Fragility Analysis of the Double-column Bent With the SCEB Under Near-field Pulse-like Ground Motions in Transverse Direction
-
摘要:
为了研究桥墩结构的震后功能可恢复性, 针对附加自复位耗能支撑(self-centering energy dissipation braces, SCEB)双柱式桥墩结构进行基于增量动力分析方法的地震易损性分析, 采用最大侧移率和残余侧移率作为性能指标, 系统探讨其在近场脉冲型地震动作用下的失效概率. 为了对比分析, 同时选取60条远场无脉冲型地震动记录对附加SCEB桥墩结构进行了易损性分析. 结果表明: 在小震作用下, SCEB仅为桥墩结构提供刚度和承载力, 在大震作用下还可提供耗能能力, 同时可以提供良好的自复位能力; 附加SCEB可有效降低桥墩结构在近场脉冲型地震动作用下的失效概率(最大侧移率和残余侧移率), 特别是残余侧移率; 附加SCEB桥墩结构在近场脉冲型地震动作用下的失效概率大于远场无脉冲型地震动作用下的失效概率. 自复位耗能支撑可有效减小桥墩结构的失效概率, 提高桥墩结构的抗震性能.
Abstract:To investigate the seismic resilience of the bridge piers, the seismic fragility analysis of double-column bent with additional SCEB was carried out based on incremental dynamic analysis method, and the maximum drift ratio and residual drift ratio were selected as performance indicators to systematically study the failure probability of the bent under near-field pulse-like ground motions. For comparative analysis, 60 far-field non-pulse-like ground motion records were also selected. Results show that SCEB only provides stiffness and strength for the bent under minor earthquakes, and it can also provide the stable energy dissipation capacity and good self-centering capacity under major earthquakes. The SCEB can effectively reduce the failure probability (maximum drift ratio and residual drift ratio) of the bent under near-field pulse-like ground motions, especially the residual drift ratio. The failure probability of the double-column bent with SCEB under near-field pulse-like ground motion was greater than that under far-field non-pulse-like ground motion.SCEB can effectively reduce the failure probability of the bent and enhance the seismic performance.
-
桥梁结构作为重要的交通生命线,在地震作用下一旦发生损伤破坏,不仅会使桥梁结构丧失使用功能,严重时可能会发生坍塌,造成人员伤亡,严重影响震后的应急救援行动,造成巨大的间接损失. 而近场脉冲型地震动具有明显的长周期和速度脉冲,在短时间内对结构输入大量的地震能量,使结构产生更为严重的损伤破坏. 因此,越来越多的学者开始关注近场脉冲型地震动对结构的影响. 唐玉红等[1]对单层单跨钢筋混凝土框架结构进行振动台模拟试验,并对试验结果进行分析,得出近场脉冲型地震动会导致钢筋混凝土结构发生更为严重的损伤破坏. 翟长海等[2]研究钢筋混凝土大跨刚构桥横桥向在近场脉冲型地震动作用下的反应,得出近场脉冲型地震动引起的桥梁反应比非脉冲型地震动引起的桥梁反应强烈. Li等[3]研究典型的公路三跨连续梁桥在近场脉冲型地震动作用下的反应,结果表明考虑含有脉冲的近场地震动,将增大连续梁桥结构的地震反应. 刘洋等[4]对型钢-混凝土组合结构桥梁进行动力时程分析,得出近场脉冲型地震动引起的桥梁结构反应更为严重. Choi等[5]为了研究近场脉冲型地震动对桥墩抗震性能的影响,进行振动台试验,结果表明在近场脉冲型地震动作用下桥墩存在较大的残余位移. 马海滨等[6]研究近场脉冲型地震动作用下公路常规梁桥的震后残余位移,结果表明结构残余位移总体上随速度脉冲幅值的增大而增大. 残余位移的存在会严重降低结构抵抗余震的能力,特别是当残余侧移率大于0.5%时,结构的修复成本将大于重建成本[7]. 因此发展具有优良自复位能力的桥梁结构具有十分重要的意义.
为了减小甚至消除残余位移,学者提出自复位结构体系. 自复位结构体系主要分为3类:摇摆结构[8-9]、预拉节点结构[10]、自复位耗能支撑结构[11]. 其中摇摆结构和预拉节点结构多用于新建结构,而自复位耗能支撑结构不仅可以用于新建结构还可以用于已有结构的加固改造. 自复位耗能支撑拥有良好的耗能能力和自复位能力[12-19],目前自复位耗能支撑主要应用于框架结构. Zhu等[13]提出一种自复位摩擦耗能支撑,将该支撑装置应用于3层和6层框架并与传统防屈曲支撑进行比较,结果表明该支撑可以有效减少框架结构的残余位移. 徐龙河等[14]将预压弹簧自恢复耗能支撑用于单榀钢框架,分析结果表明该支撑基本消除了钢框架的残余位移. 刘璐等[15]提出一种自复位防屈曲支撑,将该支撑用于一个6层钢框架,结果表明该支撑可以有效减小钢框架的最大位移,其残余位移基本为零. 谢钦等[16]将自复位耗能支撑用于9层钢框架,动力时程分析结果表明自复位耗能支撑可以有效减小钢框架的残余位移. 目前将自复位耗能支撑用于桥梁结构的研究较少. 徐龙河等[17]将预压弹簧自恢复耗能支撑应用于斜拉桥的桥塔,并对附加该支撑的斜拉桥进行动力时程分析,结果表明该支撑可以有效减小桥塔的位移和主梁的残余位移. Dong等[18-19]发展了一种自复位防屈曲约束支撑,并在钢筋混凝土双柱式桥墩之间安装该支撑,对其进行拟静力试验研究,进一步对附加该支撑的桥梁结构进行了非线性动力时程分析,表明该支撑可有效减小桥梁结构的残余位移.
目前,将自复位耗能支撑应用于桥梁结构的研究较少,且以往研究仅限于桥梁结构在某几条地震动作用下的地震响应分析,未涉及附加自复位耗能支撑桥墩结构的地震概率分析. 单条地震动激励往往难以真实反映桥梁结构的抗震性能,而大量的地震动对桥墩结构进行激励所得到的结果可以有更强的说服力. 鉴于此,本文采用附加自复位耗能支撑桥墩结构作为分析对象,同时考虑原桥墩结构和附加防屈曲支撑桥墩结构,选取60条近场脉冲型地震动记录和60条远场无脉冲型地震动记录,通过进行增量动力分析,采用最大侧移率和残余侧移率作为性能指标建立近场脉冲型地震动和远场无脉冲型地震动作用下3种桥墩结构的失效概率曲线,从损伤概率方面系统地评估附加自复位耗能支撑桥墩的抗震性能.
1. 桥墩结构模型
1.1 桥墩结构
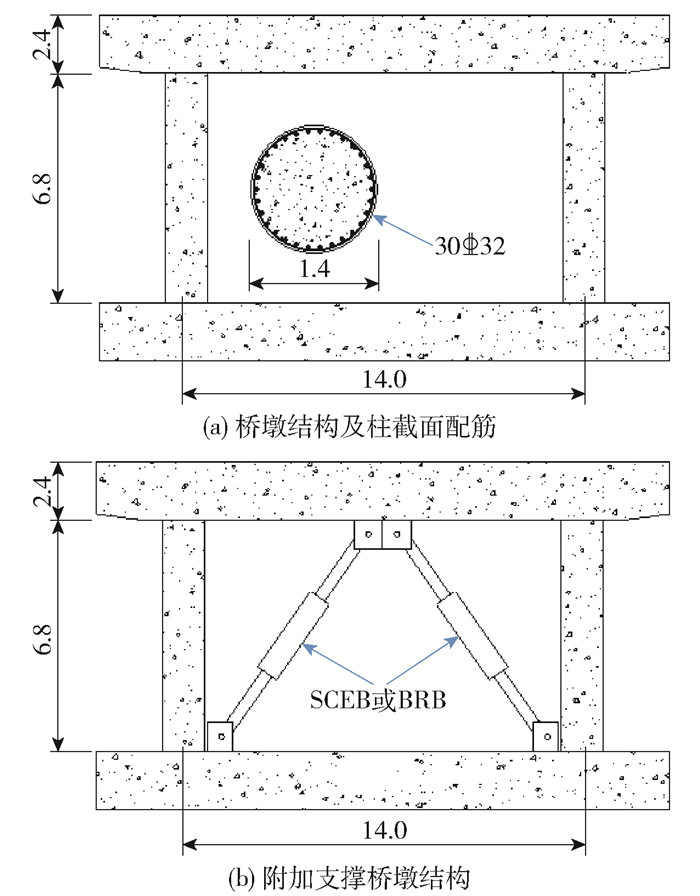
选取某山区桥梁墩柱部分,其结构形式如图 1所示,为双柱式桥墩结构. 每个桥墩直径为1.4m,桥墩高为6.8m,2个墩柱中心间距14.0m. 盖梁截面尺寸为2.0m×2.4m. 混凝土采用C35,钢筋采用HRB400,轴压比为0.2,纵筋配筋率1.56%,配箍率0.87%,保护层厚度为50mm.
为了提高该双柱式桥墩的抗震性能,拟在桥墩中采用人字形的方式布置支撑,该种布置方式可以使支撑竖直方向的分力相互抵消. 由于自复位耗能支撑(self-centering energy dissipation brace,SCEB)具有良好的耗能能力和自复位能力,本文支撑拟采用SCEB. 作为对比,本文选取纯耗能支撑——防屈曲支撑(buckling-resisting bracing,BRB),BRB通过耗能内芯产生塑性变形耗散能量. 本文考虑3种桥墩结构:原桥墩结构、附加BRB桥墩结构和附加SCEB桥墩结构.
本文所附加的支撑可以有效提高桥墩结构的刚度和承载力. 支撑作为保险丝构件,应先于桥墩结构进入屈服,因此支撑的屈服位移应小于桥墩结构的屈服位移. 根据Wang等[20]对BRB核心区的参数研究,本文将支撑设计为可承担桥墩结构水平承载力的50%. 为了对比SCEB和BRB对桥墩结构抗震性能的影响,本文控制SCEB和BRB的刚度和屈服强度相同. SCEB耗能部分采用BRB,内芯材料采用Q235,截面为十字型,内芯厚度为20mm,宽度为122mm,面积为4 480mm2,自复位部分采用组合碟簧,材料为51CrV4. BRB内芯采用Q235,十字型截面,内芯厚度为30mm,宽度为228mm,面积为12 780mm2.
1.2 数值模拟
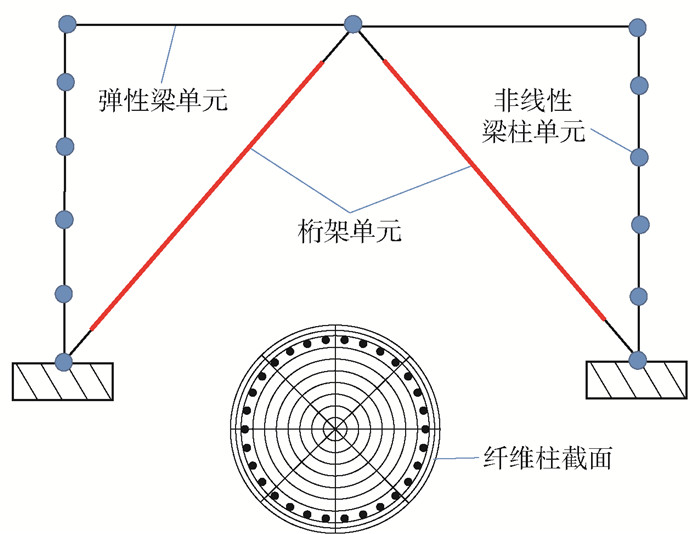
采用Opensees软件建立该双柱式桥墩结构的非线性有限元模型,如图 2所示. 墩柱采用基于非线性的梁柱单元建模,截面采用纤维截面,在纤维截面上相应赋予钢筋和混凝土本构关系. 其中墩柱混凝土采用基于Kent-Park模型的Concrete 02材料,柱内钢筋采用Steel 02材料,混凝土材料参数见表 1,钢筋材料参数见表 2. 盖梁采用弹性梁单元进行建模,上部荷载为734kN/m. 本文模型分析不考虑土-结构相互作用的影响,墩底固定.
表 1 混凝土材料参数Table 1. Concrete material parameters参数 C35 核心区 保护层 抗压强度/MPa 26.3 23.4 峰值应力压应变 0.002 0.002 屈服后抗压强度/MPa 5.27 4.68 屈服后的应变 0.013 0.004 抗拉极限强度/MPa 1.84 1.64 表 2 钢筋材料参数Table 2. Reinforcement material parameters参数 HRB400 屈服强度/MPa 393.2 弹性模量/GPa 200 刚度比 0.01 SCEB和BRB采用Truss单元建模,Truss单元只承受轴向力. 在Opensees软件中,SCEB采用SelfCentering材料,BRB采用Steel 02材料. SCEB和BRB的性能参数见表 3.
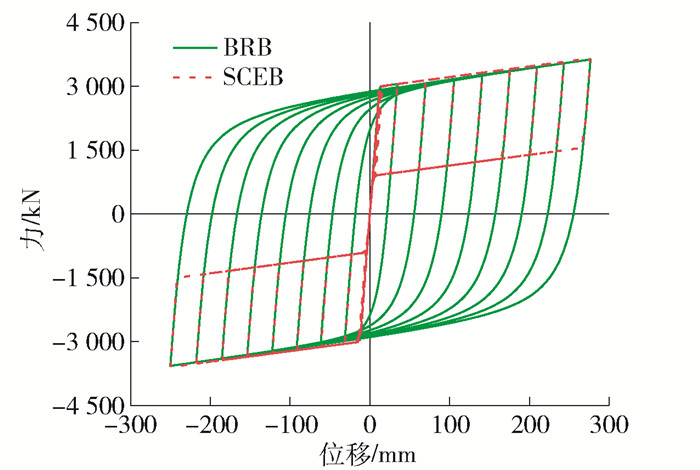
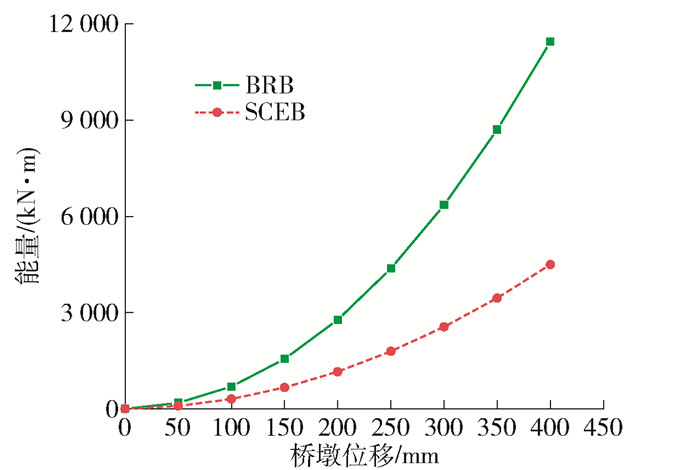
表 3 支撑的设计参数Table 3. Brace design parameters参数 SCEB BRB 第一刚度/(kN·mm-1) 250.0 250.0 第二刚度/(kN·mm-1) 2.5 2.5 屈服力/kN 3 000 3 000 图 3为BRB和SCEB在拟静力荷载作用下的滞回曲线. 从图 3中可以看出,BRB滞回曲线呈纺锤状,SCEB表现出明显的旗帜型,两者均曲线饱满,有稳定的耗能能力,BRB滞回曲线的面积明显大于SCEB滞回曲线的面积. 图 4给出SCEB和BRB的累积耗能曲线,从曲线中可以看出BRB耗能能力几乎是SCEB耗能的2倍,BRB拥有更好的耗能能力.
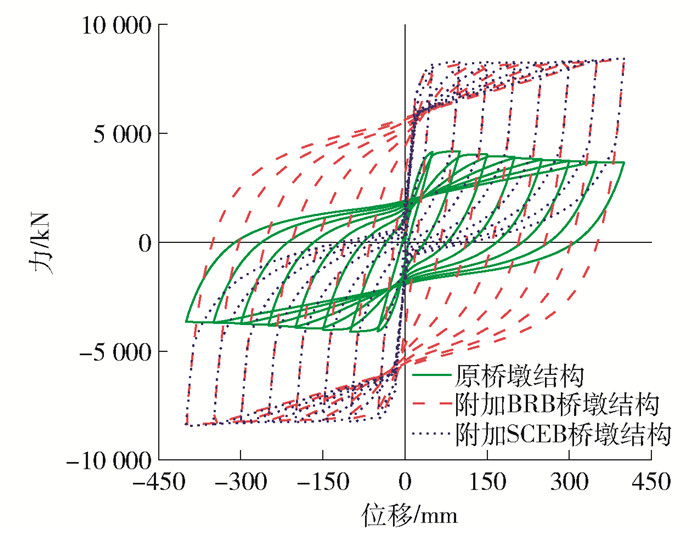
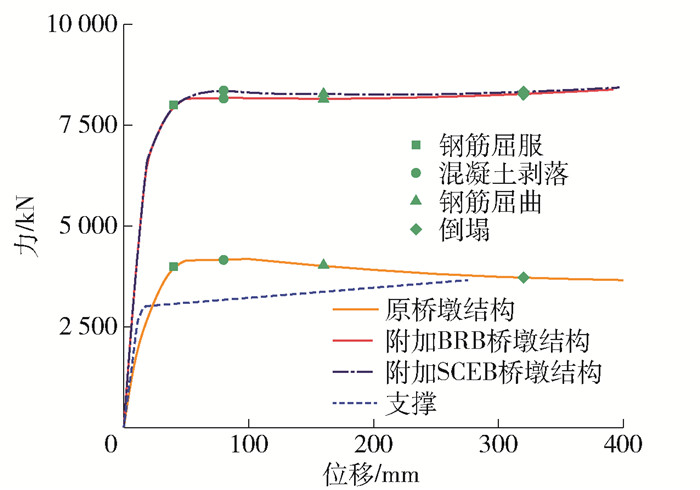
图 5为3种桥墩结构的滞回曲线,附加支撑提高了原桥墩结构的刚度和承载力,且附加SCEB桥墩结构的残余位移明显降低. 图 6为3种桥墩结构的静力推覆曲线,从图中可以看出,附加支撑桥墩结构的刚度和承载力均得到提高,支撑先于桥墩结构进入屈服,有利于更好地保护桥墩结构. 3种桥墩结构的自振周期见表 4. 原桥墩结构的自振周期为0.45 s,附加支撑之后,桥墩结构的自振周期为0.31 s,附加支撑桥墩的自振周期减小.
表 4 桥墩基本周期Table 4. Basic period of the bents桥墩结构 周期/s 原桥墩结构 0.45 附加BRB桥墩结构 0.31 附加SCEB桥墩结构 0.31 2. 地震动的选取
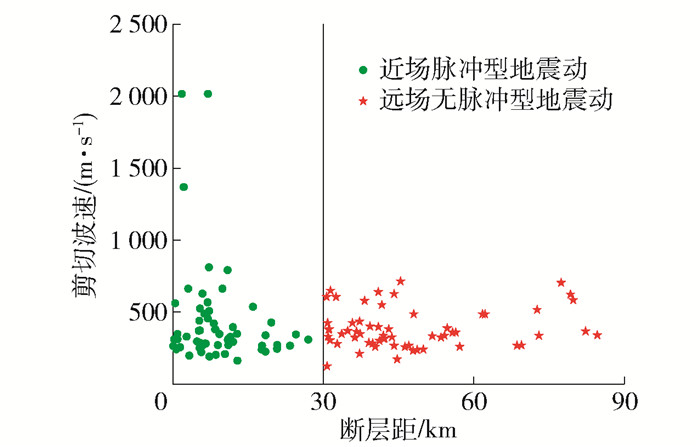
工程界常用断层距的大小来划分近、远场地震动,但目前这个界限值并未统一,Wu等[21]以30 km作为近场地震动的限值. 本文以断层距30 km来划分近、远场地震动. 近场地震动一般呈现出短持时、高幅值和大脉冲等特性,含有脉冲的近场地震动会对桥墩结构产生更加严重的破坏作用,本文脉冲型地震动的选取方法参考文献[22]. 依据以上原则,从太平洋地震工程研究中心地震动数据库(PEER Ground Motion Database)中选取了60条近场脉冲型地震动记录. 作为对比,也从数据库中选取了60条远场无脉冲型地震动记录. 地震动详细信息见表 5、6.
编号 地震名称 站台名称 年份 震级 断层距/km 地面峰值加速度/g 地面峰值速度/(cm·s-1) 1 San Fernand Pacoima Dam 1971 6.6 1.81 1.219 114.47 2 Coyote Lake Gilroy Array #2 1979 5.7 9.02 0.256 31.93 3 Coyote Lake Gilroy Array #4 1979 5.7 5.70 0.252 31.84 4 Coyote Lake Gilroy Array #6 1979 5.7 3.11 0.422 44.35 5 Imperial Valley-06 Agrarias 1979 6.5 0.65 0.183 41.68 6 Imperial Valley-06 EC County Center FF 1979 6.5 7.31 0.235 73.39 7 Imperial Valley-06 Brawley Airport 1979 6.5 10.42 0.220 40.94 8 Imperial Valley-06 El Centro Array #3 1979 6.5 12.85 0.267 47.97 9 Imperial Valley-06 El Centro Array #10 1979 6.5 8.60 0.173 50.69 10 Imperial Valley-06 El Centro-Meloland Geot.Array 1979 6.5 0.07 0.298 92.61 11 Mammoth Lakes-06 Long Valley Dam 1980 5.9 16.03 0.414 34.13 12 Morgan Hill Coyote Lake Dam 1984 6.2 0.53 1.303 78.44 13 Morgan Hill Gilroy Array #6 1984 6.2 9.85 0.292 36.49 14 N.Palm Springs Morongo Valley 1986 6.1 12.03 0.217 39.99 15 San Salvador Geotech Investig Center 1986 5.8 6.30 0.704 79.92 16 San Salvador National Geografical Inst 1986 5.8 6.99 0.534 72.99 17 Whittier Narrows-01 Bell Gardens-Jaboneria 1987 6.0 17.79 0.220 28.31 18 Whittier Narrows-01 Compton-Castlegate St 1987 6.0 23.37 0.322 29.47 19 Whittier Narrows-01 Downey-Birchdale 1987 6.0 20.79 0.348 39.92 20 Whittier Narrows-01 Downey-Co Maint Bldg 1987 6.0 20.82 0.205 30.68 21 Whittier Narrows-01 LB-Orange Ave 1987 6.0 24.54 0.228 31.45 22 Whittier Narrows-01 Santa Fe Springs - E.Joslin 1987 6.0 18.49 0.469 34.40 23 Superstition Hills-02 Kornbloom Road (temp) 1987 6.5 18.48 0.139 29.61 24 Superstition Hills-02 Parachute Test Site 1987 6.5 0.95 0.432 134.29 25 Superstition Hills-02 Poe Road (temp) 1987 6.5 11.16 0.475 41.17 26 Loma Prieta Gilroy-Historic Bldg 1989 6.9 10.97 0.285 43.39 27 Loma Prieta Gilroy Array #2 1989 6.9 11.07 0.317 40.37 28 Loma Prieta Gilroy Array #3 1989 6.9 12.82 0.368 45.43 29 Loma Prieta Saratoga-Aloha Ave 1989 6.9 8.50 0.326 45.97 30 Loma Prieta Saratoga-W Valley Coll 1989 6.9 9.31 0.331 64.91 31 Cape Mendocino Cape Mendocino 1992 7.0 6.96 1.494 122.33 32 Cape Mendocino Petrolia 1992 7.0 8.18 0.656 88.51 33 Landers Lucerne 1992 7.3 2.19 0.725 133.40 34 Northridge-01 Jensen Filter Plant 1994 6.7 5.43 0.411 111.47 35 Northridge-01 Jensen Filter Plant Generator 1994 6.7 5.43 0.571 76.13 36 Northridge-01 LA-Saturn St 1994 6.7 27.01 0.430 41.58 37 Northridge-01 LA-Sepulveda VA Hospital 1994 6.7 8.44 0.753 77.67 38 Northridge-01 LA Dam 1994 6.7 5.92 0.426 74.84 39 Northridge-01 Newhall-Fire Sta 1994 6.7 5.92 0.590 96.59 40 Northridge-01 Newhall-W Pico Canyon Rd 1994 6.7 5.48 0.419 118.18 41 Northridge-01 Pacoima Dam (downstr) 1994 6.7 7.01 0.416 44.29 42 Northridge-01 Pacoima Dam (upper left) 1994 6.7 7.01 1.285 103.38 43 Northridge-01 Pacoima Kagel Canyon 1994 6.7 7.26 0.433 51.38 44 Northridge-01 Rinaldi Receiving Sta 1994 6.7 6.50 0.874 148.00 45 Northridge-01 Sylmar-Converter Sta 1994 6.7 5.35 0.623 116.25 46 Northridge-01 Sylmar-Converter Sta East 1994 6.7 5.19 0.853 120.97 47 Northridge-01 Sylmar-Olive View Med FF 1994 6.7 5.30 0.843 129.37 48 Kobe, Japan KJMA 1995 6.9 0.96 0.834 91.10 49 Kobe, Japan Port Island (0 m) 1995 6.9 3.31 0.348 90.60 50 Kobe, Japan Takarazuka 1995 6.9 0.27 0.614 86.25 51 Kobe, Japan Takatori 1995 6.9 1.47 0.618 120.62 52 Northwest China-03 Jiashi 1997 6.1 17.73 0.274 35.25 53 Duzce, Turkey Bolu 1999 7.1 12.04 0.806 65.88 54 Duzce, Turkey Duzce 1999 7.1 6.58 0.515 84.23 55 Chi-Chi CHY024 1999 6.2 19.65 0.187 33.08 56 Kocaeli, Turkey Gebze 1999 7.5 10.92 0.261 44.63 57 Kocaeli, Turkey Izmit 1999 7.5 7.21 0.230 38.29 58 Kocaeli, Turkey Yarimca 1999 7.5 4.83 0.227 69.72 59 Yountville Napa Fire Station #3 2000 5.0 11.50 0.409 39.78 60 Denali, Alaska TAPS Pump Station #10 2002 7.9 2.74 0.333 115.72 编号 地震名称 站台名称 年份 震级 断层距/km 地面峰值加速度/g 地面峰值速度/(cm·s-1) 1 San Fernando Upland-San Antonio Dam 1971 6.6 61.73 0.058 2.89 2 San Fernando Wrightwood-6074 Park Dr 1971 6.6 62.23 0.055 3.26 3 Imperial Valley-06 Plaster City 1979 6.5 30.33 0.043 3.18 4 Imperial Valley-07 Delta 1979 5.0 49.93 0.118 3.61 5 Livermore-01 APEEL 3E 1980 5.8 30.59 0.065 3.91 6 Livermore-01 Fremont-Mission 1980 5.8 35.68 0.044 4.31 7 Livermore-01 Tracy-Sewage 1980 5.8 53.82 0.079 6.71 8 Coalinga-01 Parkfield-Cholame 12w 1983 6.4 55.77 0.047 6.34 9 Coalinga-01 Parkfield-Cholame 1E 1983 6.4 43.68 0.091 11.29 10 Coalinga-01 Parkfield-Cholame 3E 1983 6.4 40.98 0.046 6.63 11 Coalinga-01 Parkfield-Cholame 5W 1983 6.4 48.70 0.136 10.75 12 Coalinga-01 Parkfield-Fault Zone 3 1983 6.4 37.22 0.140 13.95 13 Coalinga-01 Parkfield-Gold Hill 6W 1983 6.4 47.88 0.069 5.73 14 Coalinga-01 Parkfield-Cholame 2WA 1983 6.4 44.72 0.113 9.66 15 Morgan Hill Capitola 1984 6.2 39.08 0.098 5.09 16 N. Palm Springs San Jacinto-Valley cemetery 1986 6.1 30.97 0.054 1.76 17 N. Palm Springs Hesperia 1986 6.1 72.97 0.041 2.36 18 Chalfant Valley-02 Convict Creek 1986 6.2 31.19 0.060 4.14 19 Whittier Narrows-01 Terminal Island — S Seaside 1987 6.0 40.36 0.043 4.31 20 Whittier Narrows-01 Pacoima Kagel Canyon USC 1987 6.0 36.29 0.122 7.57 21 Loma Prieta Belmont-Envirotech 1989 6.9 44.11 0.108 11.83 22 Loma Prieta Berkeley LBL 1989 6.9 79.25 0.049 8.30 23 Loma Prieta Golden Gate Bridge 1989 6.9 79.81 0.233 40.07 24 Loma Prieta Palo Alto-SLAC Lab 1989 6.9 30.86 0.277 31.11 25 Loma Prieta Salinas-John & Work 1989 6.9 32.78 0.092 11.87 26 Loma Prieta Hayward-BART Sta 1989 6.9 54.15 0.156 14.24 27 Loma Prieta Fremont — Emerson Court 1989 6.9 39.85 0.192 12.76 28 Cape Mendocino Eureka-Myrtle & West 1992 7.0 41.97 0.154 20.23 29 Landers Barstow 1992 7.3 34.86 0.130 20.45 30 Northridge-01 LA-116th St School 1994 6.7 41.17 0.208 10.19 31 Northridge-01 Malibu-Point Dume Sch 1994 6.7 33.67 0.130 8.39 32 Northridge-01 LA-Obregon Park 1994 6.7 37.36 0.355 13.57 33 Northridge-01 Inglewood-Union Oil 1994 6.7 42.20 0.091 7.12 34 Northridge-01 Newport Bch-Newport & Coast 1994 6.7 84.54 0.103 5.75 35 Northridge-01 LA-City Terrace 1994 6.7 36.62 0.263 12.78 36 Northridge-01 Bell Gardens-Jaboneria 1994 6.7 44.10 0.102 7.07 37 Northridge-01 Compton-Castlegate St 1994 6.7 47.04 0.089 8.31 38 Northridge-01 Covina-W Badillo 1994 6.7 53.45 0.105 4.78 39 Northridge-01 LA-Pico & Sentous 1994 6.7 31.33 0.186 14.23 40 Northridge-01 Lake Hughes #1 1994 6.7 35.81 0.077 9.45 41 Northridge-01 Leona Valley #2 1994 6.7 37.24 0.091 7.59 42 Northridge-01 Palmdale-Hwy 14 & Palmdale 1994 6.7 41.67 0.067 8.44 43 Northridge-01 Terminal Island-S Seaside 1994 6.7 57.20 0.148 16.48 44 Northridge-01 West Covina-S Orange Ave 1994 6.7 51.71 0.064 7.19 45 Northridge-01 San Gabriel-E Grand Ave 1994 6.7 39.31 0.142 8.09 46 Northridge-01 Huntington Bch-Waikiki 1994 6.7 69.50 0.089 5.61 47 Northridge-01 Anaheim-W Ball Rd 1994 6.7 68.62 0.074 6.06 48 Hector Mine Amboy 1999 7.1 43.05 0.150 19.74 49 Hector Mine Desert Hot Springs 1999 7.1 56.40 0.067 7.44 50 Hector Mine Fun Valley 1999 7.1 54.68 0.088 6.19 51 Hector Mine Joshua Tree 1999 7.1 31.06 0.147 19.15 52 Chi-Chi TCU006 1999 7.6 72.61 0.077 18.48 53 Chi-Chi TCU052 1999 5.9 38.25 0.082 7.09 54 Chi-Chi TCU075 1999 5.9 30.75 0.045 3.55 55 Chi-Chi TCU045 1999 6.2 77.38 0.008 1.03 56 Chi-Chi TCU068 1999 6.2 48.02 0.021 3.87 57 Chuetsu-oki, Japan Joetsu Yanagishima paddocks 2007 6.8 31.43 0.185 15.56 58 Chuetsu-oki, Japan Joetsu, Aramaki District 2007 6.8 32.54 0.064 11.78 59 Chuetsu-oki, Japan Tokamachi Chitosecho 2007 6.8 30.65 0.069 9.44 60 Iwate,Japan Matsuyama City 2008 6.9 40.98 0.084 6.09 图 7展示了所选取地震动的震级和断层距,从图中可以看出,所选地震动记录震级均在5~8级,且震级分布较均匀. 从图 8可以看出,所选取地震动记录的剪切波速分布也比较均匀.
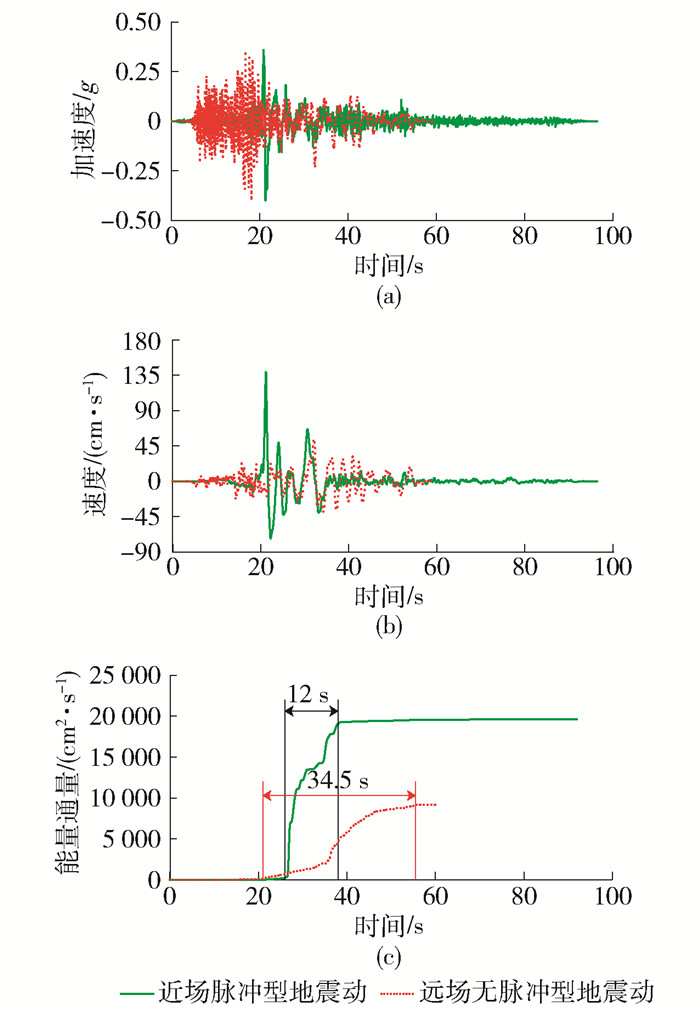
图 9给出近场脉冲型地震动——Denali, Alaska TAPS Pump Station #10和远场无脉冲型地震动——Chuetsu-oki, Japan Tokamachi Chitosecho的加速度、速度和能量通量时程曲线,2条地震动记录的幅值均调整为0.4g. 从图 8可以看出,近场脉冲型地震动含有较大的速度脉冲,其峰值速度达到了139.2 cm/s,而远场无脉冲型地震动峰值速度只有53.6 cm/s. 另外近场脉冲型地震动的能量通量在26.0~38.0 s迅速增大,达到18 840 cm2/s,而远场无脉冲型地震动的能量通量小于近场脉冲型地震动的能量通量,且其增加较为缓慢,从21.0 s到55.5 s增长8 863 cm2/s.
3. 非线性时程分析
从120条地震动中分别选取了1条近场脉冲型地震动——Denali, Alaska TAPS Pump Station #10和远场无脉冲型地震动——Chuetsu-oki, Japan Tokamachi Chitosecho进行分析,将2条地震动记录调幅至0.2 g和0.8 g并分别对不同桥墩结构进行计算.
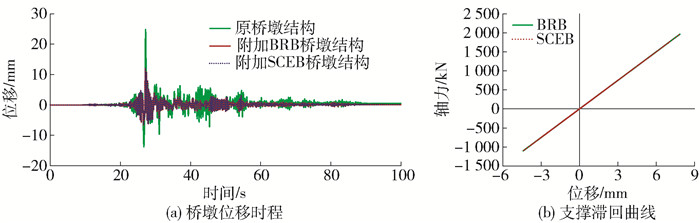
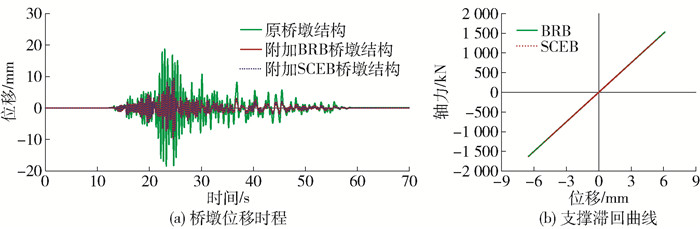
图 10、11为桥墩结构在0.2 g近场脉冲型地震动和远场无脉冲型地震动作用下的位移时程和支撑的滞回曲线. 从图 10(a)、11(a)中可以看出,附加支撑之后,桥墩结构在地震动作用下的位移反应得到降低,附加SCEB桥墩结构和附加BRB桥墩结构的位移时程曲线重合. 这是由于在小震作用下,支撑还处于弹性状态,只为桥墩结构提供刚度和承载力,这在支撑滞回曲线中也可以看出,见图 10(b)、11(b),BRB和SCEB的滞回曲线均为直线. 对比图 10(a)、11(a)可知,桥墩结构在近场脉冲型地震动作用下的位移大于在远场无脉冲型地震动作用下的位移,另外从表 7也可以看出,3种桥墩结构在0.2 g近场脉冲型地震动作用下的最大位移分别为24.9、12.1、12.1 mm;而在0.2 g远场无脉冲型地震动作用下的最大位移分别18.7、9.8、9.8 mm.
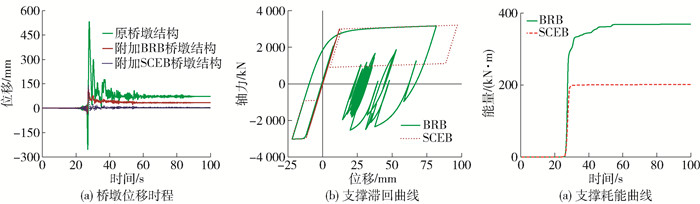
表 7 桥墩结构在地震动作用下的位移响应Table 7. Displacement responses of the bridge bents under ground motion地震动 峰值地面运动加速度/g 最大位移/mm 残余位移/mm 原桥墩结构 附加BRB桥墩结构 附加SCEB桥墩结构 原桥墩结构 附加BRB桥墩结构 附加SCEB桥墩结构 Denali,Alaska 0.2 24.9 12.1 12.1 0.0 0.0 0.0 Chuetsu-oki, Japan 18.7 9.8 9.8 0.0 0.0 0.0 Denali,Alaska 0.8 532.5 117.0 138.5 72.1 33.8 3.9 Chuetsu-oki, Japan 119.3 44.6 54.2 14.7 3.2 0.0 图 12为不同桥墩结构在0.8 g近场脉冲型地震动作用下的响应曲线,从图 12(a)中可以明显看出附加支撑之后,桥墩结构的最大位移和残余位移均得到降低,其中附加BRB桥墩结构最大位移和残余位移分别降低78.0%和53.1%,附加SCEB桥墩结构最大位移降低74.0%,而其残余位移降低94.6%. 这是因为附加支撑不仅增加桥墩结构的刚度和承载力,还为桥墩结构提供耗能能力,因此,桥墩结构的位移反应会降低. 特别地,附加SCEB桥墩结构的残余位移基本为零,这是由于SCEB还可以为桥墩结构提供自复位能力.
值得注意的是,附加BRB桥墩结构的最大位移降低78.0%,而附加SCEB桥墩结构的最大位移降低74.0%,从图 12(b)可以看出BRB和SCEB均有饱满的滞回曲线,但是BRB的滞回面积更大,图 12(c)更是直观展示在相同地震动作用下BRB的耗能能力优于SCEB的耗能能力,这可能是导致附加SCEB桥墩结构的最大位移反应略大于附加BRB桥墩结构的原因.
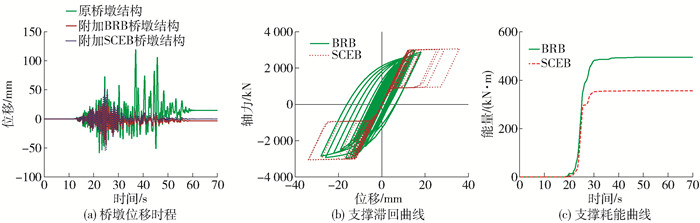
而在0.8 g远场无脉冲型地震动作用下,如图 13所示,与在近场脉冲型地震动作用下的反应类似,附加支撑之后桥墩结构的最大位移和残余位移均得到了减小,其中附加SCEB桥墩结构的残余位移基本为零. 由图 13(b)可以看出BRB和SCEB滞回曲线饱满,由图 13(c)可知BRB的耗能能力优于SCEB的耗能能力.
对比图 12、13,另外从表 7可以看出桥墩结构在近场脉冲型地震动作用下的位移反应明显大于桥墩结构在远场无脉冲型地震动作用下的位移反应,与在0.2 g地震动激励下的情况下类似.
4. 易损性分析
易损性分析是指在不同强度地震作用下结构反应超过各种破坏状态的条件概率[24]. 目前基于增量动力分析方法的地震易损性分析已经应用于结构地震易损性分析的各个领域.
4.1 易损性曲线的建立
结构的地震需求超过其承载力的概率可以通过易损性曲线来评估. 假设需求和容量呈对数正态分布,然后使用概率方程估算特定部件达到或超过特定损坏状态的概率. 本文地震动强度参数采用峰值地面运动加速度(peak ground motion acceleration, PGA),结构失效概率可表示为
$$ P=1-\phi\left[\frac{\ln \alpha-\ln M}{\sqrt{\beta_{\mathrm{D}}^2+\beta_{\mathrm{C}}^2}}\right] $$ (1) $$ \beta_{\mathrm{D}}=\sqrt{\frac{1}{N-2} \sum\limits_{i=1}^N\left[\ln D_i-\ln M\right]^2} $$ (2) 式中:P表示失效概率;ln Di表示结构地震需求的对数均值;α表示对应结构不同性能水平的限值;βD表示结构在各地震动强度下地震需求参数对数标准差平均值;βC表示结构抗震能力离差;M是地震需求的中值;$ \phi[*]$为标准正态分布函数;N为用于回归分析的数据个数.
4.2 性能指标
Upadhyay等[25]指出最大侧移率和残余侧移率能有效表征桥墩结构的损伤状态. 本文选取最大侧移率和残余侧移率作为损伤指标,为了分析结构的失效概率,需要结合损伤指标定义结构的各种损伤极限状态. 对于采用最大侧移率Δm和残余侧移率Δr作为损伤指标的所对应的各损伤极限状态值见表 8、9.
4.3 桥墩结构增量动力分析
4.3.1 以最大侧移率作为损伤指标
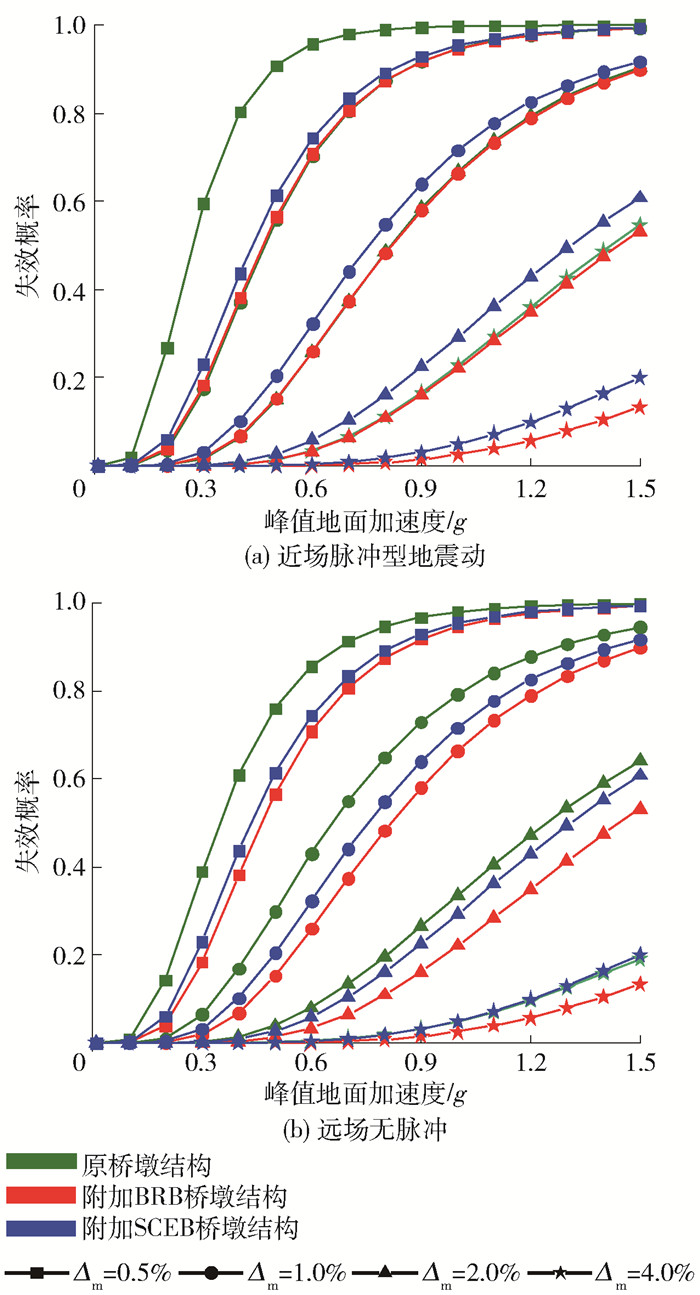
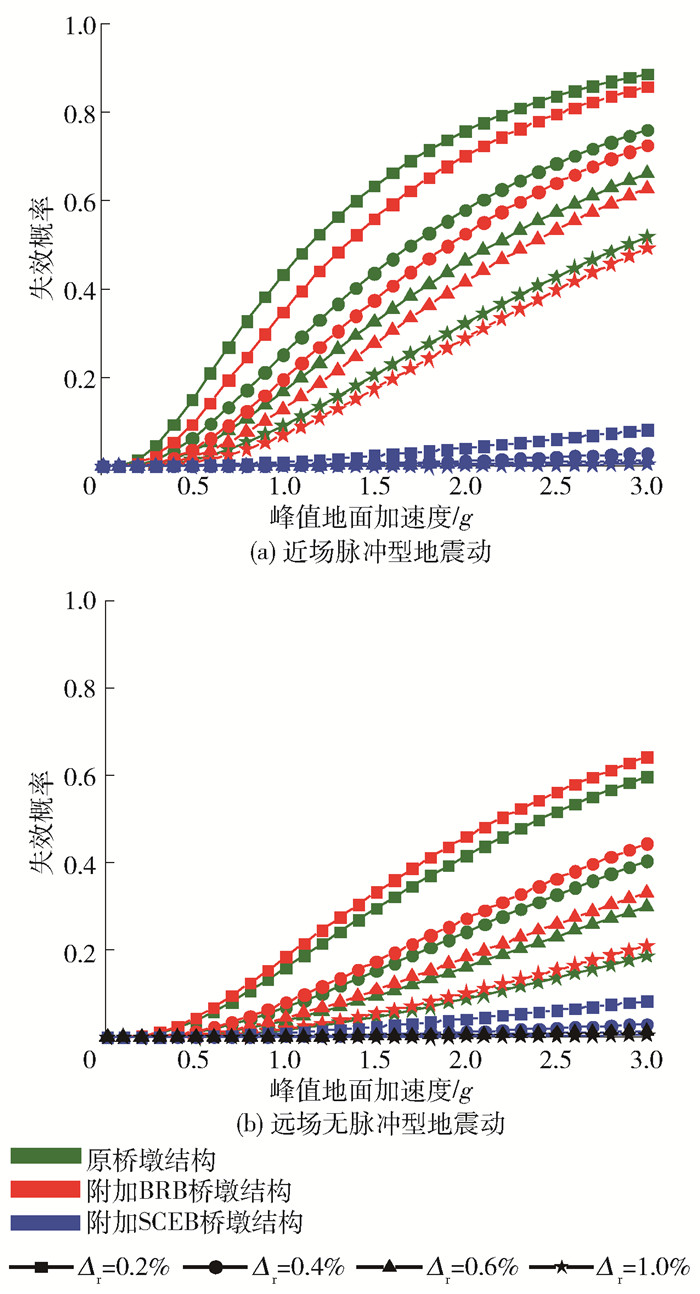
当采用最大侧移率作为损伤指标时,如图 14所示,在地震动作用下,附加支撑桥墩结构的失效概率均得到降低. 在近场脉冲型地震动作用下,PGA为0.8 g时,3种桥墩严重损伤(Δm=2%)的失效概率分别为0.48、0.11、0.16,其中附加BRB桥墩结构的失效概率降低77.1%,附加SCEB桥墩结构的失效概率降低66.7%. 可以看出附加BRB桥墩结构失效概率低于附加SCEB桥墩结构的失效概率,这可能是由于BRB的耗能能力比SCEB的耗能能力更好.
从图 14可以看出,3种桥墩结构在近场脉冲型地震动作用下的失效概率均大于在远场无脉冲型地震动作用下的失效概率. 在0.8 g近场脉冲型地震动作用下附加自复位耗能支撑桥墩结构在轻微损伤(Δm=0.5%)、中等损伤(Δm=1.0%)、严重损伤(Δm=2.0%)、倒塌(Δm=4.0%)时失效概率分别为0.89、0.55、0.16、0.02,而在远场无脉冲型地震动作用下的失效概率分别为0.87、0.42、0.06、0.
4.3.2 以残余侧移率作为损伤指标
考虑以残余侧移率作为损伤,结果如图 15所示. 由图可知,附加支撑之后,桥墩结构的失效概率均得到了降低. 在0.8 g近场脉冲型地震动作用下,3种桥墩结构可修(Δr=0.4%)的失效概率分别为0.17、0.12、0,附加BRB桥墩结构可修(Δr=0.4%)的失效概率降低29.4%,而附加SCEB桥墩结构可修的失效概率降低100.0%. 特别地,附加SCEB桥墩结构的失效概率远低于原桥墩结构和附加BRB桥墩结构的失效概率,这是由于SCEB具有自复位的能力,在震后可以减小甚至消除桥墩结构的残余位移.
通过对比3种桥墩结构在近场脉冲型地震动和远场无脉冲型地震动作用下的失效概率,与采用最大侧移率作为损伤指标的结果类似,3种桥墩结构在近场脉冲型地震动作用下更容易发生损伤.
4.3.3 以最大侧移率和残余侧移率作为损伤指标
前面讨论了3种桥墩分别以最大侧移率和残余侧移率作为损伤指标时的损伤概率,附加支撑后明显降低了桥墩结构的损伤概率,同时注意到当采用最大侧移率作为损伤指标时,附加SCEB桥墩结构极限损伤概率略高于附加BRB桥墩结构,而当采用残余侧移率作为损伤指标时,附加SCEB桥墩结构的失效概率远低于附加BRB桥墩结构和原桥墩结构,然而实际上当最大侧移率或残余侧移率任何一项超过其对应限值时桥墩结构均会失效. 考虑最大侧移率和残余侧移率的失效概率公式[27]为
$$ \begin{gathered} P=1-\phi\left[\frac{\ln \alpha_{\mathrm{m}}-\ln M_{\mathrm{m}}}{\sqrt{\beta_{\mathrm{D}, \mathrm{m}}^2+\beta_{\mathrm{C}, \mathrm{m}}^2}}\right] \times \\ \phi\left[\frac{\ln \alpha_{\mathrm{r}}-\ln M_{\mathrm{r}}}{\sqrt{\beta_{\mathrm{D}, \mathrm{r}}^2+\beta_{\mathrm{C}, \mathrm{r}}^2}}\right] \end{gathered} $$ (3) 式中:αm、αr分别表示采用最大侧移率和残余侧移率作为性能指标时所对应结构不同性能水平的限值;βD, m、βD, r分别表示结构以最大侧移率和残余侧移率作为地震需求参数的对数标准差平均值;βC, m、βC, r分别表示采用最大侧移率和残余侧移率作为性能指标时结构抗震能力离差;Mm、Mr分别表示以最大侧移率和残余侧移率作为地震需求的中值.
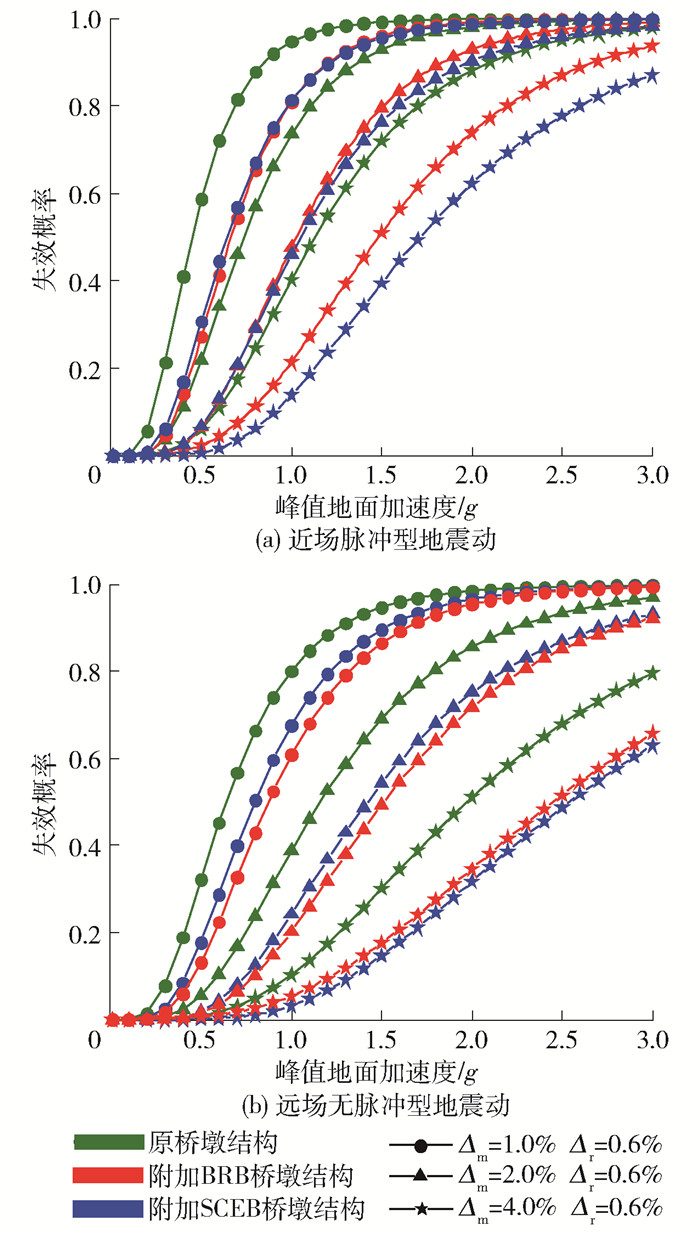
基于式(3),可以计算出考虑最大侧移率(Δm=1.0%、2.0%、4.0%)和残余侧移率(Δr=0.6%)的联合失效概率,考虑联合指标的失效概率组合方式见表 10. 由图 16可知,与考虑单个损伤指标的情况类似,附加支撑之后,桥墩结构的失效概率均得到降低,见图 16(a),在近场脉冲型地震动作用下,附加BRB桥墩结构和附加SCEB桥墩结构采用组合一的失效概率出现了交叉. 而附加SCEB桥墩结构组合二和组合三的联合失效概率要低于附加BRB桥墩结构. PGA为0.8 g时,采用组合三的联合指标时,3种桥墩结构的失效概率分别为0.25、0.11、0.06,附加BRB桥墩结构的失效概率降低了56.0%,而附加SCEB桥墩结构的失效概率降低了76.0%. 综合来看,附加SCEB桥墩结构的失效概率更低,抗震性能更优.
表 10 联合失效概率组合方式Table 10. Joint failure probability combination% 组合 Δm Δr 组合一 1.0 0.6 组合二 2.0 0.6 组合三 4.0 0.6 如图 16(b)所示,在远场无脉冲型地震动作用下,附加SCEB桥墩结构组合一和组合二的失效概率曲线大于附加BRB桥墩结构,而组合三失效概率要小于附加BRB桥墩结构. 通过对比图 16(a)(b),与采用单个损伤指标的结果类似,桥墩结构在近场脉冲型地震动作用下的失效概率大于在远场无脉冲型地震动作用下的失效概率.
值得注意的是,在近场脉冲型地震动作用下,附加BRB桥墩结构和附加SCEB桥墩结构出现了交叉. 在较小PGA时,附加BRB桥墩结构的失效概率较小,在较大PGA时,附加SCEB桥墩结构的失效概率较小,这是由于支撑为桥墩结构提供了刚度和承载力,在较小PGA时,附加支撑桥墩结构的最大位移和残余位移均较小,而在较大PGA时,SCEB可以更好地减小甚至消除残余位移. 关于在远场无脉冲型地震动作用下的情况,则是由于桥墩结构在远场无脉冲型地震动作用下的残余位移较小,桥墩结构的损坏主要以最大位移的损伤为主.
5. 结论
1) 在小震作用下,BRB和SCEB可以为桥墩结构提供刚度和承载力,在大震作用下,BRB和SCEB可以为桥墩结构提供稳定的耗能能力,有效减小桥墩结构的位移响应,特别地,SCEB还可以为桥墩结构提供良好的自复位能力,可明显减小甚至消除桥墩结构的残余位移.
2) 采用最大侧移率作为损伤指标,当BRB和SCEB具有相同刚度和屈服强度时,2种支撑均能有效地减小桥墩结构的失效概率,附加SCEB桥墩的失效概率略大于附加BRB桥墩结构的失效概率,在0.8 g近场脉冲型地震动作用下,附加BRB桥墩结构严重损伤的失效概率降低77.1%,而附加SCEB桥墩结构降低66.7%.
3) 采用残余侧移率作为损伤指标,当BRB和SCEB具有相同刚度和屈服强度时,附加SCEB桥墩结构的失效概率远低于原桥墩结构和附加BRB桥墩结构,在0.8 g近场脉冲型地震动作用下,附加SCEB桥墩结构可修的失效概率降低100.0%,而附加BRB桥墩结构仅降低29.4%.
4) 考虑最大侧移率和残余侧移率作为联合指标时,当PGA较大时,在近场脉冲型地震动作用下附加SCEB桥墩结构的抗震性能更优,PGA为0.8g时,考虑4.0%~0.6%的联合指标时,附加SCEB桥墩结构的失概率降低76.0%,附加BRB桥墩结构的失效概率降低了56.0%.
5) 3种桥墩结构在近场脉冲型地震动作用下失效概率高于远场无脉冲型地震动作用下的时效概率.
-
表 1 混凝土材料参数
Table 1 Concrete material parameters
参数 C35 核心区 保护层 抗压强度/MPa 26.3 23.4 峰值应力压应变 0.002 0.002 屈服后抗压强度/MPa 5.27 4.68 屈服后的应变 0.013 0.004 抗拉极限强度/MPa 1.84 1.64 表 2 钢筋材料参数
Table 2 Reinforcement material parameters
参数 HRB400 屈服强度/MPa 393.2 弹性模量/GPa 200 刚度比 0.01 表 3 支撑的设计参数
Table 3 Brace design parameters
参数 SCEB BRB 第一刚度/(kN·mm-1) 250.0 250.0 第二刚度/(kN·mm-1) 2.5 2.5 屈服力/kN 3 000 3 000 表 4 桥墩基本周期
Table 4 Basic period of the bents
桥墩结构 周期/s 原桥墩结构 0.45 附加BRB桥墩结构 0.31 附加SCEB桥墩结构 0.31 编号 地震名称 站台名称 年份 震级 断层距/km 地面峰值加速度/g 地面峰值速度/(cm·s-1) 1 San Fernand Pacoima Dam 1971 6.6 1.81 1.219 114.47 2 Coyote Lake Gilroy Array #2 1979 5.7 9.02 0.256 31.93 3 Coyote Lake Gilroy Array #4 1979 5.7 5.70 0.252 31.84 4 Coyote Lake Gilroy Array #6 1979 5.7 3.11 0.422 44.35 5 Imperial Valley-06 Agrarias 1979 6.5 0.65 0.183 41.68 6 Imperial Valley-06 EC County Center FF 1979 6.5 7.31 0.235 73.39 7 Imperial Valley-06 Brawley Airport 1979 6.5 10.42 0.220 40.94 8 Imperial Valley-06 El Centro Array #3 1979 6.5 12.85 0.267 47.97 9 Imperial Valley-06 El Centro Array #10 1979 6.5 8.60 0.173 50.69 10 Imperial Valley-06 El Centro-Meloland Geot.Array 1979 6.5 0.07 0.298 92.61 11 Mammoth Lakes-06 Long Valley Dam 1980 5.9 16.03 0.414 34.13 12 Morgan Hill Coyote Lake Dam 1984 6.2 0.53 1.303 78.44 13 Morgan Hill Gilroy Array #6 1984 6.2 9.85 0.292 36.49 14 N.Palm Springs Morongo Valley 1986 6.1 12.03 0.217 39.99 15 San Salvador Geotech Investig Center 1986 5.8 6.30 0.704 79.92 16 San Salvador National Geografical Inst 1986 5.8 6.99 0.534 72.99 17 Whittier Narrows-01 Bell Gardens-Jaboneria 1987 6.0 17.79 0.220 28.31 18 Whittier Narrows-01 Compton-Castlegate St 1987 6.0 23.37 0.322 29.47 19 Whittier Narrows-01 Downey-Birchdale 1987 6.0 20.79 0.348 39.92 20 Whittier Narrows-01 Downey-Co Maint Bldg 1987 6.0 20.82 0.205 30.68 21 Whittier Narrows-01 LB-Orange Ave 1987 6.0 24.54 0.228 31.45 22 Whittier Narrows-01 Santa Fe Springs - E.Joslin 1987 6.0 18.49 0.469 34.40 23 Superstition Hills-02 Kornbloom Road (temp) 1987 6.5 18.48 0.139 29.61 24 Superstition Hills-02 Parachute Test Site 1987 6.5 0.95 0.432 134.29 25 Superstition Hills-02 Poe Road (temp) 1987 6.5 11.16 0.475 41.17 26 Loma Prieta Gilroy-Historic Bldg 1989 6.9 10.97 0.285 43.39 27 Loma Prieta Gilroy Array #2 1989 6.9 11.07 0.317 40.37 28 Loma Prieta Gilroy Array #3 1989 6.9 12.82 0.368 45.43 29 Loma Prieta Saratoga-Aloha Ave 1989 6.9 8.50 0.326 45.97 30 Loma Prieta Saratoga-W Valley Coll 1989 6.9 9.31 0.331 64.91 31 Cape Mendocino Cape Mendocino 1992 7.0 6.96 1.494 122.33 32 Cape Mendocino Petrolia 1992 7.0 8.18 0.656 88.51 33 Landers Lucerne 1992 7.3 2.19 0.725 133.40 34 Northridge-01 Jensen Filter Plant 1994 6.7 5.43 0.411 111.47 35 Northridge-01 Jensen Filter Plant Generator 1994 6.7 5.43 0.571 76.13 36 Northridge-01 LA-Saturn St 1994 6.7 27.01 0.430 41.58 37 Northridge-01 LA-Sepulveda VA Hospital 1994 6.7 8.44 0.753 77.67 38 Northridge-01 LA Dam 1994 6.7 5.92 0.426 74.84 39 Northridge-01 Newhall-Fire Sta 1994 6.7 5.92 0.590 96.59 40 Northridge-01 Newhall-W Pico Canyon Rd 1994 6.7 5.48 0.419 118.18 41 Northridge-01 Pacoima Dam (downstr) 1994 6.7 7.01 0.416 44.29 42 Northridge-01 Pacoima Dam (upper left) 1994 6.7 7.01 1.285 103.38 43 Northridge-01 Pacoima Kagel Canyon 1994 6.7 7.26 0.433 51.38 44 Northridge-01 Rinaldi Receiving Sta 1994 6.7 6.50 0.874 148.00 45 Northridge-01 Sylmar-Converter Sta 1994 6.7 5.35 0.623 116.25 46 Northridge-01 Sylmar-Converter Sta East 1994 6.7 5.19 0.853 120.97 47 Northridge-01 Sylmar-Olive View Med FF 1994 6.7 5.30 0.843 129.37 48 Kobe, Japan KJMA 1995 6.9 0.96 0.834 91.10 49 Kobe, Japan Port Island (0 m) 1995 6.9 3.31 0.348 90.60 50 Kobe, Japan Takarazuka 1995 6.9 0.27 0.614 86.25 51 Kobe, Japan Takatori 1995 6.9 1.47 0.618 120.62 52 Northwest China-03 Jiashi 1997 6.1 17.73 0.274 35.25 53 Duzce, Turkey Bolu 1999 7.1 12.04 0.806 65.88 54 Duzce, Turkey Duzce 1999 7.1 6.58 0.515 84.23 55 Chi-Chi CHY024 1999 6.2 19.65 0.187 33.08 56 Kocaeli, Turkey Gebze 1999 7.5 10.92 0.261 44.63 57 Kocaeli, Turkey Izmit 1999 7.5 7.21 0.230 38.29 58 Kocaeli, Turkey Yarimca 1999 7.5 4.83 0.227 69.72 59 Yountville Napa Fire Station #3 2000 5.0 11.50 0.409 39.78 60 Denali, Alaska TAPS Pump Station #10 2002 7.9 2.74 0.333 115.72 编号 地震名称 站台名称 年份 震级 断层距/km 地面峰值加速度/g 地面峰值速度/(cm·s-1) 1 San Fernando Upland-San Antonio Dam 1971 6.6 61.73 0.058 2.89 2 San Fernando Wrightwood-6074 Park Dr 1971 6.6 62.23 0.055 3.26 3 Imperial Valley-06 Plaster City 1979 6.5 30.33 0.043 3.18 4 Imperial Valley-07 Delta 1979 5.0 49.93 0.118 3.61 5 Livermore-01 APEEL 3E 1980 5.8 30.59 0.065 3.91 6 Livermore-01 Fremont-Mission 1980 5.8 35.68 0.044 4.31 7 Livermore-01 Tracy-Sewage 1980 5.8 53.82 0.079 6.71 8 Coalinga-01 Parkfield-Cholame 12w 1983 6.4 55.77 0.047 6.34 9 Coalinga-01 Parkfield-Cholame 1E 1983 6.4 43.68 0.091 11.29 10 Coalinga-01 Parkfield-Cholame 3E 1983 6.4 40.98 0.046 6.63 11 Coalinga-01 Parkfield-Cholame 5W 1983 6.4 48.70 0.136 10.75 12 Coalinga-01 Parkfield-Fault Zone 3 1983 6.4 37.22 0.140 13.95 13 Coalinga-01 Parkfield-Gold Hill 6W 1983 6.4 47.88 0.069 5.73 14 Coalinga-01 Parkfield-Cholame 2WA 1983 6.4 44.72 0.113 9.66 15 Morgan Hill Capitola 1984 6.2 39.08 0.098 5.09 16 N. Palm Springs San Jacinto-Valley cemetery 1986 6.1 30.97 0.054 1.76 17 N. Palm Springs Hesperia 1986 6.1 72.97 0.041 2.36 18 Chalfant Valley-02 Convict Creek 1986 6.2 31.19 0.060 4.14 19 Whittier Narrows-01 Terminal Island — S Seaside 1987 6.0 40.36 0.043 4.31 20 Whittier Narrows-01 Pacoima Kagel Canyon USC 1987 6.0 36.29 0.122 7.57 21 Loma Prieta Belmont-Envirotech 1989 6.9 44.11 0.108 11.83 22 Loma Prieta Berkeley LBL 1989 6.9 79.25 0.049 8.30 23 Loma Prieta Golden Gate Bridge 1989 6.9 79.81 0.233 40.07 24 Loma Prieta Palo Alto-SLAC Lab 1989 6.9 30.86 0.277 31.11 25 Loma Prieta Salinas-John & Work 1989 6.9 32.78 0.092 11.87 26 Loma Prieta Hayward-BART Sta 1989 6.9 54.15 0.156 14.24 27 Loma Prieta Fremont — Emerson Court 1989 6.9 39.85 0.192 12.76 28 Cape Mendocino Eureka-Myrtle & West 1992 7.0 41.97 0.154 20.23 29 Landers Barstow 1992 7.3 34.86 0.130 20.45 30 Northridge-01 LA-116th St School 1994 6.7 41.17 0.208 10.19 31 Northridge-01 Malibu-Point Dume Sch 1994 6.7 33.67 0.130 8.39 32 Northridge-01 LA-Obregon Park 1994 6.7 37.36 0.355 13.57 33 Northridge-01 Inglewood-Union Oil 1994 6.7 42.20 0.091 7.12 34 Northridge-01 Newport Bch-Newport & Coast 1994 6.7 84.54 0.103 5.75 35 Northridge-01 LA-City Terrace 1994 6.7 36.62 0.263 12.78 36 Northridge-01 Bell Gardens-Jaboneria 1994 6.7 44.10 0.102 7.07 37 Northridge-01 Compton-Castlegate St 1994 6.7 47.04 0.089 8.31 38 Northridge-01 Covina-W Badillo 1994 6.7 53.45 0.105 4.78 39 Northridge-01 LA-Pico & Sentous 1994 6.7 31.33 0.186 14.23 40 Northridge-01 Lake Hughes #1 1994 6.7 35.81 0.077 9.45 41 Northridge-01 Leona Valley #2 1994 6.7 37.24 0.091 7.59 42 Northridge-01 Palmdale-Hwy 14 & Palmdale 1994 6.7 41.67 0.067 8.44 43 Northridge-01 Terminal Island-S Seaside 1994 6.7 57.20 0.148 16.48 44 Northridge-01 West Covina-S Orange Ave 1994 6.7 51.71 0.064 7.19 45 Northridge-01 San Gabriel-E Grand Ave 1994 6.7 39.31 0.142 8.09 46 Northridge-01 Huntington Bch-Waikiki 1994 6.7 69.50 0.089 5.61 47 Northridge-01 Anaheim-W Ball Rd 1994 6.7 68.62 0.074 6.06 48 Hector Mine Amboy 1999 7.1 43.05 0.150 19.74 49 Hector Mine Desert Hot Springs 1999 7.1 56.40 0.067 7.44 50 Hector Mine Fun Valley 1999 7.1 54.68 0.088 6.19 51 Hector Mine Joshua Tree 1999 7.1 31.06 0.147 19.15 52 Chi-Chi TCU006 1999 7.6 72.61 0.077 18.48 53 Chi-Chi TCU052 1999 5.9 38.25 0.082 7.09 54 Chi-Chi TCU075 1999 5.9 30.75 0.045 3.55 55 Chi-Chi TCU045 1999 6.2 77.38 0.008 1.03 56 Chi-Chi TCU068 1999 6.2 48.02 0.021 3.87 57 Chuetsu-oki, Japan Joetsu Yanagishima paddocks 2007 6.8 31.43 0.185 15.56 58 Chuetsu-oki, Japan Joetsu, Aramaki District 2007 6.8 32.54 0.064 11.78 59 Chuetsu-oki, Japan Tokamachi Chitosecho 2007 6.8 30.65 0.069 9.44 60 Iwate,Japan Matsuyama City 2008 6.9 40.98 0.084 6.09 表 7 桥墩结构在地震动作用下的位移响应
Table 7 Displacement responses of the bridge bents under ground motion
地震动 峰值地面运动加速度/g 最大位移/mm 残余位移/mm 原桥墩结构 附加BRB桥墩结构 附加SCEB桥墩结构 原桥墩结构 附加BRB桥墩结构 附加SCEB桥墩结构 Denali,Alaska 0.2 24.9 12.1 12.1 0.0 0.0 0.0 Chuetsu-oki, Japan 18.7 9.8 9.8 0.0 0.0 0.0 Denali,Alaska 0.8 532.5 117.0 138.5 72.1 33.8 3.9 Chuetsu-oki, Japan 119.3 44.6 54.2 14.7 3.2 0.0 极限状态 物理描述 Δm/% 轻微损伤 钢筋屈服,出现裂缝 0.5 中等损伤 混凝土剥落 1.0 严重损伤 钢筋屈曲,大裂缝 2.0 倒塌 倒塌 4.0 极限状态 运行 可修 不可修 倒塌 Δr/% 0.2 0.4 0.6 1.0 表 10 联合失效概率组合方式
Table 10 Joint failure probability combination
% 组合 Δm Δr 组合一 1.0 0.6 组合二 2.0 0.6 组合三 4.0 0.6 -
[1] 唐玉红, 张敏政, 戴君武. 钢筋混凝土结构在近场脉冲型地震作用下的试验分析[J]. 世界地震工程, 2007(3): 41-46. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-6069.2007.03.008 TANG Y H, ZHANG M Z, DAI J W. Experiment and analysis of reinforced concrete frame under near-field pulse-type ground motion[J]. World Earthquake Engineering, 2007(3): 41-46. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-6069.2007.03.008
[2] 翟长海, 张林春, 李爽, 等. 近场地震动对大跨刚构桥影响的分析[J]. 防灾减灾工程学报, 2010, 30(增刊1): 143-147. doi: 10.13409/j.cnki.jdpme.2010.s1.019 ZHAI C H, ZHANG L C, LI S, et al. Analysis of influence of near-field ground motion on long-span rigid frame bridge[J]. Journal of Disaster Prevention and Mitigation Engineering, 2010, 30(Suppl 1): 143-147. (in Chinese) doi: 10.13409/j.cnki.jdpme.2010.s1.019
[3] LI X L, JIANG H, SHEN D. Study on seismic safety performance for continuous girder bridge based on near-fault strong ground motions[J]. Procedia Engineering, 2012, 45: 916-922. doi: 10.1016/j.proeng.2012.08.259
[4] 刘洋, 吕大刚, 于晓辉. 近场地震作用下型钢-混凝土组合结构桥易损性分析[J]. 土木工程学报, 2016(增刊1): 56-60. doi: 10.15951/j.tmgcxb.2016.s1.010 LIU Y, LÜ D G, YU X H. Seismic fragility analysis of steel-concrete composite bridges excited by near-fault ground motions[J]. China Civil Engineering Journal, 2016(Suppl 1): 56-60. (in Chinese) doi: 10.15951/j.tmgcxb.2016.s1.010
[5] CHOI H, SAIIDI M S, SOMERVILLE P, et al. Experimental study of reinforced concrete bridge columns subjected to near-fault ground motions[J]. Aci Structural Journal, 2010, 107(1): 3-12.
[6] 马海滨, 卓卫东, 谷音, 等. 近场脉冲型地震动影响下公路常规梁桥的位移响应分析[J]. 中国公路学报, 2017, 30(12): 139-149. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-7372.2017.12.015 MA H B, ZHUO W D, GU Y, et al. Displacement response analysis of regular highway girder bridges under near-fault pulse-type ground motions[J]. China Journal of Highway and Transport, 2017, 30(12): 139-149. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-7372.2017.12.015
[7] EROCHKO J, CHRISTOPOULOS C, TREMBLAY R, et al. Residual drift response of SMRFs and BRB frames in steel buildings designed according to ASCE 7-05[J]. Journal of Structural Engineering, 2011, 137(5): 589-599. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)ST.1943-541X.0000296
[8] 杜修力, 周雨龙, 韩强, 等. 摇摆桥墩的研究综述[J]. 地震工程与工程振动, 2018, 38(5): 1-11. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DGGC201805001.htm DU X L, ZHOU Y L, HAN Q, et al. State-of-the-art on rocking piers[J]. Earthquake Engineering and Engineering Vibration, 2018, 38(5): 1-11. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DGGC201805001.htm
[9] 夏修身, 陈兴冲. 铁路高墩桥梁基底摇摆隔震与墩顶减震对比研究[J]. 铁道学报, 2011, 33(9): 102-107. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TDXB201109021.htm XIA X S, CHEN X C. Controlled rocking and pier top seismic isolation of railway bridge with tall piers[J]. Journal of the China Railway Society, 2011, 33(9): 102-107. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TDXB201109021.htm
[10] GARLOCK M M, RICLES J M, SAUSE R. Experimental studies of full-scale posttensioned steel connections[J]. Journal of Structural Engineering, 2005, 131(3): 438-448. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)0733-9445(2005)131:3(438)
[11] QIU C X, ZHU S Y. Shake table test and numerical study of self-centering steel frame with SMA braces[J]. Earthquake Engineering & Structural Dynamics, 2017, 46(1): 117-137.
[12] MILLER D J, FAHNESTOCK L A, EATHERTON M R. Development and experimental validation of a nickel-titanium shape memory alloy self-centering buckling-restrained brace[J]. Engineering Structures, 2012, 40: 288-298.
[13] ZHU S Y, ZHANG Y F. Seismic behaviour of self-centering braced frame buildings with reusable hysteretic damping brace[J]. Earthquake Engineering & Structural Dynamics, 2007, 36(10): 1329-1346.
[14] 徐龙河, 代长顺, 樊晓伟, 等. 预压弹簧自恢复耗能支撑子结构抗震性能研究[J]. 建筑结构学报, 2017, 38(6): 159-166. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JZJB201706017.htm XU L H, DAI C S, FAN X W, et al. Seismic performance research on substructures with pre-pressed spring self-centering energy dissipation brace[J]. Journal of Building Structures, 2017, 38(6): 159-166. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JZJB201706017.htm
[15] 刘璐, 吴斌. 自复位防屈曲支撑钢框架减振效果分析[J]. 建筑结构学报, 2016, 37(4): 93-101. LIU L, WU B. Seismic response of steel frames with self-centering buckling-restrained braces[J]. Journal of Building Structures, 2016, 37(4): 93-101. (in Chinese)
[16] 谢钦, 周臻, 王维影, 等. 两种设计原则下自定心屈曲约束支撑框架的抗震性能分析[J]. 振动与冲击, 2017, 36(3): 125-131. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZDCJ201703020.htm XIE Q, ZHOU Z, WANG W Y, et al. Aseismic performance analysis for braced frame systems with self-centering buckling-restrained braces with two different design criteria[J]. Vibration and Shock, 2017, 36(3): 125-131. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZDCJ201703020.htm
[17] 徐龙河, 武虎. 设置自复位耗能支撑的斜拉桥横向抗震性能研究[J]. 工程力学, 2019, 36(4): 177-187. XU L H, WU H. Seismic performance study along the transverse direction of cable-stayed bridges with self-centering energy dissipation braces[J]. Engineering Mechanics, 2019, 36(4): 177-187. (in Chinese)
[18] DONG H H, DU X L, HAN Q, et al. Performance of an innovative self-centering buckling restrained brace for mitigating seismic responses of bridge structures with double-column piers[J]. Engineering Structures, 2017, 148(1): 47-62.
[19] DONG H H, DU X L, HAN Q, et al. Hysteretic performance of RC double-column bridge piers with self-centering buckling-restrained braces[J]. Bulletin of Earthquake Engineering, 2019, 17(6): 3255-3281.
[20] WANG Y D, IBARRA L, PANTELIDES C, et al. Seismic retrofit of a three-span RC bridge with buckling-restrained braces[J/OL]. Journal of Bridge Engineering, 2016, 21(11): 04016073[2021-10-12]. https://ascelibrary.org/doi/full/10.1061/%28ASCE%29BE.1943-5592.0000937.
[21] WU Y F, H W, LI J, et al. The inelastic displacement spectra and its utilization of DDB design for seismic isolated bridges subjected to near-fault pulse-like ground motions[J]. Earthquake Spectra, 2019, 35(3): 1101-1140.
[22] 贺秋梅, 李小军, 杨宇. 近断层速度脉冲型地震动作用基础隔震建筑位移反应分析[J]. 应用基础与工程科学学报, 2014, 22(1): 1-13. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YJGX201401001.htm HE Q M, LI X J, YANG Y. Displacement response analysis of base-isolated buildings subjected to near-fault ground motions with velocity pulse[J]. Journal of Basic Science and Engineering, 2014, 22(1): 1-13. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YJGX201401001.htm
[23] Paciflc Earthquake Engineering Research. NGA-west 2-shallow crustal earthquakes in active tectonic regimes[DB/OL]. [2021-10-18]. https://ngawest2.berkeley.edu/.
[24] HWANG H, 刘晶波. 地震作用下钢筋混凝土桥梁结构易损性分析[J]. 土木工程学报, 2004, 37(6): 47-51. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TMGC200406008.htm HWANG H, LIU J B. Seismic fragility analysis of reinforced concrete bridges[J]. China Civil Engineering Journal, 2004, 37(6): 47-51. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TMGC200406008.htm
[25] UPADHYAY A, PANTELIDES C P, IBARRA L. Residual drift mitigation for bridges retrofitted with buckling restrained braces or self centering energy dissipation devices[J/OL]. Engineering Structures, 2019, 199[2021-10-18]. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.engstruct.2019.109663.
[26] UMA S R, PAMPANIN S, CHRISTOPOULOS C. Development of probabilistic framework for performance-based seismic assessment of structures considering residual deformations[J]. Journal of Earthquake Engineering, 2010, 14(7): 1092-1111.
[27] QIU C X, ZHANG Y, LI H, et al. Seismic performance of concentrically braced frames with non-buckling braces: a comparative study[J]. Engineering Structures, 2018, 154: 93-102.
-
期刊类型引用(1)
1. 梁晓,姜浩然,李芳芳. 自复位预制节段拼装中空夹层钢管混凝土桥墩地震易损性分析. 震灾防御技术. 2024(03): 613-628 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(1)



 下载:
下载: