Human Emotion Multi-classification Recognition Based on the EEG Time and Frequency Features by Using a Gaussian Kernel Function SVM
-
摘要:
为了找到一种综合分析方法,提高对脑电信号情感多分类识别的分类精确度,将DEAP数据库中的脑电数据采用经验模态分解的方法分解为多个本征模函数,并对本征模函数按不同的时长窗口进行分片,提取其功率谱密度作为脑电信号特征.将被试对音乐视频的情感评价指数用于生成情感分类标签,按"唤醒度"和"效价"2个维度将评价指数映射到二维情感模型中,分成4类.采用"一对一"的高斯核函数支持向量机对脑电特征进行多分类分析.实验结果表明:高斯核函数支持向量机的最高分类准确度达到90.9%(22号被试),平均分类准确度达到68.3%.高斯核函数支持向量机能有效地从脑电信号中识别出不同的情感状态;同时,对于相同刺激,不同的被试产生的情感状态不同;并且,在清醒状态下,脑电信号的高频子波对情感分类有更高的分类精确度.
-
关键词:
- 高斯核函数 /
- 支持向量机 /
- 情感分类 /
- 脑电图(EEG) /
- 经验模态分解(EMD) /
- 本征模函数(IMF)
Abstract:An integrated method was proposed to achieve the objective accuracy of emotion recognition from the electroencephalograph (EEG) signal. The EEG signals from DEAP data set were decomposed into multiple intrinsic mode functions (IMFs) with the empirical mode decomposition (EMD) method. After that, the power spectrum density was extracted as the EEG feature from the IMFs with different time windows. The emotion estimated scales of the subjects were mapped in the Valence-Arousal emotion model to be clustered into 4 classes. Gaussian kernel function support vector machine (SVM) was adopted to classify the emotion states. "One versus one" model was employed within the SVM to deal with the multi-classification problem. Results show that the highest accuracy of the emotion classification obtained by the Gaussian kernel function SVM acquires is 90.9% (with subject 22), and the mean accuracy is 68.31%. The results explain that the method can recognize different emotion from EEG signal effectively, and that different participants have different emotion experiences with the same stimulus, and that the EEG features from high frequency IMFs achieve higher emotion classification accuracy than that from low frequency IMFs.
-
情感作为人脑的高级功能,保障了人们正常的日常交流,提供了人们对客观环境的适应能力,同时,情感的变化在不同程度上影响着人们的学习和工作.因此,对人们情感状态的识别在医疗、教育、娱乐以及商业领域都有着重要而广阔的应用前景[1-5].情感是人们的内心体验,不同的情感会伴随复杂的神经过程和生理变化.人们情感变化除了可以通过表情、语调、身体姿态的变化来进行观察,也可以通过情感量表、心境量表等精神评测工具自评和他评.除此之外,通过生理电信号以及内分泌相关指标的变化也可以反映出人们情感的变化[6-7].然而,表情、语调和身体姿态很容易被人为地加以掩饰或者伪装,因此,从这几方面进行情感识别的真实性较差;而通过精神评价量表进行的情感识别,也很容易因答者的主观因素而发生偏差[8].相对于前面2种情感评测方法,通过对生理电信号进行分析的情感状态识别相对更加客观和准确[9]也逐渐成为研究的热点.
通过脑电信号对情感进行分析的文献中,脑电信号的特征提取一般都集中在时域或者频域,本文在特征提取方面通过经验模态函数分解(empirical mode decomposition, EMD)方法将脑电信号进行希尔伯特黄变换,随后按照时域进行分片后提取频域特征功率谱密度(power spectrum density,PSD),目的是为了在保持时域特征的前提下提取脑电信号的频域特征,期望在脑电情感分析中获得不同脑电信号频域特征与情感分类精度之间的关联性.同时,在对被试进行情感分类分析的过程中,本文对不同被试个体进行了单独分析,以获得相同的刺激环境下不同个体对刺激情感感受的规律.
本文的研究数据来源于开源数据库DEAP[10]中被试的脑电信号,主要贡献在于通过数据分析得出通过高斯核函数支持向量机(support rector machine,SVM)多分类算法对脑电信号特征进行情感分类分析取得了较好的分类效果;相同刺激媒体对不同被试所产生的情感感受和强度是不同的(表现在分类准确度的变化上);清醒状态下高频脑电信号在情感识别过程中有较好的区分度.
1. 相关工作
1.1 DEAP数据库
DEAP数据库是伦敦玛丽皇后大学开发的一个开放数据库,其主要目的是为了研究被试的情感变化,数据库主要记录了被试在接受外界音乐短片(music video,MV)刺激的情况下各种生理信号的变化.实验过程是,首先筛选1 000个MV作为备选的情感刺激媒体,随后通过评价从1 000个MV中筛选出40个作为正式的刺激媒体.实验开始后,为被试带上多导脑电测试设备、肌电测试设备、心率测试仪以及正面表情摄像设备.实验的前3 s是准备阶段,随后开始播放MV,同时记录被试1 min的各种生理电信号以及表情视频信号.在观看MV之后,由被试对观看的视频进行评价并记录评价分数.本研究抽取DEAP数据库中包含的脑电数据和情感评价值作为分析数据.脑电信号按照[被试,脑电电极,测试媒体,脑电信号]组成一个32×32×40×8 064的矩阵.同时,对应每个实验有一个被试对MV的评分矩阵,矩阵的维度是32×40×5.此评分内容对MV从Arousal、Valence、Dominance、Like和Familiarity几个方面进行了量化评价.
1.2 情感分类模型简介
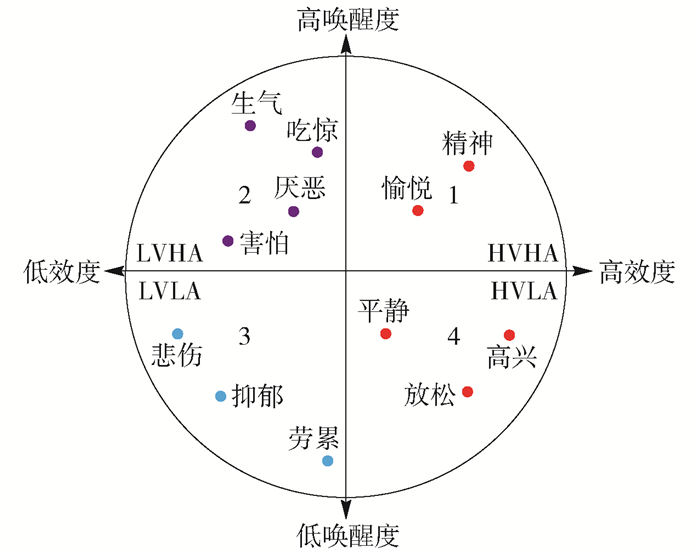
对于人类情感的系统性研究始于19世纪末James-Lange情感理论.情感分类模型主要有2种:一种是基本情感模型,另一种是维度情感模型.基本情感模型认为人的情感由基本情感构成,最早提出此观点的是Paul等[11],他们认为人类的情感由6种基本情感:生气、厌恶、害怕、高兴、悲伤和吃惊构成.这种理论认为人类的情感,用这6种基本情感就能够完全表达了.后期,也有其他的学者提出了人类的情感可以由8种基本情感,甚至22种基本情感构成,对基本情感模型的概括可见表 1.表中列举了5种被人们普遍接受的基本情感模型,其中Ekman提出的模型已被人们广泛接受.基本情感模型的局限性在于,人类的情感时常会出现几种基本情感混合的状态.例如,人们时常会感受到惊喜以及悲中带喜的状态,在这些状态下就无法用单一的基本情感模型对情感状态进行准确表达.同时,出于文化的差异仅仅用词语来表达的基本情感在不同的文化中经常会找不到对应的词语.
另外一种情感分类模型是Russell [16]于1980年提出的二维情感模型.在二维情感模型中,引入Arousal和Valence2个维度对人类的情感状态进行度量.文献[17-18]提出了更为复杂的三维情感模型,在其中引入了更多对情感进行评价的因素维度.而对于不同的情感模型,在文献[19]中从各个侧面进行了比较.本文选择二维情感模型作为生成实验情感标签数据的情感分类模型,其原因在于以下几个方面:第一,相较于离散型的基本情感模型,维度情感模型中对情感评价是连续的,因此,能够更加细腻地刻画被试的情感;第二,在维度上选择二维情感模型的原因在于,DEAP数据库中记录了5个对MV的评价指标,其中与情感相关的维度有Valance、Arousal和Dominance,而对于这3个指标来说,Valance和Arousal又是最容易被人们理解和评价的指标.为了提高原始情感分类标签的准确度,所以,采取这2个维度作为情感评价维度.
图 1展示的是一个以Valence和Arousal为坐标轴的二维情感模型,其中按照Valence和Arousal将平面分成4个区域. Valence维度反映的是人们的情感可分为正性情感和负性情感:正性情感是指使人们感到快乐和积极的情感,其对应的Valence为正;负性情感是指使人感到悲伤和消极的情感为负性情感,其对应的Valence为负.例如,高兴为正性情感,而悲伤为负性情感. Arousal维度反映的是人们感受到的情感的强度.越强的情感其Arousal值越大,而越不易察觉的情感对应的Arousal值越小.按照Valence和Arousal的正负分类,可将整个二维情感模型平面分为4个区域:HVHA(high valence high arousal)、LVHA(low valence high arousal)、LVLA(low valence low arousal)、HVLA(high valence low arousal).依据文献[16]中对基本情感词汇的评价,可将基本情感模型中的词汇按照Valance和Arousal映射到二维情感模型中,如图 1所示.将不同的情感映射到4个象限中的原因是:在DEAP进行实验的过程中,刺激媒体选择范围是来源于www.last.fm网站上面的1 000余首MV, 在这1 000首MV中又通过在线按照Valance、Arousal以及其他3个维度的评价方式进行评价后,筛选了40首MV进行测试,而这些MV在www.last.fm网站的情感分类标签并非针对被试群体,因而是不准确的,而本文通过将被试人群对于MV的自评Valance、Arousal值进行评价之后再进行映射,为每次实验的脑电图(electro encephalography,EEG)数据加上情感分类标签的标注,是更加准确的一种做法.
1.3 高斯核函数SVM算法简介
SVM的基本思想是将线性不可分类数据通过非线性变换映射到一个高维空间中,从而使原来的不可分类数据变为高维可分类数据,同时,通过在高维空间求解最优分类超平面,达到数据进行分类的效果.本文涉及的脑电数据是时序相关的非线性数据,同时对脑电数据进行特征提取之后产生的特征值矩阵又是高维度向量矩阵,因此,通过脑电数据进行情感类别分类分析,可以对这类问题表现较好的SVM方法进行分类.
SVM算法最初是一个二值分类问题,本文要想区分4种类型的情感状态,只能采用构建多个SVM分类器的方法对4类情感状态进行划分.构造的具体方法是在构造SVM分类器的时候采用“One Against One”的方法,也就是在进行SVM分类器构造的时候,每2类构造1个分类器,这样对于本研究中需要识别的4种情感类别,就需要构造6个SVM分类器对不同的2个类别进行分类判别.对一个未知的脑电特征样本进行分类分析时,将脑电特征数据分别带入6个分类器进行分类识别,对每个SVM分类器中具有最大分类预测函数值的那类进行操作.当6个分类器都对脑电特征进行分类分析之后,计票最多的类别作为未知脑电特征的情感分类类别,然后,将分类分析得到的分类标签与真实的分类标签进行对比,如果两者相同则分类正确,反之,分类不正确.将所有脑电特征进行分类分析之后就可以获得整个方法的分类精确度.
本文采取Matlab的Libsvm库对脑电特征进行情感分类训练,Libsvm库中通过svmtrain()函数对数据进行分类分析,而svmtrain()函数的参数中最重要的参数是对具体核函数的相关参数进行优化和调整.对于高斯核函数SVM来说,调优的参数主要包括惩罚因子C和核函数参数γ,具体的调优方法为网格搜索法,即通过迭代的方式,将固定范围内的C和γ按规定的步长取值后,分别带入svmtrain()函数进行交叉验证训练,对最终分类正确率的结果进行比较,将得分最高的训练模型对应的参数作为最优参数进行记录.
2. 脑电信号时频特征提取及情感分类标签生成
本研究的数据来源主要包含DEAP数据库中的2部分数据:一部分是被试的脑电信号数据,另一部分是被试对MV的情感评价数据.下面主要从脑电特征提取和情感分类标签的准备2方面对数据的准备过程进行阐述.
2.1 脑电信号数据处理和特征提取
脑电信号的分析可以从时域、频域或者两者结合的角度进行分析.从时域方面对脑电信号的特征提取和分析并不是现有分析方法中最主要的分析方面,对脑电时域特征进行提取的方法包括:事件相关电位特征(event related potential,ERP)、信号统计特征、Hjorth特征、非平稳性指标特征、分形维数特征以及高阶交叉特征等.事件相关电位在提取特征的过程中通常通过对信号幅度和时延信息的分析获得脑电信号的特征值[20].脑电信号的统计特征通常会通过功率、平均值、标准差、1st差别、2nd差别等概念对脑电信号进行特征提取[21-24]. Hjorth[25]提出了脑电信号的激活度、变化度和复杂度等概念并用其描述脑电信号的特征.在文献[26]中Kroupi等首先将脑电信号进行时间窗口划分,然后通过计算所有时间窗口内脑电信号平均值的标准差来确定脑电信号的复杂度,这个复杂度被称为脑电信号的非稳定性指标,这个指标越高说明脑电信号越不稳定.脑电信号的分形维数可以通过多种方法进行计算,例如文献[27-29]中分别用了不同的分析方法对脑电信号的分形维数进行计算,脑电信号的分形维数也经常被用来描述脑电信号的复杂程度.
脑电信号特征分析中比较受关注的是在频域方面的分析,而在频域分析中又主要从子波能量和高阶谱2个方面进行分析.子波能量特征的提取通常是通过傅里叶变换将和时间相关的脑电电压信号转换到频域,然后对不同波段的子波进行频域相关的特征提取.通常的做法是首先通过快速傅里叶变换、短时傅里叶变换或者Welch变换对原始脑电信号进行分解,在分解过程中通过窗函数(通常用Hamming窗函数)对信号进行整形和滤波,然后对不同的子波段(α:8~12 Hz,β:12~30 Hz,θ:4~8 Hz,γ:30~60 Hz)分别从能量、最大值、最小值和变化率等方面对分解后的子波段提取对应的脑电特征.
除了上述2种脑电信号特征提取方法之外,时域和频域相结合的脑电特征提取的方法也有很广泛的应用.在这些方法中通过希尔伯特黄变换对脑电信号进行分析比其他的方法的稳定性更强. Hadjidimitriou等[30]对比了通过短时傅里叶变换方法、ZAM(Zhao-Atlas-Marks)分布方法以及希尔伯特黄功率谱方法对脑电信号进行特征提取的结果,结果表明希尔伯特黄变换方法在处理信号噪声以及对非稳态信号的分析方面更加可靠.通过希尔伯特黄变换对脑电信号分析,首先是通过经验模态分解方法对原始脑电信号进行分解,然后对分解出的本征模函数再提取相应的脑电特征.
本文对脑电信号的前期处理也是采取希尔伯特黄变换将现有的脑电信号进行分解,再对分解得到的不同本征模函数(intrinsic mode function,IMF)提取其功率谱密度作为后面研究的特征.下面对EMD方法做简单的介绍,假设脑电信号为ξ(t),那么通过EMD分解脑电信号的过程可表示为
$$ \xi \left( t \right) = \sum\limits_{i = 1}^N {{\rm{IM}}{{\rm{F}}_i}\left( t \right) + {\delta _N}\left( t \right)} $$ (1) 式中:δN(t)为原始脑电信号经过EMD分解之后的残余量;N为对脑电信号进行分解后得到IMF分量的个数.经过EMD分解之后,之前复杂的脑电信号被分解为N个本征模函数,分解出的IMF分量按照先后顺序对应了脑电原始信号中按照频率从高到低的排列,同时分解出来的IMF分量同样是跟时域相关的函数.从这2点可以看出,通过EMD分解后得到的IMF分量按照分解出来的顺序在频域从高到低进行了排列,同时,IMF分量也没有丢掉时域的特征.
本文对原始脑电信号进行EMD分解之后,又对分解出来的不同的IMF在频域进行特征提取,并将提取出每个IMF的功率谱密度作为脑电信号的特征.功率谱密度所反映的物理意义是对应信号所包含的能量特征.因此,在进行信号分析的过程中,可以以功率谱密度作为脑电信号特征进行分析.由于DEAP数据库中记录的是人们在清醒状态下大脑的活动特征,在此状态下,脑电信号的有用信息主要集中在频率较高和能量相对集中的波段.文献[31-32]介绍了通过EMD方法将信号分解成多个IMF,随后对IMF进行频域特征提取的方法.本研究中通过EMD方法将脑电原始信号分解为12个IMF,对前3层IMF分量按照1 s的时间窗口进行分段后提取脑电信号的功率谱密度作为特征值加以分析,时间窗口之间没有重叠. 图 2展示了对被试1脑电通道FP1点的脑电信号进行EMD分解后得到的前5个IMF的波形.从图 2可以看到,随着展开层数的增加,IMF中包含的能量值随之减少,越靠前的IMF中包含的能量越多,频率越高.功率谱密度的物理含义是信号功率在单位频域的分布情况.因此,将提取出的脑电信号的功率谱密度作为特征值进行训练,可以反映不同情感状态下脑电信号在单位频域的变化情况.本研究涉及的脑电数据首先已经通过滤波方法去除了肌电和噪声信号,之后通过降采样的方法将脑电信号的采样频率降为128 Hz.
2.2 被试情感评价统计分析以及情感标签的准备
另外一个需要处理的数据是每个被试对MV的情感自评数据. DEAP数据库中包含了被试对40个MV五个维度(Valence、Arousal、Dominance、Like和Familiarity)的评价值.对于这5个维度的评价指标,本文提取其中对应于二维情感模型的Valence和Arousal两个维度作为本研究对情感状态进行分类的标准.
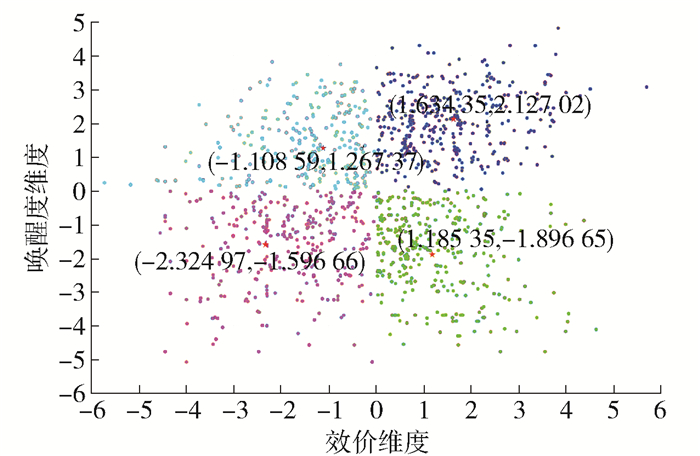
首先,将每个被试对MV的情感自评结果按Valence/Arousal两个维度的均差(简称VA值)作为被试的情感状态映射到二维情感维度空间的4个象限中.然后,用K-Means方法对映射到不同象限的VA值进行聚类分析,以求得4个象限(对应了4个情感分类)的聚类中心,并以此中心作为每个象限情感识别的阈值对实验的训练数据加上情感类别标签. 表 2、3展示了通过K-Means方法对不同象限情感状态进行聚类的分析结果.
表 2 K-Means对被试自评情感得分聚类分析得到的最终聚类中心Table 2. Cluster center of each emotion class analyzed by K-Means method维度 1(HVHA) 2(LVHA) 3(LVLA) 4(HVLA) Valence 1.634 35 -1.108 59 -2.324 97 1.185 36 Arousal 2.127 02 1.267 37 -1.596 66 -1.896 65 表 3 K-Means对被试自评情感得分聚类分析得到的每个聚类中的样本个数Table 3. Number of cases in each emotion class analyzed by K-Means method聚类种类 样本个数 1(HVHA) 348 2(LVHA) 298 3(LVLA) 282 4(HVLA) 352 如表 2所示,通过K-Means方法计算出每个情感象限中的分类中心;表 3展示了每个聚类包含的样本个数.依据表 2中给出的分类中心的VA值,将试验数据对应到4个分类象限,标上情感标签. 图 3用散点图的方式,将被试对MV的自评结果映射到二维情感平面的4个象限中,同时在每个象限中用五角星图标标出了每个情感聚类分析的中心点.
图 3中的横坐标是Valance评价值,纵坐标是Arousal评价值.其中不同颜色的散点表示的是位于不同象限内的〈Valance, Arousal〉数值对,深蓝色点对应了HVHA象限,浅蓝色点对应了LVHA象限,紫色点对应了LVLA象限,绿色点对应了HVLA象限.
3. 脑电特征情感分类结果
为了验证高斯核函数SVM方法在脑电特征情感分类问题中的有效性,将提取出的脑电特征除了通过SVM方法进行分析之外,还通过线性判别式分类法、决策树分类法、K最近邻分类法等进行了分类分析,并对实验的分类准确度进行了对比分析.然后,对不同频段的IMF通过高斯核函数SVM方法进行情感分类分析,并对得到的分类精确度进行比较,以期得到清醒状况下不同频段的脑电信号特征对应的情感分类精确度的区别.
具体的过程是:首先对脑电信号特征采用主成分分析(principal component analysis,PCA)方法确定特征中能表达95%以上的主要脑电特征,然后对每个被试进行一次分类实验,得到不同被试对应的情感分类准确度. DEAP数据库中的脑电信号采集了32个被试的多导(32导)脑电信号,对于这些信号本文通过脑电特征提取方法全部进行了提取.因为产生的脑电特征值矩阵过于庞大,同时特征向量之间存在着大量的冗余信息,所以通过PCA操作能够尽量降低特征矩阵的维度,同时在降维的过程中将信息的损失程度控制在一定范围内,从而在之后的分析中达到简化计算量的效果.每个实验都进行5折交叉验证,具体的做法是对于每个被试参与的40个实验及参与训练、验证和测试的特征样本个数,按照每个被试生成的4类情感标签的数量,将每个子类的样本数量,在Matlab中通过设置svmtrain()函数的参数v(v=5)分成5份,达到5折交叉验证的效果,其他的分类函数通过crossvalind()函数将原有的特征向量分为5份,通过循环按照3:1:1的比例将得到的样本送入分类训练函数,依次进行训练和验证,最终的平均交叉验证率为每个分类器的准确率.对于每个被试,脑电特征情感分类精确度的训练结果如表 4~6所示,表中以黑体标出的精确度是针对同一被试采用不同方法进行分类得到的精确度的最高值.
表 4 1~10号被试对应IMF1脑电特征值情感分类精确度Table 4. EEG emotion classification accuracy of 1 to 10 participants by different classification methods with IMF1 features% 分类法 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 二次方程判别式 41.1 59.0 55.9 73.2 40.5 57.7 38.8 38.4 45.5 48.6 复杂树 37.0 48.9 45.5 64.8 41.9 45.5 35.9 34.5 39.0 43.0 余弦K最近邻 44.8 74.0 72.3 89.2 66.7 75.1 47.8 44.0 64.3 61.8 加权K最近邻 45.7 73.5 72.3 88.6 65.0 75.2 48.0 48.0 61.6 60.5 线性支持向量机 45.1 58.0 59.5 78.7 51.6 59.0 41.2 40.9 53.2 55.1 二次有理核函数支持向量机 49.7 72.9 70.4 88.7 65.4 72.3 47.1 47.7 60.2 63.4 高斯核函数支持向量机 51.6 74.1 73.5 89.9 69.5 75.6 49.8 49.7 65.5 65.2 表 5 11~20号被试对应IMF1脑电特征情感分类精确度Table 5. EEG emotion classification accuracy of 11 to 20 participants by different classification methods with IMF1 features% 分类法 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 二次方程判别式 72.5 58.0 60.3 57.3 40.5 44.8 40.1 54.1 43.8 54.5 复杂树 64.2 51.1 52.1 51.4 37.2 37.5 37.6 49.5 33.8 42.0 余弦K最近邻 77.5 66.6 61.4 64.5 54.6 51.2 48.3 62.9 47.7 59.8 加权K最近邻 88.0 68.3 70.6 73.6 52.9 51.7 38.8 63.3 52 60.2 线性支持向量机 78.5 64.6 64.7 63.9 44.5 48.8 44.1 64.8 45.5 58.4 二次有理核函数支持向量机 87.3 78.3 73.6 78.4 51.6 52.7 56.3 77.6 50.5 65.6 高斯核函数支持向量机 88.9 80.7 76.1 81.7 56.6 54.7 58.9 81.2 55.5 69.5 表 6 21~32号被试对应IMF1脑电特征情感分类结果精确度Table 6. EEG emotion classification accuracy of 21 to 32 participants by different classification methods with IMF1 features分类法 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 二次方程判别式 47.9 62.3 50.8 52.4 70.0 50.6 57.2 60.2 34.6 55.0 45.0 42.3 复杂树 43.0 65.7 46.3 47.0 65.0 45.9 49.3 50.6 35.4 43.0 39.0 39.5 余弦K最近邻 66.7 90.8 55.3 75.9 89.8 62.9 64.4 78.7 50.5 59.5 51.2 58.0 加权K最近邻 65.0 89.8 52.0 76.6 90.4 63.7 63.8 78.4 47.1 58.7 49.8 57.7 线性支持向量机 49.3 74.3 53.6 53.5 77.2 56.9 61.4 62.3 42.3 55.5 48.4 43.9 二次有理核函数支持向量机 64.8 88.9 54.6 70.9 86.7 63.1 65.4 76.2 49.3 61.4 52.6 54.8 高斯核函数支持向量机 69.4 90.9 55.2 74.5 89.0 66.5 65.5 80.5 52.1 63.0 52.9 58.2 表 4~6展示了32个被试对应IMF1的脑电特征通过不同的分类方法进行分类所对应的分类精确度的值,可以看到除了24号和25号被试之外,其余的被试通过高斯核函数SVM分类方法得到的精确度最高.同时,对各被试的分类精确度按照同一种分类方法进行平均之后,可以得到通过高斯核函数SVM方法对脑电特征进行情感分类的精确度达到了68.0%.高斯核函数SVM分类算法的平均精确度达到65.0%左右.
图 4中横坐标是被试的编号,纵坐标是IMF1分量按照不同的时间窗口提取的脑电特征对应同一种分类方法获得的分类精确度的平均值.从图中可以得到,不同的分类方法对脑电特征进行情感分类时高斯核函数SVM算法的分类精确度比复杂树算法和二次方程判别式方法的更高,而在SVM算法中高斯核函数的分类精确度又比线性核函数和二次有理核函数的更高.
图 4所反映出的实际内涵是:相同的刺激媒体对不同的被试刺激后,对采集的脑电数据通过特征提取方法和分类分析方法进行情感分类识别,其情感识别的精确度却有差别.因此,可以得到不同的个体对媒体刺激所引起的情感感受是不同的,表现在二维情感模型中相同的刺激媒体对不同的被试引起的Valance值或Arousal值是有差别的,即相同的刺激强度对不同的被试其评价分数不一样,因此,通过生理信号对人们情感进行分类识别分析,需要首先进行个性化建模,在此基础上再寻求共性的情感识别模型.
将32个被试的脑电信号通过EMD分解为不同频域对应的IMF分量,对所提取的脑电特征用高斯核函数SVM进行分类,得到的平均精确度的对比如图 5所示.从图中可以看出,对包含能量较多的、频率较高的IMF1分量提取的脑电信号特征进行情感分类分析后,得到的分类精确度较高.随着包含能量的逐步递减,IMF2和IMF3的脑电信号特征对应的分类精确度逐步递减. 图 5说明在脑电信号的情感分类分析中,高频率的脑电子波应成为分析的重要波段.
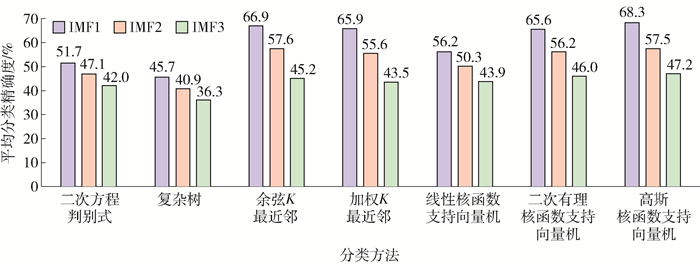
图 6展示了不同分类方法对32个被试进行情感分类分析,平均后得到的平均分类精确度的柱状图.通过高斯核函数SVM方法得到的分类精确度较高,最高的平均精确度为68.3%,最高平均精确度对应的是从IMF1中提取的脑电特征.
4. 结论
1) 本文通过人的脑电信号研究情感的分类.首先,将脑电信号进行EMD分解,将原始脑电信号分解成按照频域从高到低的IMF分量;然后,对IMF分量在时域上进行分片之后,提取分片脑电信号的功率谱密度作为被试脑电信号的特征值进行训练.对于被试在观看MV时所引起的情感状态,本文将被试的VA评价值映射到二维情感分类模型中进行分类,然后通过K-Means方法对分类进行了正确性验证,从而为不同的脑电信号打上对应的情感分类标签.在分类分析阶段,本文对比了二次方程式分类法、复杂树分类法、K最近邻分类法和不同核函数的SVM分类法.经过分析后得到,高斯核函数SVM分类法得到的分类准确度最高.
2) 通过对分类结果进行分析,发现不同个体对相同的MV刺激引起的情感评价是不一样的,同样,对不同被试进行的情感识别分析也表明其对应的情感识别精确度有很大的差别.另外,对通过EMD方法分解所得到的不同频率的IMF分量,经分析发现通过高频率的IMF分量进行情感类别分类分析,其对应的分类准确度高,这个规律也验证了人们在清醒状态下,脑电波随情感的变化主要表现在频率相对偏高的子波频段的研究结果.
3) 通过高斯核函数SVM分类法对脑电信号在时频域提取的功率谱密度特征值进行情感分类,最高分类准确度达到90.9%(被试22),平均分类准确度达到68.3%,显示了高斯核函数SVM分类法对脑电信号进行多类情感分类的有效性.
4)本文在进行脑电信号情感分析的过程中仅对不同个体进行了个体自身的情感分类识别,得到了分类的准确度,而对于被试整体的情感识别仅仅是将被试个体的情感分类准确度进行了平均,而没有考虑被试作为整体的情况下,如何对不同个体的情感标签进行整体评价和分类,这是本研究下一阶段的主要工作.
-
表 1 不同基本情感模型及对应的不同基本情感
Table 1 Different basic emotion models and correponding different basic emotions
表 2 K-Means对被试自评情感得分聚类分析得到的最终聚类中心
Table 2 Cluster center of each emotion class analyzed by K-Means method
维度 1(HVHA) 2(LVHA) 3(LVLA) 4(HVLA) Valence 1.634 35 -1.108 59 -2.324 97 1.185 36 Arousal 2.127 02 1.267 37 -1.596 66 -1.896 65 表 3 K-Means对被试自评情感得分聚类分析得到的每个聚类中的样本个数
Table 3 Number of cases in each emotion class analyzed by K-Means method
聚类种类 样本个数 1(HVHA) 348 2(LVHA) 298 3(LVLA) 282 4(HVLA) 352 表 4 1~10号被试对应IMF1脑电特征值情感分类精确度
Table 4 EEG emotion classification accuracy of 1 to 10 participants by different classification methods with IMF1 features
% 分类法 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 二次方程判别式 41.1 59.0 55.9 73.2 40.5 57.7 38.8 38.4 45.5 48.6 复杂树 37.0 48.9 45.5 64.8 41.9 45.5 35.9 34.5 39.0 43.0 余弦K最近邻 44.8 74.0 72.3 89.2 66.7 75.1 47.8 44.0 64.3 61.8 加权K最近邻 45.7 73.5 72.3 88.6 65.0 75.2 48.0 48.0 61.6 60.5 线性支持向量机 45.1 58.0 59.5 78.7 51.6 59.0 41.2 40.9 53.2 55.1 二次有理核函数支持向量机 49.7 72.9 70.4 88.7 65.4 72.3 47.1 47.7 60.2 63.4 高斯核函数支持向量机 51.6 74.1 73.5 89.9 69.5 75.6 49.8 49.7 65.5 65.2 表 5 11~20号被试对应IMF1脑电特征情感分类精确度
Table 5 EEG emotion classification accuracy of 11 to 20 participants by different classification methods with IMF1 features
% 分类法 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 二次方程判别式 72.5 58.0 60.3 57.3 40.5 44.8 40.1 54.1 43.8 54.5 复杂树 64.2 51.1 52.1 51.4 37.2 37.5 37.6 49.5 33.8 42.0 余弦K最近邻 77.5 66.6 61.4 64.5 54.6 51.2 48.3 62.9 47.7 59.8 加权K最近邻 88.0 68.3 70.6 73.6 52.9 51.7 38.8 63.3 52 60.2 线性支持向量机 78.5 64.6 64.7 63.9 44.5 48.8 44.1 64.8 45.5 58.4 二次有理核函数支持向量机 87.3 78.3 73.6 78.4 51.6 52.7 56.3 77.6 50.5 65.6 高斯核函数支持向量机 88.9 80.7 76.1 81.7 56.6 54.7 58.9 81.2 55.5 69.5 表 6 21~32号被试对应IMF1脑电特征情感分类结果精确度
Table 6 EEG emotion classification accuracy of 21 to 32 participants by different classification methods with IMF1 features
分类法 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 二次方程判别式 47.9 62.3 50.8 52.4 70.0 50.6 57.2 60.2 34.6 55.0 45.0 42.3 复杂树 43.0 65.7 46.3 47.0 65.0 45.9 49.3 50.6 35.4 43.0 39.0 39.5 余弦K最近邻 66.7 90.8 55.3 75.9 89.8 62.9 64.4 78.7 50.5 59.5 51.2 58.0 加权K最近邻 65.0 89.8 52.0 76.6 90.4 63.7 63.8 78.4 47.1 58.7 49.8 57.7 线性支持向量机 49.3 74.3 53.6 53.5 77.2 56.9 61.4 62.3 42.3 55.5 48.4 43.9 二次有理核函数支持向量机 64.8 88.9 54.6 70.9 86.7 63.1 65.4 76.2 49.3 61.4 52.6 54.8 高斯核函数支持向量机 69.4 90.9 55.2 74.5 89.0 66.5 65.5 80.5 52.1 63.0 52.9 58.2 -
[1] KIM K H, BANG S W, SANG R K. Development of person-independent emotion recognition system based on multiple physiological signals[C]//Proceedings of the Second Joint. Vol. 1. IEEE Conference Publications. Washington, DC: IEEE Computer Society, 2002: 50-51.
[2] 聂聃, 王晓韡, 段若男, 等.基于脑电的情绪识别研究综述[J].中国生物医学工程学报, 2012, 31(4):595-606. http://www.cqvip.com/QK/90680X/201204/43336534.html NIE D, WANG X W, DUAN R N, et al. A survey on EEG based emotion recognition[J]. Chinese Journal of Biomedical Engineering, 2012, 31(4):595-606. http://www.cqvip.com/QK/90680X/201204/43336534.html
[3] 陈继华, 李岚, 钱坤喜.基于多生理信号的情绪初步识别[J].生物医学工程研究, 2006, 25(3):141-146. http://www.docin.com/p-447308823.html CHEN J H, LI L, QIAN K X. Emotion recognition by physiological signals[J]. Journal of Biomedical Engineering Research, 2006, 25(3):141-146. http://www.docin.com/p-447308823.html
[4] JOHN G, FRAGOPANAGOS N, COWIE R, et al. An emotional recognition architecture based on human brain structure[C]//Proceedings of Joint International Conference on Artificial Neural Networks and Neural Information Processing. Berlin: Springer-Verlag, 2003: 1133-1140.
[5] 杨剑, 陈书燊, 皇甫浩然, 等.静息态脑电信号动态功能连接分析[J].物理学报, 2015, 64(5):374-383. http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/wlxb201505048 YANG J, CHEN S S, HUANGFU H R, et al. Dynamic functional connectivity of electroencephalogram in the resting state[J]. Acta Phys Sin, 2015, 64(5):374-383. http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/wlxb201505048
[6] KREIBIG S D. Autonomic nervous system activity in emotion:a review[J]. Biological Psychology, 2010, 84(3):394-421. doi: 10.1016/j.biopsycho.2010.03.010
[7] HU X, YU J, SONG M, et al. EEG correlates of ten positive emotions[J]. Frontiers in Human Neuroscience, 2017, 11(Article 26):1-12. doi: 10.3389/fnhum.2017.00026/full
[8] WIERZBICKA A. Human emotions:universal or culture-specific?[J]. American Anthropologist, 2010, 88(3):584-594. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/202304378_Human_Emotions_Universal_or_Culture-Specific
[9] FRAGOPANAGOS N, TAYLOR J G. Emotion recognition in human-computer interaction[J]. Signal Processing Magazine IEEE, 2005, 18(1):32-80. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0893608005000390
[10] KOELSTRA S, MUHL C, SOLEYMANI M, et al. DEAP:a database for emotion analysis:using physiological signals[J]. IEEE Transactions on Affective Computing, 2012, 3(1):18-31. doi: 10.1109/T-AFFC.2011.15
[11] PAUL E. An argument for basic emotions[J]. Cognition and Emotion, 1992, 6(3/4):169-200. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/209436215_An_Argument_For_Basic_Emotions
[12] EKMAN P. Basic emotions[M]//Handbook of Cognition and Emotion. Chichester: John Wiley & Sons, Inc., 2006: 45-60.
[13] PARROT W G. Emotions in social psychology[M]. New York:Psychology Press, 2000.
[14] FRIDJA N. The laws of emotions[J]. American Psychologist, 1998, 43(5):349-358. https://www.researchgate.net/.../297479558_The_laws_of_emotions
[15] PLUTCHIK R. The nature of emotions[J]. American Scientist, 2001, 89(4):344-350. doi: 10.1511/2001.4.344
[16] RUSSELL J A. A circumplex model of affect[J]. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 1980, 36(6):1161-1178. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/235361517_A_Circumplex_Model_of_Affect
[17] SCHLOSBERG H. Three dimensions of emotion[J]. Psychological Review, 1954, 61(2):81-88. doi: 10.1037/h0054570
[18] LOVHEIM H. A new three-dimensional model for emotions and monoamine neurotransmitters[J]. Medical Hypotheses, 2012, 78(2):341-348. doi: 10.1016/j.mehy.2011.11.016
[19] TALARICO J M. A comparison of dimensional models of emotion:evidence from emotions, prototypical events, autobiographical memories, and words[J]. Memory, 2009, 17(8):802-808. doi: 10.1080/09658210903130764
[20] FRANTZIDIS C A, BRATSAS C, PAPADELIS C L, et al. Toward emotion aware computing:an integrated approach using multichannel neurophysiological recordings and affective visual stimuli[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Technology in Biomedicine, 2010, 14(3):589-597. doi: 10.1109/TITB.2010.2041553
[21] TAKAHASHI K, TSUKAGUCHI A. Remarks on emotion recognition from multi-modal bio potential signals[C]//Systems, Man and Cybemetics. Washington, D C: IEEE Computer Society, 2004, 3(2): 1138-1143.
[22] WANG X W, NIE D, LU B L. EEG-based emotion recognition using frequency domain features and support vector machines[C]//Proceedings of Neural Information Processing, International Conference, ICONIP 2011, Shanghai, China, November 13-17, 2011. Berlin: Springer, 2011: 734-743.
[23] LIU Y, SOURINA O. Real-time fractal-based valence level recognition from EEG[M]//Transactions on Computational Science XVⅢ. Berlin: Springer, 2013: 101-120.
[24] MURUGAPPAN M, RAMACHANDRAN N, SAZALI Y. Classification of human emotion from EEG using discrete wavelet transform[J]. Journal of Biomedical Science & Engineering, 2010, 3(4):390-396. http://www.academia.edu/358745/Classification_of_Human_Emotion_From_EEG_Using_Discrete_Wavelet_Transform
[25] HJORTH B. EEG analysis based on time domain properties[J]. Electroencephalography & Clinical Neurophysiology, 1970, 29(3):306-310. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/0013469470901434
[26] KROUPI E, YAZDANI A, EBRAHIMI T. EEG correlates of different emotional states elicited during watching music videos[C]//Affective Computing and Intelligent Interaction. Memphis: Springer International Publishing AG, 2011: 457-466.
[27] ANSARI-ASL K, CHANEL G, PUN T. A channel selection method for EEG classification in emotion assessment based on synchronization likelihood[C]//Proceedings of Signal Processing Conference, 2007, European. New York: IEEE, 2007: 1241-1245.
[28] KHOSROWABADI R, RAHMAN A W B A. Classification of EEG correlates on emotion using features from Gaussian mixtures of EEG spectrogram[C]//Proceedings of International Conference on Information and Communication Technology for the Muslim World. New York: IEEE, 2010: E102-E107.
[29] SORUINA O, LIU Y. A fractal-based algorithm of emotion recognition from EEG using arousal-valence model[C]//Bio-signals 2011-Proceedings of the International Conference on Bio-Inspired Systems and Signal Processing, Rome, Italy, 26-29 January. Setubal: Science and Technology Publications, 2011: 209-214.
[30] HADJIDIMITRIOU S K, HADJILEONTIADIS L J. Toward an EEG-based recognition of music liking using time-frequency analysis[J]. IEEE Transactions on Bio-medical Engineering, 2012, 59(12):3498-3510. doi: 10.1109/TBME.2012.2217495
[31] 袁玲, 杨帮华, 马世伟.基于HHT和SVM的运动想象脑电识别[J].仪器仪表学报, 2010, 31(3):649-654. http://www.wenkuxiazai.com/doc/e7e2ea0ff12d2af90242e61b-4.html YUAN L, YANG B H, MA S W. Discrimination of movement imagery EEG based on HHT and SVM[J]. Chinese Journal of Scientific Instrument, 2010, 31(3):649-654. http://www.wenkuxiazai.com/doc/e7e2ea0ff12d2af90242e61b-4.html
[32] 陆苗, 邹俊忠, 张见, 等.基于IMF能量熵的脑电情感特征提取研究[J].生物医学工程研究, 2016, 35(2):71-74. http://www.cqvip.com/QK/91690X/200928/31921955.html LU M, ZOU J Z, ZHANG J, et al. Emotion electroencephalograph (EEG) recognition based on IMF energy entropy[J]. Journal of Biomedical Engineering Research, 2016, 35(2):71-74. http://www.cqvip.com/QK/91690X/200928/31921955.html
-
期刊类型引用(11)
1. 梁明晶,王璐,温昕,曹锐. 多特征融合的脑电情绪分类. 计算机工程与应用. 2023(05): 155-159 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 王晨,胡景钊,刘科,王洁琼,郑佳宾,吴东亚,冯筠. 基于脑电通道增强的情绪识别方法. 西北大学学报(自然科学版). 2022(04): 560-570 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 李春雨,何峰,綦宏志,郭晓艺,陈龙,明东. 基于共空间模式和支持向量机算法的食物偏好脑电分类研究. 中国生物医学工程学报. 2022(03): 266-272 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 薛峰,李希建,徐恩宇. 基于GA-SVM耦合模型的煤与瓦斯突出危险性预测. 矿业工程研究. 2022(03): 39-44 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 董寅冬,任福继,李春彬. 基于线性核主成分分析和XGBoost的脑电情感识别. 光电工程. 2021(02): 15-23 .  百度学术
百度学术
6. 孙梦青. 基于时频域信息提取的数字音频乐音识别仿真. 计算机仿真. 2021(07): 415-418+428 .  百度学术
百度学术
7. 王小亮,张秉华,杜玮,绳金房. 近红外光谱结合PSO-SVM算法快速定量分析鲨肝醇片. 中国药师. 2021(08): 571-574 .  百度学术
百度学术
8. 赵一凡,卞良,张飞飞. 基于布谷鸟算法优化支持向量机应用于胸痛三联征的分类诊断研究. 生物医学工程研究. 2019(01): 54-58 .  百度学术
百度学术
9. 孙颖,胡艳香,张雪英,段淑斐. 面向情感语音识别的情感维度PAD预测. 浙江大学学报(工学版). 2019(10): 2041-2048 .  百度学术
百度学术
10. 刘家卓,谢云,陈学强,邬洋. 基于HHT的视觉疲劳脑电特征提取. 中国医学物理学杂志. 2018(12): 1473-1478 .  百度学术
百度学术
11. 于国龙,崔忠伟,熊伟程,左羽. EEG注意力监测技术在教学中的应用研究. 贵州师范学院学报. 2018(09): 7-10 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(36)



 下载:
下载: