Catalytic Performance of Regularly Morphological and Porous Catalysts for the Oxidation of Volatile Organic Compounds
-
摘要:
大部分挥发性有机物(volatile organic compounds,VOCs)污染大气环境,危害人身健康,严格控制VOCs的排放迫在眉睫.催化氧化是消除VOCs的有效途径,关键在于研发新型高效催化剂.简要综述了近年来笔者课题组在规整形貌过渡金属氧化物、介孔金属氧化物、大孔金属氧化物、大孔复合金属氧化物及其负载过渡金属氧化物和贵金属纳米催化剂的制备及其对VOCs氧化的催化性能.结果表明,催化剂的活性与其比表面积、孔结构、粒子分散度、粒径、吸附氧物种浓度、低温还原性、反应物活化能力、金属氧化物或贵金属(合金)与载体之间的相互作用等因素有关.此外,还展望了此类研究工作的未来发展趋势.
Abstract:Most of volatile organic compounds (VOCs) pollute the atmosphere environment and are harmful to human health, hence it is urgent to strictly control the emission of VOCs. Catalytic oxidation is an effective pathway for the removal of VOCs, in which the key issue is the development of novel and high-performance catalysts. In this review, we briefly summarize the preparation and catalytic performance of regularly morphological transition metal oxide, mesoporous metal oxide, macroporous metal oxide, macroporous mixed metal oxide, and their supported transition metal oxide and noble metal nanocatalysts that have been investigated by our research group. It was found that catalytic performance was associated with the factors, such as specific surface area, pore structure, particle dispersion, particle size, adsorbed oxygen species concentration, low-temperature reducibility, reactant activation ability or interaction between metal oxide or noble metal (alloy) and support. In addition, the development trend in future work on such a topic has been envisioned.
-
挥发性有机物(volatile organic compounds, VOCs)是大气污染的主要来源之一,这些来自机动车与船舶制造、喷涂油漆、化工与印刷、制鞋与制药、橡胶塑料加工、厨房油烟等行业的有机物(低碳烃、芳烃、醇、酮、醚、酯、醛、羧酸、胺及含卤素的有机物等)绝大多数具有毒性、恶臭味且易燃易爆,部分VOCs是致癌物或对臭氧层有破坏作用.我国大气环境中的VOCs含量较高呈增长趋势.调查结果显示,北京地区大气中98%以上的VOCs主要来自人为源排放.在颁发的《国家中长期科学和技术发展规划纲要(2006—2020年)》中指出,改善生态与环境是事关经济社会可持续发展和人民生活质量提高的重大问题.我国环境污染严重,生态系统退化加剧,污染物无害化处理能力低,在要求整体环境状况有所好转的前提下实现经济持续快速增长,对环境科技创新提出重大战略需求.突破城市群大气污染控制等关键技术、开发非常规污染物控制技术、重污染行业清洁生产集成技术等具有重大意义.因此,加大环境治理力度,严格控制污染源排放迫在眉睫.消除VOCs的主要方法有物理法(吸附法、吸收法、膜分离法等)和化学法(催化氧化法、焚烧法、等离子体法和光催化法等),其中催化氧化法是目前公认最有效的彻底消除VOCs的手段,而催化剂是实现该过程的核心所在.迄今为止,对VOCs氧化性能较好的催化材料为过渡金属氧化物和负载贵金属.由于贵金属价格昂贵且供应紧张,造成催化剂成本过高.而过渡金属氧化物催化剂造价低,但其低温催化性能低于贵金属催化剂的.常用的过渡金属氧化物颗粒大、比表面积小,导致高活性晶面暴露比例较低,不利于VOCs和氧气分子的吸附和活化,从而大大影响其催化活性.而且,当反应温度较高时,过渡金属氧化物纳米粒子容易发生团聚,导致其催化性能显著降低.若将过渡金属氧化物制成具有规整形貌或多孔结构,则可大大提高其比表面积和高活性晶面暴露率,有利于反应物分子的扩散和活化吸附,从而显著提高其对VOCs的完全氧化活性.
在过去的几年里,人们研发了大量的规整形貌过渡金属氧化物、介孔金属氧化物、大孔金属氧化物、大孔复合金属氧化物及其负载过渡金属氧化物和贵金属纳米催化剂,许多作者从不同侧面对大部分催化材料的制备方法及其消除VOCs的催化活性进行了综述[1-11].基于笔者课题组近年来的相关研究工作,本文简要总结了规整形貌和多孔材料及其负载过渡金属氧化物和贵金属催化剂对典型VOCs氧化消除的催化性能[12-100].需要指出的是,催化活性一般使用VOCs转化率达到一定程度(如10%、50%、90%或100%)时的反应温度(T10%、T50%、T90%或T100%)来表示.通常,催化剂的T10%、T50%、T90%或T100%随着空速的升高而升高.因此,只有在相同空速条件下,可使用T10%、T50%、T90%或T100%来比较各催化剂的活性.也可使用在某一反应温度下VOCs反应的比速率来表示催化活性,但是比较各催化剂的活性时必须在相同反应温度进行.对于负载贵金属催化剂,通常利用转化频率(turnover frequency, TOF)来比较催化剂的活性,但是也需要在相同反应温度下才有可比性.
1. 规整形貌过渡金属氧化物催化剂
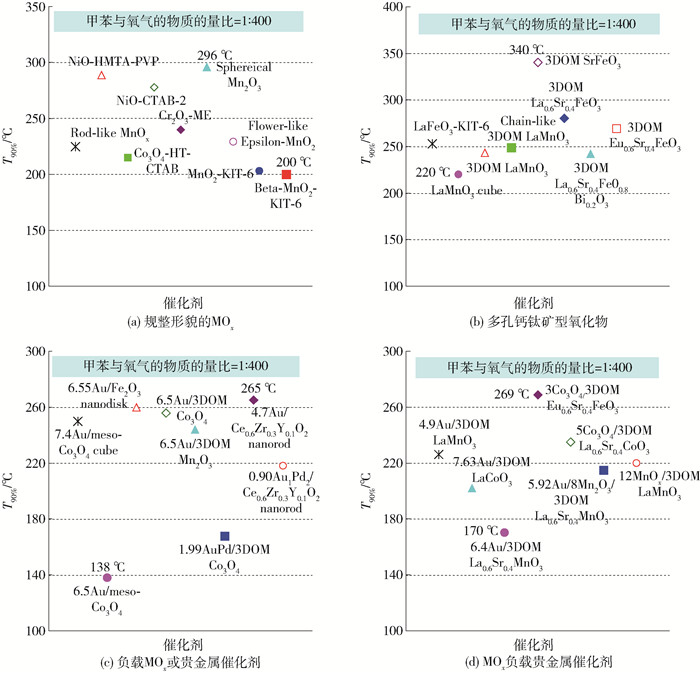
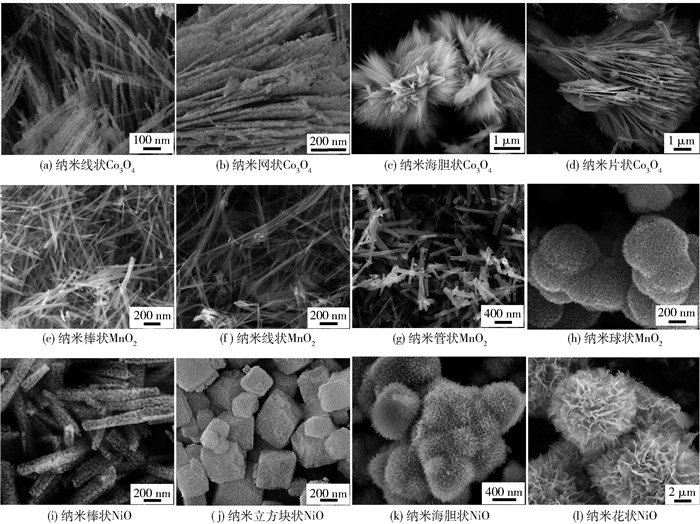
图 1示出了采用不同方法制得的部分规整形貌过渡金属氧化物催化剂的扫描电子显微镜(scanning electron microscopy,SEM)照片[12-19]. 图 2比较了部分规整形貌过渡金属氧化物、介孔金属氧化物、大孔金属氧化物、大孔复合金属氧化物及其负载过渡金属氧化物和贵金属纳米催化剂在空速为20 000 mL/(g·h)时对甲苯氧化的催化活性[12-18, 32-39, 42-44, 46-55, 60-61, 71, 75-79, 85-87, 91-97].由图 2可看出,不同的催化剂具有不同的催化活性,其中多孔结构的金属氧化物的催化活性高于规整形貌催化剂的,而负载贵金属或合金催化剂的性能最好.采用水热法和溶剂热法分别制备了α-MnO2纳米棒、纳米线、纳米管和Mn2O3纳米花,四方相α-MnO2的比表面积为45~83 m2/g,立方相Mn2O3纳米花的比表面积为162 m2/g.催化剂的表面吸附氧浓度和低温还原性按照α-MnO2纳米棒、α-MnO2纳米管、Mn2O3纳米花、α-MnO2纳米线的顺序降低,其中α-MnO2纳米棒催化剂在空速为20 000 mL/(g·h)时对甲苯氧化的T50%和T90%分别为210、225 ℃[12].通过改变水热和溶剂热条件,分别制得棒状四方相α-MnO2、花状菱方相ε-MnO2和哑铃状四方相β-MnO2,比表面积分别为53、30、114 m2/g,表面吸附氧浓度和低温还原性按照α-MnO2、ε-MnO2、β-MnO2的顺序降低.在20 000 mL/(g·h)的空速下,α-MnO2、ε-MnO2、β-MnO2催化剂对甲苯氧化的T90%分别为238、229、241 ℃[13].
采用表面活性剂辅助的溶剂热法制备出比表面积为31~66 m2/g的纳米花状和链状的NiO-HMTA(hexamethylenetetramine)、NiO-HMTA-PEG(poly(ethylene glycol))、NiO-HMTA-PVP(polyvinyl pyrrolidone)和NiO-urea催化剂,其中NiO-HMTA-PVP催化剂具有最高的比表面积和吸附氧浓度,对甲苯氧化显示最高的催化活性(当空速为20 000 mL/(g·h)时,T50%和T90%分别为253、266 ℃)[14].采用以CTAB(cetyltrimethylammonium bromide)和SDS(sodium dodecyl sulfate)为表面活性剂的微乳液法合成了立方相氧化镍纳米棒和纳米块,其中NiO-CTAB-2具有最大的比表面积为46 m2/g,在20 000 mL/(g·h)的空速下,该催化剂对甲苯氧化的T50%和T90%分别为256、278 ℃[15].
以PEG或CTAB为表面活性剂,采用溶剂热法和微乳液法分别制备了具有多孔结构的纳米线状或棒状Co3O4催化剂(比表面积为47~52 m2/g),多孔结构的Co3O4催化剂比体相催化剂具有更高的吸附氧浓度和更好的低温还原性,其中以CTAB为表面活性剂所制得的Co3O4-HT(hydrothermal)-CTAB催化剂对甲苯氧化表现出最好的催化性能(在20 000 mL/(g·h)的空速下T50%和T90%分别为195、215 ℃)[16].采用乙二胺辅助的溶剂热法制备了纳米片堆积而成的微球状Co3O4(比表面积为66 m2/g),其低温还原性和吸附氧浓度均高于体相Co3O4的,对甲苯氧化的T50%和T90%分别为230、254 ℃(空速为20 000 mL/(g·h))[17].采用溶剂热法和微乳液法分别制得菱方晶相圆柱体状和蛋糕状Cr2O3,与体相Cr2O3相比,蛋糕状Cr2O3具有更高的比表面积、吸附氧浓度和更好的低温还原性,甲苯氧化显示优异的催化活性(在20 000 mL/(g·h)的空速下T50%和T90%分别为229、240 ℃)[18].
若将少量贵金属负载到规整形貌过渡金属氧化物表面可进一步提高其催化活性.例如,采用熔融盐法制备的0.13%(本文均指质量分数) Ag/Mn2O3纳米线在40 000 mL/(g·h)空速下对甲苯完全氧化温度T100%低至220 ℃[19].若制成双金属氧化物催化剂,则可改善其催化性能.例如,采用无模板的水热法制备了Co3-xMnxO4 (x=0.75, 1.0, 1.50)复合氧化物,发现随着Co含量的增加,Co3-xMnxO4催化剂的活性也相应地提高,其中呈三维蒲公英状的Co2.25Mn0.75O4催化剂显示最好的甲苯催化氧化活性:当空速为40 000 mL/(g·h)时甲苯氧化反应速率(rcat)为8.9 μmol/(g·s),甲苯完全氧化温度T100%为239 ℃[20].笔者先采用油相法制备PdW超薄纳米片,然后将之负载到TiO2上,从而制得TiO2/PdW负载催化剂.研究结果表明,TiO2/PdW-S1的比表面积为86 m2/g, 氢气消耗量为39.1 μmol/g,在40 000 mL/(g·h)的空速下对苯氧化的T50%和T90%分别为178、200 ℃,当反应温度为170 ℃时,苯氧化反应速率(rPd)为13.8 μmol/(g·s),TOFPd为22.2×10-3 s-1[21].
规整形貌的单晶态过渡复合金属氧化物对典型VOCs氧化也具有良好的催化活性.例如,采用溶剂热法制备了呈单晶态的四方相钙钛矿型氧化物La0.6Sr0.4CoO3-δ纳米线催化剂,发现与多晶态的La0.6Sr0.4CoO3-δ相比,单晶态的La0.6Sr0.4CoO3-δ对甲苯氧化具有更好的催化活性:当空速为20 000 mL/(g·h)时,甲苯氧化的T50%和T90%分别为235、245 ℃[22].采用熔融盐法制备了多孔结构的LaMnO3微球和立方块,观察到立方块状LaMnO3催化剂表现出较好的甲苯催化氧化活性(在20 000 mL/(g·h)的空速下,T50%和T90%分别为170、220 ℃),这与该催化剂较高的表面Mn4+/Mn3+物质的量比和低温还原性有关[23].通过在不同温度下水热处理前驱物,制备了La0.5Sr0.5MnO3-δ催化剂,发现呈单晶态的La0.5Sr0.5MnO3-δ立方块催化剂对甲苯氧化显示最高的催化活性(当空速为20 000 mL/(g·h)时,甲苯完全氧化温度T100%为280 ℃)[24].同样地,采用水热法制备的单晶态块状La0.6Sr0.4MnO3+δ催化剂具有较高的比表面积(15.9 m2/g)和对甲苯氧化较好的催化性能(当空速为20 000 mL/(g·h)时,T50%和T100%分别为262、290 ℃)[25].在球状La1-xSrxMO3-δ(M=Co,Mn)催化剂中,球状La0.6Sr0.4CoO2.76和球状La0.5Sr0.5MnO3-δ催化剂对甲苯氧化具有优良的催化性能(当空速为20 000 mL/(g·h)时T80%为219 ℃[26],T100%为255 ℃[27]),这与催化剂表面较高的高价态Co或Mn浓度、表面吸附氧浓度以及单晶结构有关.同时在A和B位进行部分取代也可提高钙钛矿型氧化物(ABO3)的催化性能.例如,采用水热法制备的La1-xSrxM1-yFeyO3(M=Mn, Co; x=0, 0.4; y=0.1, 1.0)催化剂中,La0.6Sr0.4Co0.9Fe0.1O3对甲苯氧化的催化活性最高(当空速为20 000 mL/(g·h)时,T100%为245 ℃)[28].以纺锤体状单晶态CuO、片状单晶态La2O3和硝酸盐为金属源, 采用水热法制备了具有纺锤体状、棒状和短链状的单晶类钙钛矿型氧化物La2-xSrxCuO4(x=0, 1)纳微米催化剂,研究发现,Sr掺杂可增加催化剂的表面吸附氧和Cu3+浓度以及低温还原性,从而使其对甲烷氧化表现出较好的催化性能[29],特别是以12 mol/L KOH为碱源制得LaSrCuO4催化剂的T90%为667 ℃(空速为50 000 mL/(g·h))[30].采用水热法制备了呈单晶态的球状和棒状类钙钛矿型氧化物YBa2Cu3O7催化剂, 发现在50 000 mL/(g·h)的空速下,以球状Y2O3为前驱体所制得的HT-sp_Y2O3-YBCO催化剂对甲烷氧化显示出最佳的催化性能(T90%为711 ℃)[31].
根据以上规整形貌过渡金属氧化物催化剂在空速为20 000 mL/(g·h)时对甲苯氧化的活性可知,催化活性(T90%)按照Co3O4-HT-CTAB、纳米棒状α-MnO2、花状ε-MnO2、棒状α-MnO2、Cr2O3、哑铃状β-MnO2、微球状Co3O4、NiO-HMTA-PVP、NiO-CTAB-2的顺序降低,而钙钛矿型氧化物催化剂的活性则按照单晶态块状La0.6Sr0.4MnO3+δ、La0.6Sr0.4CoO3-δ、La0.6Sr0.4Co0.9Fe0.1O3、多孔LaMnO3的顺序增加.
2. 介孔金属氧化物催化剂
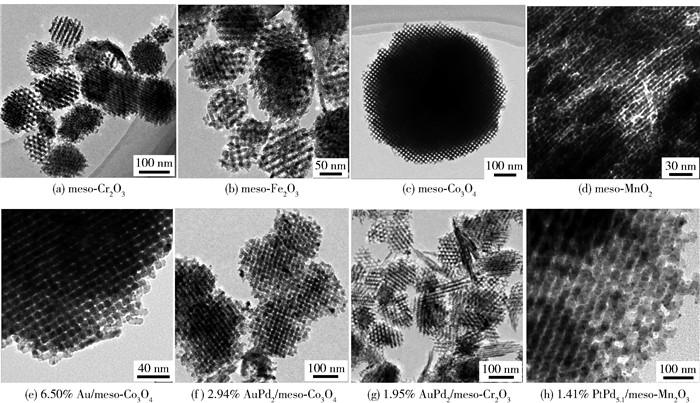
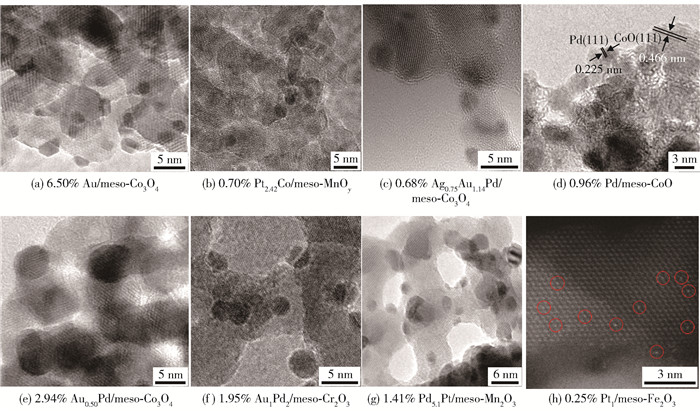
图 3为典型介孔金属氧化物及部分负载贵金属催化剂的透射电子显微镜(transmission electron microscopy,TEM)照片[32-39, 60].以三维有序介孔二氧化硅(KIT-6)为硬模板,采用无溶剂热法和超声辅助法制备了有序介孔氧化铬(比表面积为73~106 m2/g),其中于240 ℃所制备的介孔氧化铬(meso-Cr-240)具有最高的比表面积(106 m2/g)、优异的低温还原性、多种氧化态铬共存和丰富的表面氧物种,对甲苯和乙酸乙酯氧化显示最高的催化活性(当空速为20 000 mL/(g·h)时,T90%分别为234、190 ℃,表观活化能分别为79.8、51.9 kJ/mol)[32].经过不同温度焙烧由超声辅助的KIT-6纳米浇铸法制得了介孔氧化铬催化剂,其中在400 ℃焙烧所得的介孔氧化铬(meso-Cr-400)具有最大的比表面积(124 m2/g)、最高的表面氧物种浓度和最好的低温还原性,因而对甲醛、丙酮和甲醇氧化表现出最佳的催化性能(当空速为30 000 mL/(g·h)时,T90%分别为117、124、130 ℃,表观活化能也最低,分别为45.6、49.7、50.8 kJ/mol)[33].
采用超声波辅助的三维有序介孔二氧化硅(SBA-16)纳米浇铸法制备的高度有序介孔MnO2和Co3O4的比表面积(分别为266、313 m2/g)很大,高于文献报道最高值的2~3倍,将之用于甲苯氧化后发现,在20 000 mL/(g·h)的空速下,有序介孔MnO2和Co3O4的T90%分别为230、270 ℃,这与发达的有序介孔结构、优良的低温还原性和高的比表面积有关[34].以KIT-6和SBA-16为硬模板,采用真空浸渍法制备了比表面积分别为121、118 m2/g的三维有序介孔氧化钴(Co-KIT6和Co-SBA16),优良的低温还原性和丰富的表面氧物种使其对甲苯和甲醇氧化具有优异的催化活性(当空速为30 000 mL/(g·h)时,Co-KIT6的T90%分别为190、139 ℃,表观活化能分别为59.9、50.1 kJ/mol),其中Co-KIT6的催化活性略高于Co-SBA16的[35].采用同样方法制备了比表面积为102~184 m2/g的三维有序或虫洞状介孔四方相MnO2(MnO2-SBA16和MnO2-KIT6)和立方相Co3O4(Co3O4-SBA16和Co3O4-KIT6),发现催化剂的表面吸附氧物种浓度和低温还原性按照MnO2- KIT6、MnO2-SBA16、MnO2-体相以及Co3O4-KIT6、Co3O4-SBA16、Co3O4-体相的顺序降低,与其催化活性的顺序相一致.对甲苯氧化反应,介孔MnO2催化剂的活性(T90%为217 ℃)优于介孔Co3O4催化剂的(T90%为233 ℃).根据催化活性数据与表征结果,笔者认为高的比表面积和表面吸附氧物种浓度、良好的低温还原性和高质量的三维有序介孔结构是催化剂具有优异性能的关键因素[36].
采用沉淀-浸渍法制备了三维有序介孔β-MnO2负载纳米Au催化剂(5%Au/β-MnO2),发现在Au负载过程中使用的沉淀剂种类对β-MnO2、Au纳米颗粒和Au/β-MnO2催化剂的物化性质具有重要影响.以NaOH为沉淀剂所制得的Au/β-MnO2催化剂具有最高的表面Mn3+与Mn4+、Oads与Olatt、Au3+与Au0原子比以及最好的低温还原性,使其在空速为60 000 mL/(g·h)的条件下,对苯和甲苯氧化的T90%分别为250、220 ℃,这一优异催化性能与其较高的Au纳米粒子分散度、较高的氧化态Au和吸附氧物种浓度、较好的低温还原性和较强的Au与β-MnO2之间的相互作用有关[37].
采用丙三醇还原法从有序介孔氧化钴(meso-Co3O4)制备了meso-CoOx和meso-CoO催化剂(比表面积为48~98 m2/g).研究发现,meso-CoOx因具有较大的比表面积和与meso-CoO类似的表面元素组成而对邻二甲苯氧化表现出最高的催活性(T90%为244 ℃且在该温度下邻二甲苯氧化反应速率是meso-Co3O4的9倍),meso-CoOx优良的催化活性与其表面丰富的Co2+物种(活性中心)相关,Co2+协同表面氧空位高效地活化氧气分子而形成活性氧物种(O2-和O22-),特别是超氧物种[38].采用以KIT-6为模板的真空浸渍法和柠檬酸(citric acid, CA)辅助的热分解法制备了三维有序介孔氧化铁和虫孔状介孔氧化铁,经400 ℃焙烧所得三维有序介孔氧化铁(Fe-KIT6-400)和虫孔状介孔氧化铁(Fe-CA-400)的比表面积最高(分别为113、165 m2/g),且Fe-CA-400具有最好的低温还原性和最高的表面吸附氧物种浓度,因而Fe-CA-400催化剂对丙酮和甲醇氧化显示最佳的活性(当空速为20 000 mL/(g·h)时,T90%分别低至186、189 ℃,表观活化能分别为70.7、60.9 kJ/mol)[39].
对于负载金属催化剂,载体对其催化活性起到很重要的作用.为了准确揭示催化活性位,笔者采用KIT-6纳米浇铸法制备了PdxPt(x=0.43~8.52)合金催化剂(比表面积为26~32 m2/g).研究结果表明,Pd和Pt在PdxPt合金中分布均匀,Pt的引入显著影响Pd的氧化还原性,PdxPt合金比单Pd具有更强的活化甲烷能力,其中Pd2.41Pt催化剂对甲烷氧化表现出最高的活性(当空速为100 000 mL/(g·h)时,T90%为322 ℃; 在280 ℃时,TOFPd、TOFPt、TOFPd+Pt和比速率(rcat)分别为0.85×10-3 s-1、1.98×10-3 s-1、0.59×10-3 s-1和4.46 μmol/(g·s)).基于表征结果与活性数据,笔者认为Pd2.41Pt优良的催化性能可归因于良好的介孔结构、PdPt合金形成和PdO-PtO2共存以及良好的活化甲烷和氧气能力[40].
钙钛矿型氧化物对VOCs氧化具有良好的催化活性,笔者以硝酸镧和硝酸铁为金属源、以乙醇水溶液为溶剂、以KIT-6或SiO2微球为模板,采用超声波辅助的重复浸渍法分别制备了具有蠕虫状介孔结构的正交相LaFeO3(LFO-1和LFO-2)催化剂,其中以KIT-6为模板所制得的LFO-1具有发达的蠕虫状介孔结构、较高的比表面积(138 m2/g)、较高的表面吸附氧物种浓度和较好的低温还原性,因而对甲苯氧化显示较好催化活性(T90%为253 ℃)[41].
介孔过渡金属氧化物在空速为20 000 mL/(g·h)的条件下对甲苯氧化的活性依照Co-KIT6、介孔MnO2、有序介孔MnO2、介孔Co3O4、meso-Cr2O3、LFO-1、有序介孔Co3O4顺序降低.
3. 大孔复合金属氧化物催化剂
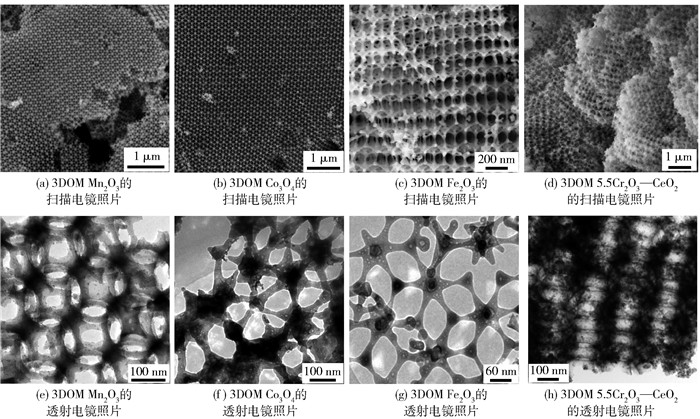
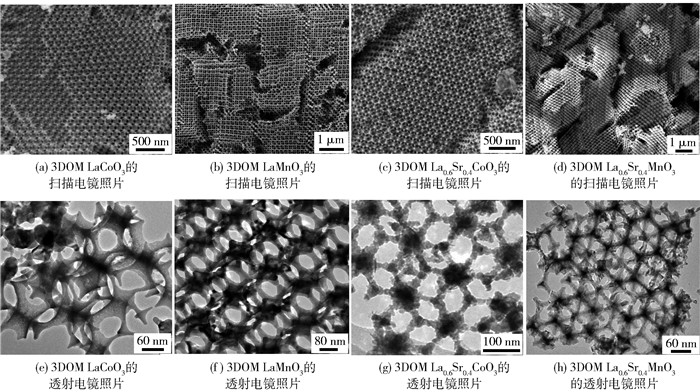
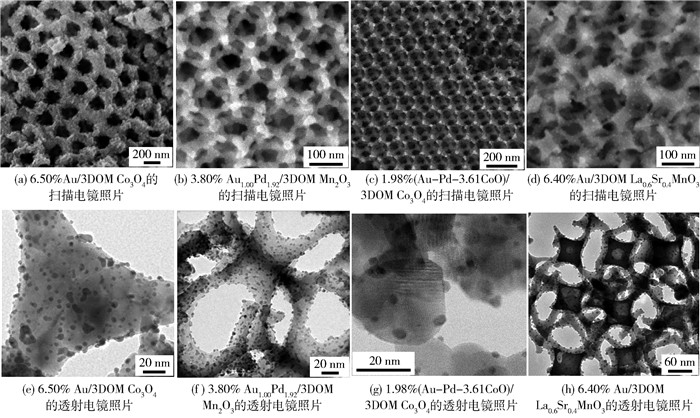
图 4、5为三维有序大孔(three-dimensionally ordered macropore,3DOM)金属氧化物催化剂的SEM和TEM照片[73-81, 85-91].采用表面活性剂辅助的PMMA(poly(methyl methacrylate))胶晶模板法制备了菱方相3DOM LaMnO3,发现表面活性剂(三嵌段共聚物(P123)和(聚乙二醇(PEG400))种类显著影响LaMnO3的孔结构和比表面积.同时使用PEG400和P123为表面活性剂所制得LaMnO3-PP-1-3具有高质量的3DOM结构且其骨架中含有纳米孔洞(比表面积为37~39 m2/g). LaMnO3-PP-2具有较高的表面Mn4+与Mn3+物质的量比、较高的吸附氧物种浓度和较好的低温还原性,因而对甲苯氧化表现出较高的催化活性(当空速为20 000 mL/(g·h)时,T50%为222 ℃,T90%为243 ℃,表观活化能为57 kJ/mol)[42].以L-赖氨酸(L-lysine)为表面活性剂,采用PMMA胶晶模板法制备了具有介孔孔壁的菱方相3DOM LaMnO3催化剂,双模孔结构的催化剂具有较高的比表面积(32~38 m2/g)、较高的表面吸附氧浓度和较好的低温还原性,在空速为20 000 mL/(g·h)的反应条件下,具有大孔-介孔双模孔结构的LaMnO3-PL-2催化剂显示出最高的活性(T90%为249 ℃,表观活化能为57 kJ/mol)[43].改变表面活性剂对所得钙钛矿型氧化物的孔结构产生影响,例如,聚乙二醇和乙二醇的联用有利于形成具有空心球状菱方相LaMO3(M=Mn, Co)和实心球状立方相MOx(M=Mn, Co).结果表明,球状催化剂比其纳米粒子催化剂具有更高的比表面积(21~33 m2/g)和表面吸附氧浓度以及更好的低温还原性,且LaCoO3空心球催化剂对甲苯氧化的活性最好(当空速为20 000 mL/(g·h)时,T90%为237 ℃)[44].以二甲氧基四乙二醇(dimethoxytetraethylene glycol, DMOTEG)、乙二醇、PEG400、L-赖氨酸或P123为表面活性剂,采用PMMA微球模板法制备了具有纳米孔洞的菱方相3DOM La0.6Sr0.4MnO3(3DOM LSMO),其大孔孔径和比表面积分别为165~214 nm和32~40 m2/g,表面活性剂性质影响催化剂的形貌结构,DMOTEG和PEG400有利于生成高质量的3DOM结构(当DMOTEG与PEG400体积比为0.6时所制得催化剂记为LSMO-DP3),LSMO-DP3催化剂具有最高的吸附氧物种浓度和比表面积以及最好的低温还原性,因此对甲烷氧化显示最佳的催化活性(当空速为30 000 mL/(g·h)时,T90%为661 ℃和表观活化能为56.6 kJ/mol)[45].采用以嵌段共聚物F127、PEG、乙醇(ethanol, EtOH)或L-赖氨酸为表面活性剂的PMMA胶晶模板法制备了具有介孔或纳米孔洞的3DOM La0.6Sr0.4FeO3(分别记为LSF-F127、LSF-PEG、LSF-PEG-EtOH和LSF-Lysine)催化剂,所制得的3DOM LSF催化剂均具有正交相钙钛矿结构,其中LSF-PEG催化剂对甲苯氧化的活性最高(当空速为20 000 mL/(g·h)时,T90%为280 ℃). 3DOM LSF催化剂的优良催化性能与其较大的比表面积、较高的氧吸附浓度、较好的低温还原性和高质量的3DOM结构相关[46].采用F127、PEG、L-赖氨酸或木糖醇辅助的PMMA胶晶模板法制备了正交相3DOM La0.6Sr0.4Fe0.8Bi0.2O3(LSFB)催化剂,以木糖醇为表面活性剂所制得的3DOM LSFB催化剂对甲苯氧化显示最高的催化活性(当空速为20 000 mL/(g·h)时,T90%为242 ℃,表观活化能为46 kJ/mol),这与其具有较高的Fe4+与Fe3+物质的量比和表面吸附氧物种浓度以及较好的低温还原性相关[47].
在蔗糖(sucrose)或L-赖氨酸存在的前提下,采用柠檬酸辅助的PMMA胶晶模板法制备了立方相3DOM SrFeO3-δ(分别记为SFO-0、SFO-Sucrose和SFO-Lysine),比表面积为34~61 m2/g,当空速为20 000 mL/(g·h)时,SFO-0催化剂对甲苯氧化的活性最高(T90%为340 ℃),归因于高的比表面积和吸附氧物种浓度以及较好的低温还原性[48].在一定量的EG存在下采用柠檬酸辅助的PMMA胶晶模板法合成了立方相3DOM SrFeO3-δ(记为SFO-xEG(x=1,3,6)).结果表明,SFO-3EG具有最高的比表面积(34 m2/g)、较多的活性氧物种、良好的低温还原性以及高质量的3DOM结构,对甲苯氧化表现出最好的催化活性(当空速为5 000 mL/(g·h)时,T90%为310 ℃)[49].
采用葡萄糖和乙二胺辅助的水热法制备了具有多孔结构的正交相SrFeO3(SFO)空心球,比表面积为18~27 m2/g,其中在葡萄糖与乙二胺体积比为0.3/1.0和水热温度为170 ℃的条件下合成的SFO-3催化剂具有最高的比表面积和吸附氧物种浓度以及最好的低温还原性,其对甲苯氧化的催化活性最高(当空速为20 000 mL/(g·h)时,T90%为298 ℃)[50].采用蔗糖辅助的PMMA胶晶模板法制备了斜方晶相的3DOM EuFeO3(记为EFO-sucrose-1),发现在制备时引入蔗糖显著影响所得催化剂的比表面积和孔结构,EFO-sucrose-1催化剂对甲苯氧化表现出最高的活性(当空速为20 000 mL/(g·h)时,T90%为347 ℃,表观活化能为82 kJ/mol)[51].在正交相3DOM Eu1-xSrxFeO3(x=0, 0.4)催化剂中,A位掺杂后形成的3DOM Eu0.6Sr0.4FeO3(ESFO)具有最小的晶粒尺寸(25 nm)、最大的比表面积(31.3 m2/g)、最高的表面吸附氧量以及最好的低温还原性,因而对甲苯氧化显示最佳的催化活性(当空速为20 000 mL/(g·h)时,T90%为305 ℃,表观活化能为81 kJ/mol)[52].在3DOM ABO3载体上负载过渡金属氧化物可改善催化性能.例如,yCoOx/3DOM-ESFO(y=1%~10%)催化剂的比表面积为22.6~41.0 m2/g,CoOx的粒径为7~11 nm且均匀分散于载体表面,当Co3O4负载量为6%时,催化剂对甲苯氧化的活性最高:当空速为20 000 mL/(g·h)时,T90%为270 ℃,表观活化能为72 kJ/mol[53-54].采用葡萄糖辅助的水热法制备了比表面积为15~26 m2/g的正交相多孔LaFeO3(LFO)催化剂,发现在170 ℃水热处理所得LFO-170催化剂对甲苯氧化显示出最好的活性(当空速为20 000 mL/(g·h)时,T90%为270 ℃,表观活化能为50 kJ/mol)[55].
采用PMMA胶晶模板法制备了具有介孔孔壁的有序大孔催化剂3DOM-m La1-xCexCoO3(比表面积为16.5~35.4 m2/g),发现3DOM-m La0.7Ce0.3CoO3对甲烷氧化的催化活性最优:在空速为30 000 mL/(g·h)的条件下T90%为555 ℃,在300 ℃时的TOF最高(4.07×10-6 s-1)[56].采用PMMA胶晶模板法先制备了3DOM La0.6Sr0.4MnO3,再将其三维有序大孔的孔壁拆解为多足状纳米粒子.发现多足状纳米催化剂比有序大孔催化剂具有更好的催化活性(当空速为50 000 mL/(g·h)时T90%为438 ℃,在375 ℃时反应速率(rcat)为2.36×10-6 mol/(g·s),表观活化能为67 kJ/mol),其催化活性的提升归因于更多的表面活性氧物种、更好的晶格氧活动度以及新暴露的(110)晶面[57].类钙钛矿型氧化物(A2BO4)对VOCs氧化也具有良好的催化活性.例如,采用PEG辅助的水热法制备的正方相类钙钛矿型氧化物La2-xSrxCuO4(LSCO-PEG)具有较高的比表面积(18.3 m2/g)、最多的吸附氧物种以及较好的低温还原性,对甲烷氧化显示优良的催化活性[58].采用柠檬酸辅助的PMMA胶晶模板法制备了正交相3DOM La2CuO4(比表面积为46 m2/g),该催化剂具有较好的低温还原性,对甲烷氧化的T90%为672 ℃(空速为50 000 mL/(g·h))[59].
在空速为20 000 mL/(g·h)条件下,三维有序大孔复合氧化物催化剂对甲苯氧化的活性按照空心球状LaCoO3、LSFB、LaMnO3-PP-2、LaMnO3-PL-2、6% CoOx/ESFO(LFO)、LSF-PEG、SFO-3、ESFO、SFO-3EG、SFO-0、EFO-sucrose-1顺序降低,而在空速为30 000~50 000 mL/(g·h)条件下对甲烷氧化的催化活性按照3DOM La0.6Sr0.4MnO3、3DOM-m La0.7Ce0.3CoO3、LSMO-DP3、LSCO-PEG顺序降低.
4. 介孔金属氧化物负载贵金属催化剂
图 6为部分介孔金属氧化物负载贵金属催化剂的TEM照片[60-72].采用KIT-6纳米浇铸法和PVA(polyvinyl alcohol)保护的NaBH4还原法制备了立方相有序介孔Co3O4负载Au纳米催化剂(比表面积为91 m2/g,Au粒径为2.8 nm),其中6.4% Au/Co3O4催化剂具有最高的吸附氧浓度,当空速为20 000 mL/(g·h)时,对苯、甲苯和邻二甲苯氧化的T90%分别为189、138、162 ℃,相应的TOFAu分别为0.44×10-3、0.41×10-3、0.45×10-3 s-1[60].采用溶剂热法和PVA保护的还原法制备了单分散立方晶相的介孔Co3O4微球负载Au纳米催化剂(比表面积为22.4 m2/g,Au粒径为3.2~3.9 nm),发现7.4% Au/Co3O4具有最高的表面吸附氧物种浓度,在空速为20 000 mL/(g·h)的条件下,对甲苯氧化的T90%、TOFAu和比速率(rAu)分别为250 ℃、0.5×10-3 s-1和2.9×10-6 mol/(g·s)[61].在有序介孔Co3O4负载AuPd合金纳米催化剂中,当Au与Pd物质的量比为1:2时2.94% Au0.5Pd/Co3O4催化剂(比表面积为114.5 m2/g,AuPd合金粒径为3.5 nm)的活性最高:当空速为20 000 mL/(g·h)时,对甲烷氧化的T90%为324 ℃和TOFAuPd为12.23×10-3 s-1,这是由于该催化剂具有较高的吸附氧浓度和较好的低温还原性所致[62].采用熔融盐法和PVA保护的还原法制备了立方相Co3O4八面体负载AuPd合金纳米催化剂(Au与Pd物质的量比为1.00:1.92,比表面积为1.3 m2/g,AuPd合金粒径为2.7 nm),其中0.96% AuPd1.92/Co3O4催化剂在空速为40 000 mL/(g·h)时对甲苯氧化的T90%为180 ℃,而对邻二甲苯的T90%为187 ℃[63].
采用KIT-6纳米浇铸法、甘油还原法和PVA保护的还原法制备了立方相有序介孔CoO负载Pd纳米催化剂(比表面积为65.1 m2/g,Pd粒径为3.7 nm),由于0.96% Pd/CoO催化剂具有较多的吸附氧物种而使其在空速为40 000 mL/(g·h)时对邻二甲苯氧化的催化活性最佳(T90%、TOFPd和比速率(rPd)分别为173 ℃、0.0054 s-1和0.16 μmol/(g·s)[64].采用PMMA胶晶模板法和PVA保护的还原法制得立方相3DOM Co3O4负载Au-Pd-xCoO纳米催化剂(比表面积为65 m2/g左右,Au-Pd-xCoO的粒径为2.6~3.1 nm),观察到1.98% (Au-Pd-3.61CoO)/3DOM Co3O4对甲烷氧化的T90%、TOFPd和比速率(rPd)分别为362 ℃、0.011 8 s-1和110.5 μmol/(g·s)[65].二元贵金属合金的催化活性高于单一贵金属的,而三元贵金属合金的催化活性优于二元贵金属合金的.例如,在三维有序介孔Co3O4负载AgAuPd纳米催化剂中,当Ag、Au、Pd物质的量比为0.75:1.14:1.00时,所得0.68% Ag0.75Au1.14Pd/meso-Co3O4催化剂(比表面积为120 m2/g,AgAuPd的粒径为2.9 nm)对甲醇氧化的T90%、TOFAgAuPd和比速率(rAgAuPd)分别为112 ℃、13.0×10-3 s-1和0.99 μmol/(g·s)[66].由三维有序介孔Cr2O3负载AuPd纳米催化剂(Au与Pd物质的量比为1:2,比表面积为61 m2/g,AuPd的粒径为3.1 nm)可知,1.95% Au1Pd2/meso-Cr2O3催化剂在空速为20 000 mL/(g·h)的条件下对甲苯氧化的T90%、TOFAuPd和比速率(rAu和rPd)分别为165 ℃、0.62×10-3 s-1、9.67 μmol/(g·s)和8.64 μmol/(g·s)[67].
采用KIT-6纳米浇铸法和PVA保护的还原法制备了菱方相三维有序介孔Mn2O3负载PdPt合金纳米催化剂,观察到1.41% Pd5.1Pt/meso-Mn2O3催化剂(比表面积为85.1 m2/g,PdPt的粒径为2.2 nm)在空速为20 000 mL/(g·h)的条件下对甲烷氧化的T90%、TOFPdPt和比速率(rPdPt)分别为425 ℃、1.02×10-3 s-1和6.39 μmol/(g·s)[68].将PdPt合金换成AuRu合金,制得了立方相三维有序介孔Mn2O3负载AuRu合金纳米催化剂(Au与Ru物质的量比为0.98,比表面积为98.8 m2/g,AuRu的粒径为2~5 nm),发现0.97% AuRu/meso-Mn2O3在20 000 mL/(g·h)的空速下对甲烷氧化的T90%为540 ℃[69].在三维有序介孔MnOy负载PtCo合金纳米催化剂中,当Pt与Co物质的量比为2.42时,MnOy由立方相Mn2O3和ε-MnO2组成,比表面积为96.9 m2/g,PtCo的粒径为2.8 nm,0.70% Pt2.42Co/meso-MnOy催化剂在高达80 000 mL/(g·h)的空速下对甲醇氧化的T90%低至86 ℃[70].由6.55% Au/菱方相Fe2O3纳米催化剂(比表面积为18.9 m2/g,Au粒径为2.2 nm)可知,在20 000 mL/(g·h)的空速下,对甲苯氧化的T90%、TOFAu和比速率(rAu)分别为260 ℃、0.61×10-3 s-1和0.21 μmol/(g·s)[71].近年来,单原子催化因其充分利用贵金属而备受关注,单原子催化剂的活性达到最佳值.例如,当空速为20 000 mL/(g·h)时,0.25% Pt1/菱方相meso-Fe2O3单原子催化剂(比表面积为89.8 m2/g)对苯氧化的T90%、TOFPt(160 ℃)和比速率(rcat)分别为198 ℃、2.69 s-1和21.99 μmol/(g·s)[72].
根据活性数据可知,催化剂在空速为20 000 mL/(g·h)时对甲苯氧化的活性按照0.25% Pt1/meso-Fe2O3、6.4% Au/有序介孔Co3O4、1.95% Au1Pd2/meso-Co3O4、0.96% AuPd1.92/八面体状Co3O4、7.4% Au/介孔微球状Co3O4、6.55% Au/Fe2O3的顺序降低,而在空速为20 000 mL/(g·h)时对甲烷氧化的活性则按照0.97% AuRu/meso- Mn2O3、1.41% Pd5.1Pt/meso-Mn2O3、1.98% (Au-Pd-3.61CoO)/3DOM Co3O4、2.94% Au0.5Pd/有序介孔Co3O4的顺序增加.
5. 大孔金属氧化物负载贵金属催化剂
图 7为3DOM金属氧化物负载贵金属催化剂的SEM和TEM照片[65, 75-79, 86].过渡金属氧化物对VOCs氧化具有优良的催化活性,若制成大孔结构,提高比表面积,可进一步改善其催化性能.例如,采用不同表面活性剂辅助的PMMA胶晶模板法制备了具有纳米介孔壁的菱方相3DOM α-Fe2O3(比表面积为32~46 m2/g,大孔孔径为180~200 nm),其中Fe2O3-3催化剂对甲苯氧化表现出最高的活性:当空速为20 000 mL/(g·h)时,T50%和T90%分别为253、293 ℃[73].双金属复合氧化物的催化活性通常高于单一金属氧化物的.例如,采用硬模板法制备了3DOM CeO2、3DOM Cr2O3和3DOM xCr2O3-CeO2催化剂(比表面积为35~47 m2/g),发现3DOM 5.5Cr2O3-CeO2对三氯乙烯氧化显示最优的催化性能,在20 000 mL/(g·h)的空速下T90%为255 ℃[74].
在3DOM过渡金属氧化物表面负载一定量的贵金属,可显著提高催化活性.采用PMMA胶晶模板法和聚乙二醇保护的硼氢化钠还原法分别制备了3DOM Co3O4及其负载的xAu/3DOM Co3O4催化剂,研究结果表明,3DOM Co3O4和xAu/3DOM Co3O4的比表面积为22~27 m2/g,金粒径为2.4~3.7 nm,且均匀分散于载体表面,其中6.5% Au/3DOM Co3O4具有最高的催化甲苯氧化活性(当空速为40 000 mL/(g·h)时,T90%为256 ℃)[75].
若将贵金属制成双金属或合金结构,即可提高催化活性和改善热稳定性.例如,在3DOM Co3O4表面负载AuPd合金而制成xAuPd/3DOM Co3O4催化剂,发现负载AuPd合金的催化性能明显优于负载单贵金属的,其中1.99% AuPd/3DOM Co3O4催化剂对甲苯氧化反应具有最高的催化活性、最低的活化能(33 kJ/mol)和最好的(水)热稳定性,在40 000 mL/(g·h)的空速下,T50%和T90%分别为164、168 ℃[76].
将载体改为3DOM Mn2O3,负载Au后所得xAu/3DOM Mn2O3催化剂的比表面积为34~38 m2/g,粒径为3.0~3.5 nm的Au纳米粒子高分散于3DOM Mn2O3载体表面.当空速为40 000 mL/(g·h)时,5.8% Au/3DOM Mn2O3催化剂表现出最好的催化甲苯氧化活性(T90%为244 ℃),且负载Au催化剂的甲苯氧化活化能(54 kJ/mol)远低于载体的(95 kJ/mol)[77].在进一步负载AuPd合金后所得xAuPdy/3DOM Mn2O3催化剂中,粒径为2~4 nm的AuPd合金纳米粒子均匀分布于载体表面,3.8% AuPd1.92/3DOM Mn2O3催化剂对甲苯氧化显示优异的活性(在40 000 mL/(g·h)的空速下T90%为162 ℃)[78].若在AuPd双贵金属合金中再掺杂过渡金属M(M=Mn, Cr, Fe, Co)而制成Au-Pd-xM/3DOM Mn2O3催化剂,研究发现Au-Pd-xM的粒径为3.6~4.4 nm且高分散于载体表面,其中1.94% Au-Pd-0.21Co/3DOM Mn2O3催化剂对邻二甲苯氧化具有优异的催化活性,当空速为40 000 mL/(g·h)时,T90%为229 ℃,同时该催化剂对甲烷氧化也具有很好的活性(当空速为40 000 mL/(g·h)时,T50%和T90%分别为365、442 ℃,在140 ℃时二甲苯反应速率(rN)为2.59 μmol/(g·s),在340 ℃时甲烷氧化反应速率(rPd)为339.0 μmol/(g·s))[79].
将Au、Pd或AuPd改为Pt而制得xPt/3DOM Mn2O3催化剂(比表面积为33~36 m2/g),粒径为3.6~4.4 nm的Pt纳米粒子均匀地分布在载体表面,甚至部分Pt纳米粒子镶嵌在载体的骨架上.在40 000 mL/(g·h)的空速下,2.3% Pt/3DOM Mn2O3对甲苯氧化显示最高的催化活性(T50%和T90%分别为165、194 ℃)[80].为了考察不同贵金属对催化活性的影响,笔者制备了xM/3DOM 26.9% CeO2-Al2O3 (M=Au, Ag, Pd, Pt)催化剂,其比表面积为102~108 m2/g,大孔孔径为180~200 nm,介孔孔径为4~6 nm,且粒径为3~4 nm的贵金属粒子高分散于载体孔道上.当空速为20 000 mL/(g·h)时,0.27% Pt/3DOM 26.9% CeO2-Al2O3催化剂具有最佳催化甲苯氧化性能(T90%=198 ℃)[81].
将载体换为具有可变化合价态的稀土氧化物,再负载双(贵)金属纳米粒子,同样可改善催化剂的活性.例如,在CoxPd/3DOM CeO2催化剂中,Pd与Co形成核壳结构,Pd@Co的平均粒径为3.5~4.5 nm且均匀分散在3DOM CeO2表面,其中0.77% Co3.5Pd/3DOM CeO2催化剂在40 000 mL/(g·h)的空速下对甲烷氧化具有优异的催化性能(T90%为480 ℃,活化能为58 kJ/mol)[82].采用PMMA胶晶模板法和聚乙二醇保护的硼氢化钠还原法制备了3DOM CeO2负载AuPd纳米催化剂(xAuPdy/3DOM CeO2),直径为3~4 nm的AuPd粒子高分散于3DOM CeO2载体表面,其中2.85% AuPd1.87/3DOM CeO2催化剂在20 000 mL/(g·h)的空速下对三氯乙烯氧化显示很好的催化活性(T90%为415 ℃,活化能为33 kJ/mol)以及良好的水热稳定性和抗氯中毒性能[83].为了提高催化剂的抗氯中毒性能,笔者制备了xAuyPd/3DOM TiO2催化剂(比表面积大小为49~53 m2/g),发现粒径为3~4 nm的AuPd纳米粒子均匀分散于3DOM TiO2的孔道表面,0.91% Au0.51Pd/3DOM TiO2催化剂对三氯乙烯氧化的T90%为400 ℃(空速为20 000 mL/(g·h))[84].
由以上活性数据可知,在空速为40 000 mL/(g·h)时催化剂对甲苯氧化的活性按照3.8% AuPd1.92/3DOM Mn2O3、1.99% AuPd/3DOM Co3O4、2.3% Pt/3DOM Mn2O3、0.27% Pt/3DOM 26.9% CeO2-Al2O3、5.8% Au/3DOM Mn2O3、6.5% Au/3DOM Co3O4、Fe2O3-3的顺序降低.
6. 大孔复合金属氧化物负载贵金属催化剂
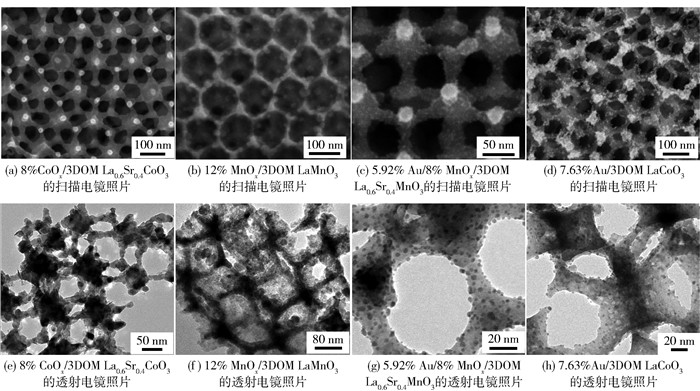
图 8为3DOM复合金属氧化物负载过渡金属氧化物或贵金属催化剂的SEM和TEM照片[86, 87, 91, 92].采用PMMA胶晶模板法和PVA保护的还原法制备了菱方相3DOM LaMnO3负载纳米Au催化剂.结果表明,4.9% Au/3DOM LaMnO3的比表面积为32.7 m2/g,Au粒子的直径为2~5 nm,在空速为20 000 mL/(g·h)条件下,该催化剂对甲苯氧化的T90%、TOFAu和比速率(rAu)分别为226 ℃、0.002 8 s-1和2.1 μmol/(g·s)[85].在A位进行部分取代可提高ABO3的催化活性.例如,6.4% Au/3DOM La0.6Sr0.4MnO3催化剂(比表面积为31.1 m2/g,Au粒径为2~5 nm)在空速为20 000 mL/(g·h)时对甲苯氧化的活性(T90%为170 ℃)[86]高于4.9% Au/3DOM LaMnO3的[85].钴系钙钛矿型氧化物对VOCs氧化的催化活性优于锰系钙钛矿型氧化物的. 7.63% Au/3DOM LaCoO3(比表面积为24.2 m2/g,Au粒径为2~4 nm)在20 000 mL/(g·h)的空速下对甲苯氧化的T90%为202 ℃,TOFAu为1.04×10-3 s-1[87].若先将贵金属掺入钙钛矿型氧化物的晶格中,再采用原位还原法将贵金属离子还原为金属纳米粒子,使其均匀分散在钙钛矿型氧化物的表面,可以获得性能优良的催化剂.例如,采用原位PMMA胶晶模板法先制备了菱方相3DOM La0.6Sr0.4Mn0.96Pd0.04O3,再经还原后制得1.18% Pd/3DOM La0.6Sr0.4MnO3(比表面积为24.2 m2/g,Pd的粒径为5.5 nm)催化剂,其在空速为40 000 mL/(g·h)时对甲烷氧化反应的T90%和比速率(rPd)分别为583 ℃和7.3 μmol/(g·s)[88].与Au、Pd、Pt等相比,Ag的价格较便宜,负载Ag催化剂对甲烷氧化也具有优良的催化性能.例如,采用PMMA胶晶模板法和PVA保护的还原法制备了菱方相3DOM La0.6Sr0.4MnO3负载Ag纳米催化剂,发现3.63% Ag/3DOM La0.6Sr0.4MnO3(比表面积为41.5 m2/g,Ag粒径为3.2 nm)对甲烷氧化的T90%为524 ℃,TOFAg为11.8×10-5 s-1,比速率(rcat)为61.8×10-4 μmol/(g·s)(空速为30 000 mL/(g·h))[89, 90].
过渡金属氧化物对VOCs氧化具有优良的催化活性,若在多孔载体表面负载一定量的过渡金属氧化物,可获得高性能的催化剂.例如,采用原位PMMA胶晶模板法制备了菱方相3DOM La0.6Sr0.4CoO3负载Co3O4催化剂[91]和3DOM LaMnO3负载MnOx催化剂[92],发现在空速为20 000 mL/(g·h)条件下,8% Co3O4/3DOM La0.6Sr0.4CoO3(比表面积为29.7 m2/g)对甲苯氧化的T90%为227 ℃[91],而12% MnOx/3DOM LaMnO3(比表面积为25.0 m2/g)对甲苯氧化的T90%为215 ℃,比速率(rcat)为0.029 μmol/(g·s),以及对甲醇氧化的T90%为137 ℃,比速率(rcat)为0.027 μmol/(g·s)[92].由于贵金属和过渡金属氧化物均对VOCs氧化具有活性,若构建“贵金属/过金属氧化物/多孔载体”催化剂,则可望获得性能优异的催化材料.例如,0.93% Au/11.2% MnOx/3DOM SiO2(Au和MnOx的粒径分别为3.6、22.6 nm,比表面积为220 m2/g)在空速为20 000 mL/(g·h)的条件下对甲苯氧化的T90%为255 ℃[93]. 1.3% Pt/8.9% Co3O4/3DOM Al2O3(Pt和Co3O4的粒径分别为2.6、18.3 nm,比表面积为102.2 m2/g)在空速为20 000 mL/(g·h)的条件下对甲苯氧化的T90%为160 ℃[94]. 1.67% Mn3O4-2% Au/3DOM La0.6Sr0.4CoO3(Au和Mn3O4的粒径分别为3.48 nm和5~10 nm,比表面积为19.9 m2/g)在空速为20 000 mL/(g·h)的条件下对甲苯氧化的T90%为230 ℃、TOFAu为3.90×10-3 s-1和比速率(rAu)为20.5 μmol/(g·s)[95].采用原位PMMA胶晶模板法和PVA保护的还原法制备了菱方相3DOM La0.6Sr0.4MnO3负载MnOx和Au纳米催化剂,结果表明,5.92% Au/8% MnOx/3DOM La0.6Sr0.4MnO3(比表面积为21.9 m2/g,Au粒径为3.5 nm)在20 000 mL/(g·h)的空速下对甲苯氧化的T90%、TOFAu和比速率(rAu)分别为220 ℃、0.137 s-1和697 μmol/(g·s)[96].采用PMMA胶晶模板法、等体积浸渍法和PVA保护的还原法制备了立方晶相结构的3DOM CoFe2O4负载MnOx和PdPt合金纳米催化剂,研究发现,1.81% Pd2.1Pt/6.70% MnOx/3DOM CoFe2O4(PdPt合金的粒径为3.0 nm,比表面积为27.8 m2/g)对甲烷氧化的T90%和TOFPdPt分别为372 ℃和37.44×10-3 s-1(空速为20 000 mL/(g·h))[97].
双贵金属形成合金结构有利于提高催化活性和催化剂的稳定性.例如,在菱方相3DOM La0.6Sr0.4MnO3负载AuPd合金纳米催化剂中,3% AuPd2/3DOM La0.6Sr0.4MnO3(比表面积为33.8 m2/g,Au粒径为2.2 nm)对甲烷氧化的T90%、TOFAuPd和比速率(rAuPd)分别为336 ℃、16×10-3 s-1和117 μmol/(g·s)(空速为50 000 mL/(g·h))[98].在立方相3DOM CoCr2O4负载AuPd合金纳米催化剂中,1.93% AuPd1.95/3DOM CoCr2O4(AuPd合金的粒径为3.3 nm,比表面积为34.9 m2/g)在20 000 mL/(g·h)的空速下对甲烷氧化的T90%、TOFAuPd和比速率(rAuPd)分别为394 ℃、8.23×10-3 s-1和60 μmol/(g·s)[99].在3DOM CoCr2O4负载AuPt合金纳米催化剂中,0.98% Au0.98Pt/3DOM CoCr2O4(AuPt合金的粒径为3.0 nm,比表面积为33.1 m2/g)对甲烷氧化的T90%为354 ℃,比速率(rcat)为4.56 μmol/(g·s)(空速为20 000 mL/(g·h))[100].
由活性数据可看出,在空速为20 000 mL/(g·h)的条件下催化剂对甲苯氧化的活性按照1.3% Pt/8.9% Co3O4/3DOM Al2O3、6.4% Au/3DOM La0.6Sr0.4MnO3、7.63% Au/3DOM LaCoO3、12% MnOx/3DOM LaMnO3、5.92% Au/8% MnOx/3DOM La0.6Sr0.4MnO3、8% Co3O4/3DOM La0.6Sr0.4CoO3(4.9% Au/3DOM LaMnO3)、1.67% Mn3O4-2% Au/3DOM La0.6Sr0.4CoO3、0.93% Au/11.2% MnOx/3DOM SiO2的顺序减小,而在空速为20 000~50 000 mL/(g·h)的条件下催化剂对甲烷氧化的活性则按照3% AuPd2/3DOM La0.6Sr0.4MnO3、0.98% Au0.98Pt/3DOM CoCr2O4、1.81% Pd2.1Pt/6.70% MnOx/3DOM CoFe2O4、1.93% AuPd1.95/3DOM CoCr2O4、3.63% Ag/3DOM La0.6Sr0.4MnO3的顺序减小.
影响催化剂对甲烷或典型VOCs氧化的催化活性的主要因素为比表面积、孔结构、粒子在载体表面的分散度、粒径、吸附氧物种浓度、低温还原性、O2或VOCs活化能力以及金属氧化物或贵金属(合金)与载体之间的相互作用等.笔者利用X射线衍射、扫描电镜、透射电镜、选区电子衍射、高角环形暗场-扫描透射电子显微镜、氮气吸附-脱附、激光拉曼、X射线光电子能谱、氢气程序升温还原、氧气程序升温脱附、傅里叶变换红外光谱和原位漫反射傅里叶变换红外光谱等技术表征了催化剂的物化性质.根据规整形貌过渡金属氧化物、介孔金属氧化物、大孔金属氧化物、大孔复合金属氧化物及其负载过渡金属氧化物和贵金属纳米催化剂的表征结果,笔者认为每个系列催化剂中活性最好的催化剂均具有高的比表面积、发达的孔结构、高的粒子分散度、小的粒径、高的吸附氧物种浓度、好的低温还原性、强的O2或VOCs活化能力、强的金属氧化物或贵金属(合金)与载体之间的相互作用.
7. 结论与展望
采用表面活性剂辅助的水热法、溶剂热法或微乳液法合成了规整形貌过渡金属氧化物催化剂,采用KIT-6、SBA-16及表面活性剂辅助的纳米浇铸法制备了介孔过渡金属氧化物催化剂,采用PMMA胶晶模板法及表面活性剂辅助的胶晶模板法制备了大孔(复合)金属氧化物催化剂,采用等体积浸渍法、PVA保护的硼氢化钠或乙二醇还原法制备了多孔(复合)金属氧化物负载过渡金属氧化物或贵金属(合金)催化剂.基于表征结果和活性数据,笔者认为催化剂的优良催化性能与其较高的比表面积、较发达的孔结构、较高的粒子分散度、较小的粒径、较高的吸附氧物种浓度、较好的低温还原性、较强的O2或VOCs活化能力、较强的金属氧化物或贵金属(合金)与载体之间的相互作用等有关.
虽然笔者课题组在规整形貌过渡金属氧化物、介孔金属氧化物、大孔金属氧化物、大孔复合金属氧化物及其负载过渡金属氧化物和贵金属纳米催化剂的研发方面做了大量的工作,且部分催化剂的性能也较好,但是大多数催化剂的成本偏高,尚难达到工业化应用.在今后的研究工作中,可以就以下几个方面进行改进和完善:1)优化催化剂配方(选用合适的载体和制备更加规整的介孔催化材料)、制备方法及表征技术,获得新型高效催化剂,揭示活性位与催化性能之间的构效关系;2)制备单原子贵金属催化剂是一个有效降低贵金属用量的策略;3)制备疏水耐硫催化剂,进一步改善催化剂的抗水性能抗二氧化硫中毒性能;4)制备具有核壳结构的催化剂,进一步提高其热稳定性;5)借助原位技术并结合量化计算结果,分析典型VOCs在催化剂上氧化时的中间物种演变过程,探明催化反应机理;6)结合实际应用条件,评价多组分混合VOCs的综合消除效果.
-
-
[1] 邓积光, 刘雨溪, 张磊, 等.甲烷催化燃烧研究进展(上)[J].石油化工, 2013, 42(1):1-7. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/gych200403001 DENG J G, LIU Y X, ZHANG L, et al. Advancements in catalysts for catalytic combustion of natural gas (Ⅰ)[J]. Petrochemical Technology, 2013, 42(1):1-7. (in Chinese) http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/gych200403001
[2] 邓积光, 刘雨溪, 张磊, 等.甲烷催化燃烧研究进展(下)[J].石油化工, 2013, 42(2):125-133. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8144.2013.02.001 DENG J G, LIU Y X, ZHANG L, et al. Advancements in catalysts for catalytic combustion of natural gas (Ⅱ)[J]. Petrochemical Technology, 2013, 42(2):125-133. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8144.2013.02.001
[3] 戴洪兴, 邓积光, 夏云生, 等.三维有序孔过渡金属氧化物制备及催化应用[J].无机盐工业, 2012, 44(5):55-58. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-4990.2012.05.018 DAI H X, DENG J G, XIA Y S, et al. Hard-templating fabrication and catalytic applications of three-dimensionally ordered meso- and macroporous transition-metal oxides[J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2012, 44(5):55-58. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-4990.2012.05.018
[4] 邓积光, 何胜男, 谢少华, 等.用于消除挥发性有机物的有序多孔金属氧化物催化剂的研究进展[J].高等学校化学学报, 2014, 35(6):1119-1129. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/gdxxhxxb201406001 DENG J G, HE S N, XIE S H, et al. Research advancements of ordered porous metal oxide catalysts for the oxidative removal of volatile organic compounds[J]. Chemical Journal of Chinese Universities, 2014, 35(6):1119-1129. (in Chinese) http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/gdxxhxxb201406001
[5] LIU Y X, DENG J G, XIE S H, et al. Catalytic removal of volatile organic compounds using ordered porous transition metal oxide and supported noble metal catalysts[J]. Chinese Journal of Catalysis, 2016, 37(8):1193-1205. doi: 10.1016/S1872-2067(16)62457-9
[6] ZHAO X T, XIE S H, YANG H G, et al. Catalytic removal of volatile organic compounds over porous catalysts[J]. The Global Environmental Engineers, 2015, 2(1):1-14.
[7] WANG Y, ARANDIYAN H, BAGHERI A, et al. Recent advances in porous metal oxides for heterogeneous catalysis:a review[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2017, 5:8825-8846. doi: 10.1039/C6TA10896B
[8] ARANDIYAN H, WANG Y, SUN H Y, et al. Ordered meso- and macroporous perovskite oxide catalysts for emerging applications[J]. Chemical Communications, 2018, 54(50):6484-6502. doi: 10.1039/C8CC01239C
[9] HUANG H B, XU Y, FENG Q Y, et al. Low temperature catalytic oxidation of volatile organic compounds:a review[J]. Catalysis Science & Technology, 2015, 5:2649-2669. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=ac30bed5bf272d692a8ff35eb1185b58&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
[10] KAMAL M S, RAZZAK S A, HOSSAIN M M. Catalytic oxidation of volatile organic compounds (VOCs)-a review[J]. Atmospheric Environment, 2016, 140:117-134. doi: 10.1016/j.atmosenv.2016.05.031
[11] HE C, CHENG J, ZHANG X, et al. Recent advances in the catalytic oxidation of volatile organic compounds:a review based on pollutant sorts and sources[J]. Chemical Reviews, 2019, 119:4471-4568. doi: 10.1021/acs.chemrev.8b00408
[12] WANG F, DAI H X, DENG J G, et al. Manganese oxides with rod-, wire-, tube-, and flower-like morphologies:highly effective catalysts for the removal of toluene[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2012, 46(7):4034-4041. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=6afad29b14f409a31288d06fa37a3edb&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
[13] SHI F J, WANG F, DAI H X, et al. Rod-, flower-, and dumbbell-like MnO2:highly active catalysts for the combustion of toluene[J]. Applied Catalysis A:General, 2012, 433/434:206-213. doi: 10.1016/j.apcata.2012.05.016
[14] BAI G M, DAI H X, DENG J G, et al. Porous NiO nanoflowers and nanourchins:highly active catalysts for toluene combustion[J]. Catalysis Communications, 2012, 27:148-153. doi: 10.1016/j.catcom.2012.07.008
[15] BAI G M, DAI H X, DENG J G, et al. The microemulsion preparation and high catalytic performance of mesoporous NiO nanorods and nanocubes for toluene combustion[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2013, 219:200-208. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2013.01.008
[16] BAI G M, DAI H X, DENG J G, et al. Porous Co3O4 nanowires and nanorods:highly active catalysts for the combustion of toluene[J]. Applied Catalysis A:General, 2013, 450:42-49. doi: 10.1016/j.apcata.2012.09.054
[17] WANG F, DAI H X, DENG J G, et al. Nanoplate-aggregate Co3O4 microspheres for toluene combustion[J]. Chinese Journal of Catalysis, 2014, 35(9):1475-1481. doi: 10.1016/S1872-2067(14)60072-3
[18] BAI G M, DAI H X, LIU Y X, et al. Preparation and catalytic performance of cylinder- and cake-like Cr2O3 for the oxidation of toluene[J]. Catalysis Communications, 2013, 36:43-47. doi: 10.1016/j.catcom.2013.02.025
[19] DENG J G, HE S N, XIE S H, et al. Ultralow loading of silver nanoparticles on Mn2O3 nanowires derived with molten salts:a high-efficiency catalyst for the oxidative removal of toluene[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2015, 49(18):11089-11095.
[20] WANG Y, ARANDIYAN H, LIU Y X, et al. Template-free scalable synthesis of flower-like Co3-xMnxO4 spinel catalysts for toluene oxidation[J]. ChemCatChem, 2018, 10(16):3429-3434. doi: 10.1002/cctc.201800598
[21] LIANG Y J, LIU Y X, DENG J G, et al. Coupled palladium-tungsten bimetallic nanosheets/TiO2 hybrids with enhanced catalytic activity and stability for the oxidative removal of benzene[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2019, 53(10):5926-5935. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=0ddf9a290f85828c3f4b444c65843988&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
[22] DENG J G, ZHANG L, DAI H X, et al. Single-crystalline La0.6Sr0.4CoO3-δ nanowires/nanorods derived hydrothermally without the use of a template:catalysts highly active for toluene complete oxidation[J]. Catalysis Letters, 2008, 123:294-300. doi: 10.1007/s10562-008-9422-8
[23] WANG Y Z, DENG J G, DENG S X, et al. Morphologically controlled synthesis of porous spherical and cubic LaMnO3 with high activity for the catalytic removal of toluene[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2014, 6(20):17394-17401. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=7c74876f6dfff076ebb04352d6093af2
[24] DENG J G, ZHANG Y, DAI H X, et al. Effect of hydrothermal treatment temperature on the catalytic performance of single-crystalline La0.5Sr0.5MnO3-δ microcubes for the combustion of toluene[J]. Catalysis Today, 2008, 139(1/2):82-87.
[25] DENG J G, ZHANG L, DAI H X, et al. A study on the relationship between low-temperature reducibility and catalytic performance of single-crystalline La0.6Sr0.4MnO3+δ microcubes for toluene combustion[J]. Catalysis Letters, 2009, 130(3/4):622-629. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=270f61acfebc941ebf7d911053d625e7
[26] DENG J G, ZHANG L, DAI H X, et al. Strontium-doped lanthanum cobaltite and manganite:highly active catalysts for toluene complete oxidation[J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2008, 47(21):8175-8183. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=b70473e4128376d54d7a3bf50e73dd74&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
[27] DENG J G, ZHANG L, DAI H X, et al. Hydrothermally fabricated single-crystalline strontium-substituted lanthanum manganite microcubes for catalytic combustion of toluene[J]. Journal of Molecular Catalysis A:Chemical, 2009, 299(1/2):60-67. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=9806276f1cdd5773a6fc1b88f55a7872
[28] DENG J G, DAI H X, LIU Y X, et al. Hydrothermal fabrication and catalytic properties of La1-xSrxM1-yFeyO3 (M=Mn, Co) that are highly active for the removal of toluene[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2010, 44(7):2618-2623.
[29] 张悦, 张磊, 邓积光, 等.水热法制备特定形貌单晶La2-xSrxCuO4及甲烷催化氧化性能[J].催化学报, 2009, 30(4):347-354. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-9837.2009.04.014 ZHANG Y, ZHANG L, DENG J G, et al. Hydrothermal fabrication and catalytic performance of single-crystalline La2-xSrxCuO4 (x=0, 1) with specific morphologies for methane oxidation[J]. Chinese Journal of Catalysis, 2009, 30(4):347-354. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-9837.2009.04.014
[30] ZHANG L, ZHANG Y, DAI H X, et al. Hydrothermal synthesis and catalytic performance of single-crystalline La2-xSrxCuO4 for methane oxidation[J]. Catalysis Today, 2010, 153(3/4):143-149.
[31] ZHANG Y, ZHANG L, DENG J G, et al. Hydrothermal fabrication and catalytic properties of YBa2Cu3O7 single crystallites for methane combustion[J]. Catalysis Letters, 2010, 135(1/2):126-134. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=49a848b4a6095fd0baf1afd7b72dcb32
[32] XIA Y S, DAI H X, JIANG H Y, et al. Mesoporous chromia with ordered three-dimensional structure for the complete oxidation of toluene and ethyl acetate[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2009, 43(21):8355-8360. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=bb830f61c6d7c2e5e5844f2f5648039c&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
[33] XIA Y S, DAI H X, ZHANG L, et al. Ultrasound-assisted nanocasting fabrication and high catalytic activity of three-dimensionally ordered mesoporous chromia for the combustion of formaldehyde, acetone, and methanol[J]. Applied Catalysis B:Environmental, 2010, 100(1/2):229-237.
[34] DENG J G, ZHANG L, DAI H X, et al. Ultrasound-assisted nanocasting fabrication of ordered mesoporous MnO2 and Co3O4 with high surface areas and polycrystalline walls[J]. The Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 2010, 114(6):2694-2700. doi: 10.1021/jp910159b
[35] XIA Y S, DAI H X, JIANG H Y, et al. Three-dimensional ordered mesoporous cobalt oxides:highly active catalysts for the oxidation of toluene and methanol[J]. Catalysis Communications, 2010, 11(15):1171-1175. doi: 10.1016/j.catcom.2010.07.005
[36] DU Y C, MENG Q, WANG J S, et al. Three-dimensional mesoporous manganese oxides and cobalt oxides:high-efficiency catalysts for the removal of toluene and carbon monoxide[J]. Microporous and Mesoporous Materials, 2012, 162:199-206. doi: 10.1016/j.micromeso.2012.06.030
[37] YE Q, ZHAO J S, HUO F F, et al. Nanosized Au supported on three-dimensionally ordered mesoporous β-MnO2:highly active catalysts for the low-temperature oxidation of carbon monoxide, benzene, and toluene[J]. Microporous and Mesoporous Materials, 2013, 172:20-29. doi: 10.1016/j.micromeso.2013.01.007
[38] XIE S H, LIU Y X, DENG J G, et al. Insights into the active sites of ordered mesoporous cobalt oxide catalysts for the total oxidation of o-xylene[J]. Journal of Catalysis, 2017, 352:282-292. doi: 10.1016/j.jcat.2017.05.016
[39] XIA Y S, DAI H X, JIANG H Y, et al. Three-dimensionally ordered and wormhole-like mesoporous iron oxide catalysts highly active for the oxidation of acetone and methanol[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2011, 186(1):84-91. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2010.10.073
[40] ZHAO X T, LIU Y X, DENG J G, et al. Mesoporous PdxPt alloys:high-performance catalysts for methane combustion[J]. Molecular Catalysis, 2017, 442:191-201. doi: 10.1016/j.mcat.2017.09.002
[41] GAO B Z, DENG J G, LIU Y X, et al. Mesoporous LaFeO3 catalysts for the oxidation of carbon monoxide and toluene[J]. Chinese Journal of Catalysis, 2013, 34(12):2223-2229. doi: 10.1016/S1872-2067(12)60689-5
[42] LIU Y X, DAI H X, DU Y C, et al. Controlled preparation and high catalytic performance of three-dimensionally ordered macroporous LaMnO3 with nanovoid skeletons for the combustion of toluene[J]. Journal of Catalysis, 2012, 287:149-160. doi: 10.1016/j.jcat.2011.12.015
[43] LIU Y X, DAI H X, DU Y C, et al. Lysine-aided PMMA-templating preparation and high performance of three-dimensionally ordered macroporous LaMnO3 with mesoporous walls for the catalytic combustion of toluene[J]. Applied Catalysis B:Environmental, 2012, 119-120:20-31. doi: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2012.02.010
[44] LIU Y X, DAI H X, DENG J G, et al. Controlled generation of uniform spherical LaMnO3, LaCoO3, Mn2O3, and Co3O4 nanoparticles and their high catalytic performance for carbon monoxide and toluene oxidation[J]. Inorganic Chemistry, 2013, 52:8665-8676. doi: 10.1021/ic400832h
[45] ARANDIYAN H, DAI H X, DENG J G, et al. Three-dimensionally ordered macroporous La0.6Sr0.4MnO3 with high surface areas:active catalysts for the combustion of methane[J]. Journal of Catalysis, 2013, 307:327-339. doi: 10.1016/j.jcat.2013.07.013
[46] ZHAO Z X, DAI H X, DENG J G, et al. Three-dimensionally ordered macroporous La0.6Sr0.4FeO3-δ:high-efficiency catalysts for the combustion of toluene[J]. Microporous and Mesoporous Materials, 2012, 163:131-139. doi: 10.1016/j.micromeso.2012.07.006
[47] ZHAO Z X, DAI H X, DENG J G, et al. Preparation of three-dimensionally ordered macroporous La0.6Sr0.4Fe0.8Bi0.2O3-δ and their excellent catalytic performance for the combustion of toluene[J]. Journal of Molecular Catalysis A:Chemical, 2013, 366:116-125. doi: 10.1016/j.molcata.2012.09.014
[48] JI K M, DAI H X, DENG J G, et al. Three-dimensionally ordered macroporous SrFeO3-δ with high surface area:active catalysts for the complete oxidation of toluene[J]. Applied Catalysis A:General, 2012, 425-426:153-160. doi: 10.1016/j.apcata.2012.03.013
[49] JI K M, DAI H X, DAI J X, et al. PMMA-templating preparation and catalytic activities of three-dimensional macroporous strontium ferrites with high surface areas for toluene combustion[J]. Catalysis Today, 2013, 201:40-48. doi: 10.1016/j.cattod.2012.03.061
[50] JI K M, DAI H X, DENG J G, et al. One-pot hydrothermal preparation and catalytic performance of porous strontium ferrite hollow spheres for the combustion of toluene[J]. Journal of Molecular Catalysis A:Chemical, 2013, 370:189-196. doi: 10.1016/j.molcata.2013.01.013
[51] JI K M, DAI H X, DENG J G, et al. Catalytic toluene oxidation over the three-dimensionally ordered macroporous EuFeO3 catalysts fabricated by the sucrose-assisted polymethyl methacrylate-templating method[J]. Solid State Sciences, 2014, 27:36-42. doi: 10.1016/j.solidstatesciences.2013.10.011
[52] JI K M, DAI H X, DENG J G, et al. Catalytic removal of toluene over three-dimensionally ordered macroporous Eu1-xSrxFeO3 perovskites[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2013, 214:262-271. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2012.10.083
[53] JI K M, DAI H X, DENG J G, et al. Three-dimensionally ordered macroporous Eu0.6Sr0.4FeO3 supported cobalt oxides:highly active nanocatalysts for the combustion of toluene[J]. Applied Catalysis B:Environmental, 2013, 129:539-548. doi: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2012.10.005
[54] JI K M, DAI H X, DENG J G, et al. A comparative study of bulk and 3DOM-structured Co3O4, Eu0.6Sr0.4FeO3, and Co3O4/Eu0.6Sr0.4FeO3:preparation, characterization, and catalytic activities for toluene combustion[J]. Applied Catalysis A:General, 2012, 447-448:41-48. doi: 10.1016/j.apcata.2012.09.004
[55] JI K M, DAI H X, DENG J G, et al. Glucose-assisted hydrothermal preparation and catalytic performance of three-dimensionally porous LaFeO3 for toluene combustion[J]. Journal of Solid State Chemistry, 2013, 199:164-170. doi: 10.1016/j.jssc.2012.12.017
[56] ARANDIYAN H, SCOTT J, WANG Y, et al. Meso-molding three-dimensional macroporous perovskites:a new approach to generate high-performance nanohybrid catalysts[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2016, 8(4):2457-2463. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=30bf4abec655fb2a29e088cad3414ef1&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
[57] WANG Y, ARANDIYAN H, TAHINI H A, et al. The controlled disassembly of mesostructured perovskites as an avenue to fabricating high performance nanohybrid catalysts[J]. Nature Communications, 2017, 8:15553. doi: 10.1038/ncomms15553
[58] ZHANG L, ZHANG Y, DENG J G, et al. Surfactant-aided hydrothermal preparation and catalytic performance of La2-xSrxCuO4 single-crystallites for methane combustion[J]. Journal of Natural Gas Chemistry, 2012, 21:69-75. doi: 10.1016/S1003-9953(11)60335-6
[59] YUAN J, DAI H X, ZHANG L, et al. PMMA-templating preparation and catalytic properties of high-surface-area three-dimensional macroporous La2CuO4 for methane combustion[J]. Catalysis Today, 2011, 175:209-215. doi: 10.1016/j.cattod.2011.04.013
[60] LIU Y X, DAI H X, DENG J G, et al. Mesoporous Co3O4 supported gold nanocatalysts:highly active for the oxidation of carbon monoxide, benzene, toluene, and o-xylene[J]. Journal of Catalysis, 2014, 309:408-418. doi: 10.1016/j.jcat.2013.10.019
[61] YANG H G, DAI H X, DENG J G, et al. Porous cube-aggregated Co3O4 microsphere-supported gold nanoparticles for oxidation of carbon monoxide and toluene[J]. ChemSusChem, 2014, 7(6):1745-1754. doi: 10.1002/cssc.201400050
[62] WU Z X, DENG J G, LIU Y X, et al. Three-dimensionally ordered mesoporous Co3O4 supported Au-Pd alloy nanoparticles:high-performance catalysts for methane combustion[J]. Journal of Catalysis, 2015, 332:13-24. doi: 10.1016/j.jcat.2015.09.008
[63] WANG Z W, LIU Y X, YANG T, et al. Catalytic performance of cobalt oxide-supported gold-palladium nanocatalysts for the removal of toluene and o-xylene[J]. Chinese Journal of Catalysis, 2017, 38(2):207-216. doi: 10.1016/S1872-2067(16)62569-X
[64] XIE S H, LIU Y X, DENG J G, et al. Mesoporous CoO-supported palladium nanocatalysts with high performance for o-xylene combustion[J]. Catalysis Science & Technology, 2018, 8:806-816. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=00f6c8bd792c4145aec78fa8e54f46b0
[65] XIE S H, LIU Y X, DENG J G, et al. Efficient removal of methane over the cobalt monoxide doped AuPd nanocatalysts[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2017, 51(4):2271-2279. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=a88ace874975728c4312df6979848601
[66] YANG J, LIU Y X, DENG J G, et al. AgAuPd/meso-Co3O4:high-performance catalysts for methanol oxidation[J]. Chinese Journal of Catalysis, 2019, 40(6):837-848. doi: 10.1016/S1872-2067(18)63205-X
[67] WU Z X, DENG J G, XIE S H, et al. Mesoporous Cr2O3 supported Au-Pd alloy nanoparticles:high-performance catalysts for the oxidation of toluene[J]. Microporous and Mesoporous Materials, 2016, 224:311-322. doi: 10.1016/j.micromeso.2015.11.061
[68] XU P, WU Z X, DENG J G, et al. Catalytic performance enhancement by alloying Pd with Pt on ordered mesoporous manganese oxide for methane combustion[J]. Chinese Journal of Catalysis, 2017, 38(1):92-105. doi: 10.1016/S1872-2067(16)62567-6
[69] HAN Z, FANG J Y, XIE S H, et al. AuRu/meso-Mn2O3:a highly active and stable catalyst for methane combustion[J]. IOP Conference Series:Materials Science and Engineering, 2018, 359:012022. doi: 10.1088/1757-899X/359/1/012022
[70] YANG J, LIU Y X, DENG J G, et al. PtxCo/meso-MnOy:highly efficient catalysts for low-temperature methanol combustion[J]. Catalysis Today, 2019, 332:168-176. doi: 10.1016/j.cattod.2018.06.052
[71] HAN W, DENG J G, XIE S H, et al. Gold supported on iron oxide nanodisk as efficient catalyst for the removal of toluene[J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2014, 53(9):3486-3494. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=ba9804d95d69f0790f40fd9c305d7699
[72] YANG K, LIU Y X, DENG J G, et al. Three-dimensionally ordered mesoporous iron oxide-supported single-atom platinum:highly active catalysts for benzene combustion[J]. Applied Catalysis B:Environmental, 2019, 244:650-659. doi: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2018.11.077
[73] ZHANG R Z, DAI H X, DU Y C, et al. P123-PMMA dual-templating generation and unique physicochemical properties of three-dimensionally ordered macroporous iron oxides with nanovoids in the crystalline walls[J]. Inorganic Chemistry, 2011, 50(6):2534-2544. doi: 10.1021/ic1023604
[74] ZHANG X, LIU Y X, DENG J G, et al. 3DOM Cr2O3-CeO2:high-performance catalysts for the oxidative removal of trichloroethylene[J]. Catalysis Today, 2019, doi:10. 1016/j.cattod. 2019. 01. 071.
[75] XIE S H, DAI H X, DENG J G, et al. Au/3DOM Co3O4:highly active nanocatalysts for the oxidation of carbon monoxide and toluene[J]. Nanoscale, 2013, 5(22):11207-11219. doi: 10.1039/c3nr04126c
[76] XIE S H, DENG J G, ZANG S M, et al. Au-Pd/3DOM Co3O4:highly active and stable nanocatalysts for toluene oxidation[J]. Journal of Catalysis, 2015, 322:38-48. doi: 10.1016/j.jcat.2014.09.024
[77] XIE S H, DAI H X, DENG J G, et al. Preparation and high catalytic performance of Au/3DOM Mn2O3 for the oxidation of carbon monoxide and toluene[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2014, 279:392-401. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2014.07.033
[78] XIE S H, DENG J G, LIU Y X, et al. Excellent catalytic performance, thermal stability, and water resistance of 3DOM Mn2O3-supported Au-Pd alloy nanoparticles for the complete oxidation of toluene[J]. Applied Catalysis A:General, 2015, 507:82-90. doi: 10.1016/j.apcata.2015.09.026
[79] XIE S H, LIU Y X, DENG J G, et al. Effect of transition metal doping on the catalytic performance of Au-Pd/3DOM Mn2O3 for the oxidation of methane and o-xylene[J]. Applied Catalysis B:Environmental, 2017, 206:221-232. doi: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2017.01.030
[80] PEI W B, LIU Y X, DENG J G, et al. Partially embedding Pt nanoparticles in the skeleton of 3DOM Mn2O3: an effective strategy for enhancing catalytic stability in toluene combustion[J/OL]. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, 2019. doi: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2019.117814.
[81] YANG H G, DENG J G, LIU Y X, et al. Preparation and catalytic performance of Ag, Au, Pd or Pt nanoparticles supported on 3DOM CeO2-Al2O3 for toluene oxidation[J]. Journal of Molecular Catalysis A:Chemical, 2016, 414:9-18. doi: 10.1016/j.molcata.2015.12.010
[82] XIE S H, LIU Y X, DENG J G, et al. Three-dimensionally ordered macroporous CeO2-supported Pd@Co nanoparticles:highly active catalysts for methane oxidation[J]. Journal of Catalysis, 2016, 342:17-26. doi: 10.1016/j.jcat.2016.07.003
[83] ZHANG X, LIU Y X, DENG J G, et al. Alloying of gold with palladium: an effective strategy to improve the chlorine-resistant behavior and catalytic stability of 3DOM CeO2-supported catalysts in trichloroethylene combustion[J]. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, 2019, in press.
[84] ZHANG X, LIU Y X, DENG J G, et al. AuPd/3DOM TiO2 catalysts:good activity and stability for the oxidation of trichloroethylene[J]. Catalysts, 2018, 8(12):666. doi: 10.3390/catal8120666
[85] LIU Y X, DAI H X, DENG J G, et al. PMMA-templating generation and excellent catalytic performance of chain-like ordered macroporous LaMnO3 supported gold nanocatalysts for the oxidation of carbon monoxide and toluene[J]. Applied Catalysis B:Environmental, 2013, 140/141:317-326. doi: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2013.04.025
[86] LIU Y X, DAI H X, DENG J G, et al. Au/3DOM La0.6Sr0.4MnO3:highly active nanocatalysts for the oxidation of carbon monoxide and toluene[J]. Journal of Catalysis, 2013, 305:146-153. doi: 10.1016/j.jcat.2013.04.025
[87] LI X W, DAI H X, DENG J G, et al. Au/3DOM LaCoO3:high-performance catalysts for the oxidation of carbon monoxide and toluene[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2013, 228:965-975. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2013.05.070
[88] ZHAO X T, ZHANG R, LIU Y X, et al. In-situ reduction-derived Pd/3DOM La0.6Sr0.4MnO3:good catalytic stability in methane combustion[J]. Applied Catalysis A:General, 2018, 568:202-212. doi: 10.1016/j.apcata.2018.10.011
[89] ARANDIYAN H, DAI H X, DENG J G, et al. Dual-templating synthesis of three-dimensionally ordered macroporous La0.6Sr0.4MnO3-supported Ag nanoparticles:controllable alignments and super performance for the catalytic combustion of methane[J]. Chemical Communications, 2013, 49(91):10748-10750. doi: 10.1039/c3cc46312e
[90] ARANDIYAN H, DAI H X, DENG J G, et al. Three-dimensionally ordered macroporous La0.6Sr0.4MnO3 supported Ag nanoparticles:highly active catalysts for the combustion of methane[J]. Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 2014, 118(27):14913-14928. doi: 10.1021/jp502256t
[91] LI X W, DAI H X, DENG J G, et al. In situ PMMA-templating preparation and excellent catalytic performance of Co3O4/3DOM La0.6Sr0.4CoO3 for toluene combustion[J]. Applied Catalysis A:General, 2013, 458:11-20. doi: 10.1016/j.apcata.2013.03.022
[92] LIU Y X, DAI H X, DENG J G, et al. In-situ poly(methyl methacrylate)-templating generation and excellent catalytic performance of MnOx/3DOM LaMnO3 for the combustion of toluene and methanol[J]. Applied Catalysis B:Environmental, 2013, 140-141:493-505. doi: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2013.04.051
[93] YANG H G, DENG J G, XIE S H, et al. Au/MnOx/3DOM SiO2:highly active catalysts for toluene oxidation[J]. Applied Catalysis A:General, 2015, 507:139-148. doi: 10.1016/j.apcata.2015.09.043
[94] YANG H G, DENG J G, LIU Y X, et al. Pt/Co3O4/3DOM Al2O3:highly effective catalysts for toluene combustion[J]. Chinese Journal of Catalysis, 2016, 37(6):934-946. doi: 10.1016/S1872-2067(15)61095-6
[95] JIANG Y, XIE S H, YANG H G, et al. Mn3O4-Au/3DOM La0.6Sr0.4CoO3:high-performance catalysts for toluene oxidation[J]. Catalysis Today, 2017, 281:437-446. doi: 10.1016/j.cattod.2016.05.012
[96] JIANG Y, DENG J G, XIE S H, et al. Au/MnOx/3DOM La0.6Sr0.4MnO3:highly active nanocatalysts for the complete oxidation of toluene[J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2015, 54(3):900-910.
[97] LI X Y, LIU Y X, DENG J G, et al. Enhanced catalytic performance for methane combustion of 3DOM CoFe2O4 by co-loading MnOx and Pd-Pt alloy nanoparticles[J]. Applied Surface Science, 2017, 403:590-600. doi: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2017.01.237
[98] WANG Y, ARANDIYAN H, SCOTT J. High performance Au-Pd supported on 3D hybrid strontium-substituted lanthanum manganite perovskite catalysts for methane combustion[J]. ACS Catalysis, 2016, 6(10):6935-6947. doi: 10.1021/acscatal.6b01685
[99] WANG Z W, DENG J G, LIU Y X, et al. Three-dimensionally ordered macroporous CoCr2O4-supported Au-Pd alloy nanoparticles:highly active catalysts for methane combustion[J]. Catalysis Today, 2017, 281:467-476. doi: 10.1016/j.cattod.2016.05.035
[100] JIANG X Y, LIU Y X, DENG J G, et al. AuPt/3DOM CoCr2O4:highly active catalysts for the combustion of methane[J]. The Global Environmental Engineers, 2017, 4:24-36. doi: 10.15377/2410-3624.2017.04.3
[1] 李坚, 薛红弟, 梁文俊, 等.等离子体法去除HCHO的实验研究[J].北京工业大学学报, 2006, 32(6): 534-537. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0254-0037.2006.06.013 LI J, XUE H D, LIANG W J, et al. Experimental research on removal of formaldehyde with discharge plasma[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Technology, 2006, 32(6): 534-537. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0254-0037.2006.06.013
[2] 梁文俊, 李坚, 李晶欣, 等.自发极化等离子体反应器降解甲苯废气的研究[J].北京工业大学学报, 2010, 36(11): 1579-1584. doi: 10.11936/bjutxb2010111579 LIANG W J, LI J, LI J X, et al. Study on degradation of toluene waste gas by spontaneous polarization plasma reactor[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Technology, 2010, 36(11): 1579-1584. (in Chinese) doi: 10.11936/bjutxb2010111579
[3] 张磊, 穆青, 戴洪兴, 等. Ce0.6Zr0.4O2和BaSO4微纳米粒子的水热合成与表征[J].北京工业大学学报, 2010, 36(3): 359-363. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Conference/7437458 ZHANG L, MU Q, DAI H X, et al. Hydrothermal synthesis and characterization of Ce0.6Zr0.4O2 and BaSO4 micro/nano particles[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Technology, 2010, 36(3): 359-363. (in Chinese) http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Conference/7437458
[4] 乔小晶, 李妍, 李旺昌, 等. SiC纳米线的合成与表征[J].北京工业大学学报, 2013, 39(4): 599-603. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=bjgydxxb201304019 QIAO X J, LI Y, LI W C, et al. The synthesis and characterization of SiC nanowires[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Technology, 2013, 39(4): 599-603. (in Chinese) http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=bjgydxxb201304019
[5] 李绍元, 马文会, 周阳, 等. PS模板法制备铜纳米颗粒[J].北京工业大学学报, 2013, 39(10): 1581-1585. doi: 10.11936/bjutxb2013101581 LI S Y, MA W H, ZHOU Y, et al. PS template preparation of copper nanoparticles[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Technology, 2013, 39(10): 1581-1585. (in Chinese) doi: 10.11936/bjutxb2013101581




 下载:
下载: