[J]. Brain Pathology, 2018, 28(2): 143-154. doi: 10.1111/bpa.12514
[45] GILLIES R J, KINAHAN P E, HRICAK H. Radiomics: images are more than pictures, they are data[J]. Radiology, 2016, 278(2): 563-577. doi: 10.1148/radiol.2015151169
[46] PARK Y W, YUN S C, SONG E K, et al. Radiomics features of hippocampal regions in magnetic resonance imaging can differentiate medial temporal lobe epilepsy patients from healthy controls[J]. Scientific Reports, 2020, 10(1): 19567. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-76283-z
[47] CHINCARINI A, SENSI F, REI L, et al. Integrating longitudinal information in hippocampal volume measurements for the early detection of Alzheimer's disease[J]. NeuroImage, 2016, 125(5): 834-847.
[48] ZHANG Z, LIU Y, JIANG T, et al. Altered spontaneous activity in Alzheimer's disease and mild cognitive impairment revealed by regional homogeneity[J]. NeuroImage, 2012, 59(2): 1429-1440. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2011.08.049
[49] BARRAGAN-MONTERO A, JAVAID U, VALDES G, et al. Artificial intelligence and machine learning for medical imaging: a technology review[J]. Physica Medica, 2021, 83: 242-256. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmp.2021.04.016
[50] GLEICHGERRCHT E, MUNSELL B C, ALHUSAINI S, et al. Artificial intelligence for classification of temporal lobe epilepsy with ROI-level MRI data: a worldwide ENIGMA-epilepsy study[J]. Neuroimage Clinical, 2021, 31: 102765. doi: 10.1016/j.nicl.2021.102765
-
期刊类型引用(2)
1. 刘海,张昊,崔国旭,李洪亮,景国玺,何悦波. TGDI汽油机噪声源时域分离方法研究. 内燃机学报. 2023(02): 158-165 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 李博,江朝晖,谢军,饶元,张武. 基于迁移学习的园艺作物叶部病害识别及应用. 中国农学通报. 2021(07): 138-143 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(3)



 下载:
下载: