Analysis of Fuel Consumption Distribution Characteristics and Influencing Factors of Beijing Urban Expressway Based on Taxi Operation Data
-
摘要:
为了分析城市道路车辆油耗分布特征及影响因素,以辅助交通节能减排控制策略的制定和实施,将北京市城市快速路出租车实际运行数据按道路、交通和工况条件进行划分,以累积油耗百分比、累积运行时间百分比、相对瞬时油耗及百公里油耗为指标,利用对比分析和方差分析方法,细致研究各条件影响下出租车油耗特征.分析结果表明:道路纵坡对车辆油耗具有显著影响,上坡相对瞬时油耗和百公里油耗较高,下坡较低;平面线形对油耗无显著影响.路段油耗与车辆运行时间成正比,因此,缓解道路拥堵、减少行程时间将带来较大节能效果.高速交通条件下油耗贡献率近50%,相对瞬时油耗较高,然而其百公里油耗最低,因此,对于固定距离的出行而言,保持高速较为节能.加速工况下燃油消耗占总油耗的53%,且其相对瞬时油耗和百公里油耗也较高;匀速工况居中,保持匀速是驾驶节能的较好选择.三因素对油耗影响程度大小为:交通条件>运行工况>道路条件,表明驾驶出行时,为减少行程油耗应尽量提前规划路线,绕避拥堵路段;同时,也表明缓解道路拥堵将能有效减少道路交通能耗排放.
Abstract:Taxi operation data of urban expressway under different combinations of three factors including road type, traffic condition and driving mode was divided and then extracted. Taking cumulative fuel consumption percentage (CFCP), cumulative operation time percentage (COTP), relative instantaneous fuel consumption (RIFC) and fuel consumption per hundred kilometer (FCPHK) as indicators, distribution characteristics and influencing factors of fuel consumption were analyzed. Results show that road longitudinal slope has significant impact on vehicle fuel consumption. RIFC and FCPHK are higher on uphill while lower on downhill. Horizontal alignment has no significant effect on fuel consumption. There is a positive correlation between operation time and fuel consumption, which indicates that the fuel consumption is reduced by mitigating traffic congestion and reducing travel time. In high-speed traffic condition, FCPHK is higher while RIFC is lower. At a fixed distance travel, it is more energy-efficient to maintain a higher speed. CFCP nearly occupies high percent (53%) of total fuel consumption and its FCPHK and RIFC are higher than that of other driving modes. The rank of three factors of fuel consumption influencing degrees is traffic condition > driving mode > road type, which suggests that in order to reduce the fuel consumption, it's better to plan routes in advance and avoid congested road. Meanwhile, it also reveals that the mitigation of traffic jam effectively reduces the energy consumption.
-
Keywords:
- urban traffic /
- expressway /
- taxi /
- fuel consumption characteristics /
- energy-saving countermeasures
-
交通领域节能减排形势日益严峻,因为机动车是城市交通参与主体,所以针对其道路油耗分布特征及影响因素开展分析研究对交通节能减排控制策略的制定和实施具有重要意义.
除车辆本身性能外,道路条件、交通条件和驾驶技能是影响车辆能耗的重要因素[1-5].早在2005年,道路条件(上坡、下坡等)就作为能耗排放影响参数被引入美国发布的MOVES模型中[6],随着道路条件的变化,车辆运行阻力产生差异,导致能耗排放不同,而交通条件(即交通流的拥堵、稳定或顺畅)的差异则影响车辆整体运行状态,进而影响车辆油耗.此外,同等道路、交通条件下,不同的驾驶操作将直接影响车辆运行工况状态(加速、减速、匀速和怠速),导致不同的燃油消耗[7-8],研究结果显示驾驶水平对车辆油耗影响范围可达30%[9].
城市快速路作为典型的连续流设施,相比普通道路,车辆运行受交通控制设施影响较小,车辆油耗分布特征相对清晰,针对其开展多因素影响下的油耗分布特征研究,能为其他城市道路的油耗相关分析提供支持.另外,出租车作为城市交通的重要组成部分,具有运行时间长、范围广、里程远、车型车龄一致、驾驶员固定等特点,油耗排放特征具有一定的代表性,数据覆盖面广,能为研究的开展提供坚实的数据基础.因此,以北京市出租车实际运行数据为基础,综合考虑车辆运行的道路条件、交通条件及运行工况三方面的影响因素,分析城市快速出租车油耗分布特征及影响趋势,可为城市区域节能减排策略的制定和实施提供支持.
1. 数据提取及划分
1.1 原始数据采集与预处理
本文数据来源于北京市出租车控制器局域网络(controller area network,CAN)总线数据采集终端. CAN总线数据采集终端由北斗/GPS双模定位模块和车载诊断系统(on-board diagnositc,OBD)终端模块组成,可实时获取车辆运行数据并通过3G网络上传至监控平台.终端可采集的数据包括:采集时间、车牌号码、仪表盘车速(整数,km/h)、瞬时油耗(L/h)、GPS经纬度、累计行程、空调状态、发动机转速、发动机扭矩等,采集频率1 Hz.共采集1个工作日307辆1.6 L排量、2年车龄、手动档的现代伊兰特出租车运行数据,数据总量约114万条,总运行时间约3 167 h,每辆出租车每天平均运行时间约10.3 h.
根据车辆实际运行环境及本身性能限制进行数据预处理:1)北京市城市快速路设计限速80 km/h,且出租车行业管理严格,较少出现超速现象.据此剔除速度大于100 km/h的数据样本. 2)计算出租车的加速度,考虑车辆物理性能极限,剔除加速度绝对值大于20 km/(h·s)的数据样本.
1.2 快速路数据匹配与提取
依据道路平、纵线形特征,将北京市二、三、四环快速路划分为基本路段、桥区(上坡、下坡)和弯道3种道路条件,各道路条件定义如下.
1) 基本路段:快速路主线上两座立交桥坡底之间的平面直线路段.
2) 桥区:快速路立交桥主线始于坡底、止于坡顶的直线路段.
3) 弯道:快速路主线转弯半径为500~2 000 m的弯道区域.
利用Google Earth软件获取各道路条件不同路段中线起始点GPS坐标(其中,弯道额外获取线形四分位点GPS坐标作为数据提取校验点),共获得99条基本路段、156条桥区、14条弯道路段GPS坐标.利用MatLab软件将出租车运行数据与各路段坐标匹配,提取连续且运行时间大于5 s、完整驶过路段的运行数据.共获得3 703组基本路段、3 506组上坡、3 411组下坡、497组弯道路段出租车运行数据.
1.3 交通条件划分
一般而言,驾驶员趋向选择允许的最高速度行驶,因此,车辆运行速度在一定程度上反映运行环境.依据车辆速度将交通条件划分为低速区间、中速区间及高速区间3类.以出租车瞬时速度及油耗为参数,利用K-means聚类方法确定不同道路条件下交通条件划分阈值,如表 1所示.
表 1 不同道路条件下交通条件速度区间及瞬时油耗Table 1. Speed range and instantaneous fuel consumption of different traffic conditions under different road type道路条件 低速区间 中速区间 高速区间 速度区间/
(km·h-1)瞬时油耗/
(L·h-1)速度区间/
(km·h-1)瞬时油耗/
(L·h-1)速度区间/
(km·h-1)瞬时油耗/
(L·h-1)基本路段 [0, 26] 1.80 (26,50] 2.64 (50, 100] 3.13 上坡 [0, 23] 1.86 (23, 47] 2.87 (47, 100] 3.38 下坡 [0, 28] 1.67 (28, 51] 2.66 (51, 100] 2.35 弯道 [0, 26] 1.68 (26, 50] 2.54 (50, 100] 3.02 聚类结果表明:各道路条件下,划分交通条件的速度阈值相似,低中速划分阈值为23~28 km/h,中高速划分阈值为47~51 km/h.此外,车辆瞬时油耗随车速的增加呈现上升趋势.
1.4 运行工况划分
车辆行驶过程可视为不同运行工况(加速、减速、匀速和怠速)的有序组合.依据车辆运行速度和加速度参数,识别出租车运行工况,各工况定义如表 2所示.
表 2 工况定义Table 2. Definition of driving modes工况类型 工况定义 怠速 完全停止,速度=0 km/h,加速度=0 km/(h·s) 匀速 匀速段内速度振幅<1 km/h 加速 起步 起始速度<3 km/h,整体趋势为加速,加速段内允许<2 s的匀速段 加速 整体趋势为加速,加速段内允许<2 s的匀速段 减速 整体趋势为减速,减速段内允许<2 s的匀速段 由于离合操控,车辆怠速起步时涉及较高比例的发动机空转,可能导致与其他加速过程不同的油耗特征.因此,若加速工况起始速度小于3 km/h,即从静止起步或在较低速度加速时,则将其定义为起步工况.依据表 1提取不同道路条件、交通条件下,出租车运行工况数据段.
为获取城市快速路油耗特征,本文选取累积油耗百分比(cumulative fuel consumption percentage,CFCP)、累积运行时间百分比(cumulative operation time percentage,COTP)、相对瞬时油耗(relative instantaneous fuel consumption,RIFC)(累积油耗百分比/累计时间百分比)及百公里油耗(fuel consumption per hundred kilometer,FCPHK)4个指标进行分析.累积油耗百分比及累积运行时间百分比主要用于分析快速路出租车油耗分布特征;相对瞬时油耗用于表征以时间为度量的燃油效率;百公里油耗用于表征以距离为度量的燃油效率.
2. 城市快速路出租车油耗分布
2.1 城市快速路出租车运行概况
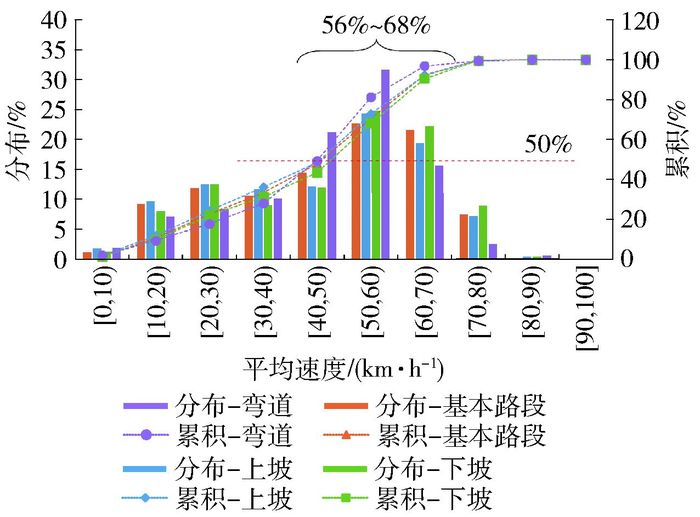
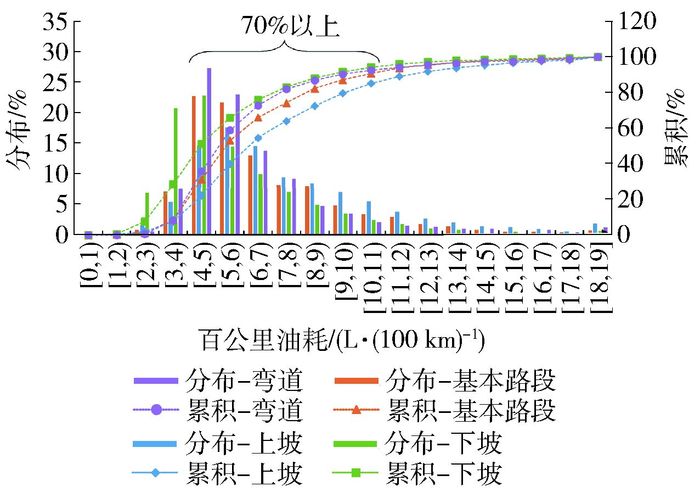
城市快速路各道路条件下车辆平均运行速度和百公里油耗分布如图 1、2所示.
图 1表明,不同道路条件下平均运行速度分布较为相似,出租车多以40~70 km/h的速度运行(56%~68%),半数以上的路段平均运行速度高于50 km/h. 图 2表明,快速路不同道路条件下车辆油耗均集中分布在4~11 L/(100 km)内(约占比70%).上坡时百公里油耗整体较高,下坡时偏低,基本路段和弯道时居中,表明道路坡度对车辆百公里油耗具有一定影响.
2.2 城市快速路出租车油耗分布特征
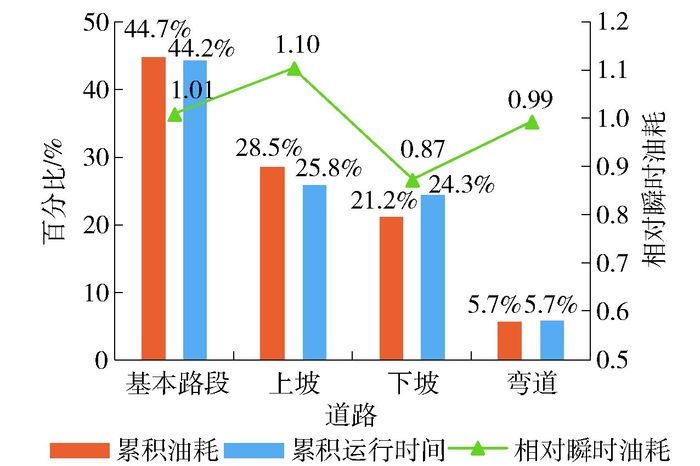
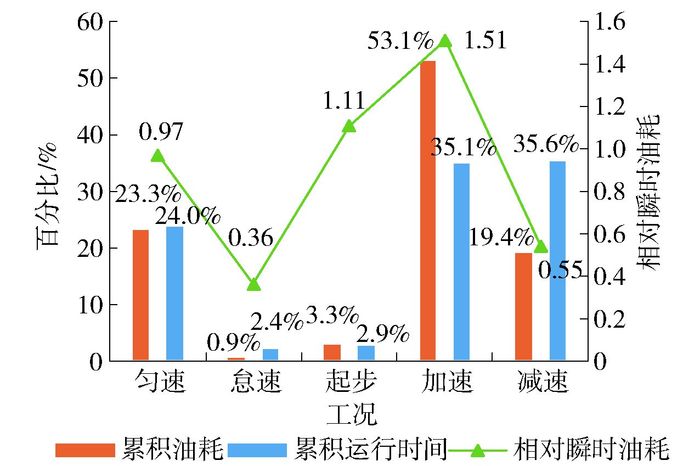
不同道路条件下累积油耗、累积运行时间百分比和相对瞬时油耗如图 3所示.结果表明:各道路条件下累积油耗与累积运行时间呈正相关关系,因此,通过解决城市道路拥堵、减少道路运行时间,能够有效减少交通能耗.弯道累积油耗与运行时间占比较少,可能是较少的弯道路段选取引起的.在基本路段和弯道条件下,相对瞬时油耗接近1;上坡相对瞬时油耗较高,下坡较低,表明道路纵坡对车辆油耗具有影响,而平面弯道对车辆油耗影响较小.
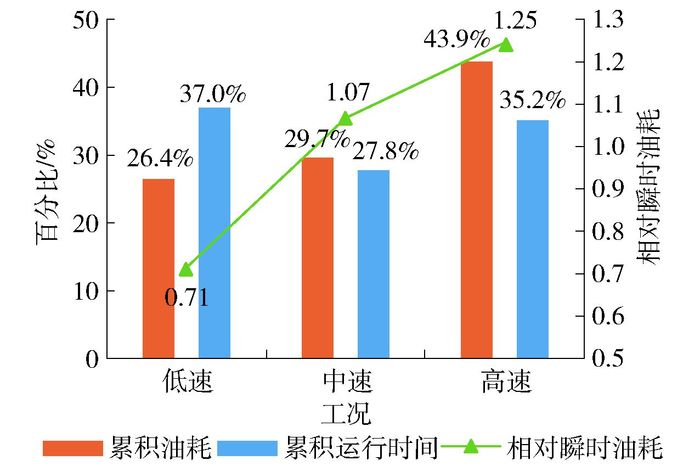
在不同交通条件下,累积油耗、累积运行时间百分比和相对瞬时油耗如图 4所示.高速条件下燃油消耗占比近50%.与表 1类似,随运行速度增加,相对瞬时油耗升高,表明从时间度量来看,在同等运行时间下,车辆保持高速运行时将消耗更多燃油.
不同运行工况下累积油耗、累积运行时间百分比和相对瞬时油耗如图 5所示.加速工况油耗占比达53%,是快速路油耗的主要贡献者.加、减速工况运行时间占比合计约72.5%,而匀速占比仅为24%,表明快速路车辆运行时加减速行为频发,较少保持匀速行驶状态.就相对瞬时油耗而言,加速工况较高,减速工况较低,匀速工况居中.因此,长时间处于加速可能消耗大量燃油;同时,通过观察前车状态,采取缓减速操作延长减速时间可减少燃油消耗.将车辆运行状态视为多种工况时间维度的有序组合,则通过短时加速、长时减速驾驶策略可有效减少车辆油耗,为生态驾驶操作方法的研究提供了新的思路.此外,匀速工况相对瞬时油耗居中且操作负荷较低,因此,尽量保持车辆匀速行驶是获得较高燃油经济性的最便捷手段.
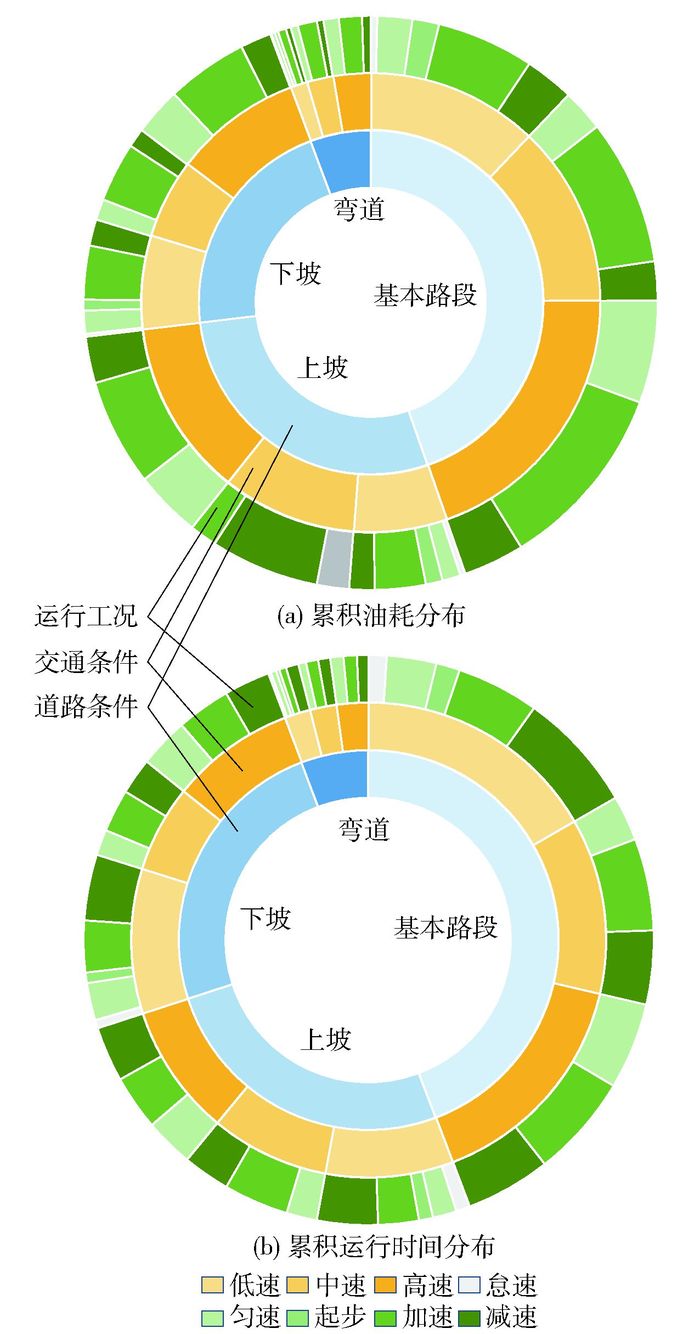
按道路条件—交通条件—运行工况层级,绘制各条件下累积油耗、累积运行时间分布,如图 6所示. 图 6表明不同道路条件下,不同交通条件累积油耗与累积运行时间占比与图 4类似;同时,不同道路、交通条件下,运行工况累积油耗及累积运行时间分布也与图 5类似,表明在局部环境、单因素影响下车辆累积油耗和运行时间分布存在一定的相似性.
2.3 城市快速路车辆油耗影响因素
基于城市快速路出租车运行数据,研究道路条件、交通条件及运行工况3个因素对车辆百公里油耗的影响.其中,怠速工况无百公里油耗,其能耗特征主要与发动机特性相关,本文暂不考虑.本文采用方差分析寻求3种因素(道路条件(4)×交通条件(3)×工况(4))影响下、共计102 932组出租车运行数据百公里油耗,结果显示道路条件、交通条件和运行工况均对车辆百公里油耗有显著性影响(F(3, 102 932)=85.89, F(2, 102 932)=2 474.87, F(3, 102 932)=1 752.80, p<0.05).
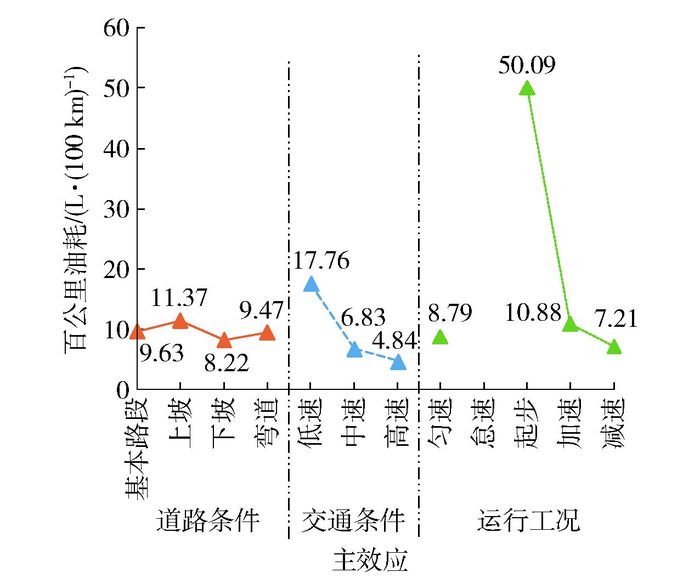
各因素主效应影响下车辆百公里油耗如图 7所示.就道路条件来看,基本路段和弯道路段百公里油耗差异不具有统计学意义(p=0.483),但与上坡、下坡路段百公里油耗之间的差异均具有统计学意义,表明城市快速路平面弯道对出租车百公里油耗无影响,而纵向坡道对出租车百公里油耗影响较大.就交通条件来看,不同速度区间百公里油耗相互之间的差异具有统计学意义;随着速度提高,百公里油耗显著降低.就运行工况来看,各工况百公里油耗相互之间的差异具有统计学意义,其中起步工况百公里油耗最高,因此,驾驶员应通过观察前方交通流状况、合理加减速、避免车辆频繁起停以提高燃油经济性;加速工况次之,减速工况百公里油耗最低.
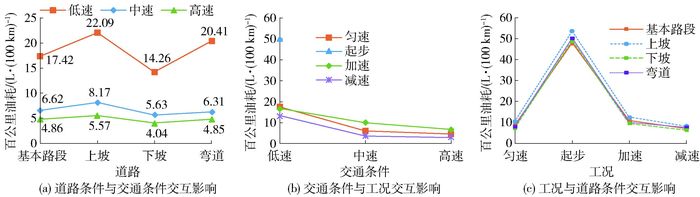
在主效应因素交互影响下出租车百公里油耗如图 8所示.交互影响分析表明,道路条件与交通条件对出租车百公里油耗具有交互影响(F(6, 102 932)=44.14, p<0.05),如图 8(a)所示.各道路条件下出租车油耗均呈随速度升高而降低的趋势;差异主要来自不同道路条件下百公里油耗随速度区间的变化幅度,与中、高速交通条件相比,低速条件下道路纵坡对油耗影响更为明显.交通条件和工况对出租车油耗具有交互影响(F(4, 102 932)=38.14, p<0.05),油耗差异主要来自低速条件下的匀速和加速工况,如图 8(b)所示.在低速条件下,加速工况与匀速工况百公里油耗相似.道路条件与工况对出租车油耗具有交互影响(F(9, 102 932) = 7.37, p<0.05),如图 8(c)所示.在各道路条件下,不同工况百公里油耗趋势与图 7相似,起步最高,减速最低;差异主要来自基本路段条件下不同工况的百公里油耗分布.
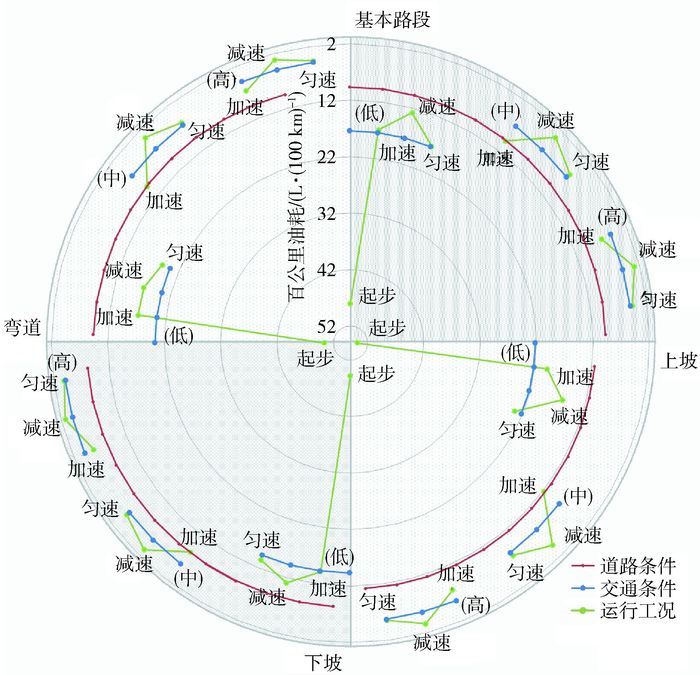
不同道路条件、交通条件及运行工况下车辆百公里油耗雷达图如图 9所示.
起步工况下油耗最高;在同等交通条件下,加速、减速和匀速工况的百公里油耗分布与图 7类似,而不同交通条件之间百公里油耗差异较大,不同道路条件对百公里油耗影响较小.因此,车辆百公里油耗影响因素重要性排序为:交通条件>运行工况>道路条件,表明在驾车出行时,应重点关注路况,尽量绕避拥堵路段,以减少车辆燃油消耗.同时,尽可能减少频繁的加减速操作.
3. 结论
1) 本文采集北京市出租车城市快速路运行数据并依据道路条件、交通条件及运行工况划分,在此基础上分析各因素影响下城市快速路车辆油耗分布特征及影响因素.从道路条件来看,道路纵坡对油耗具有显著影响,而平面弯道对油耗影响较小.从交通条件来看,虽然高速条件下油耗贡献较大,且相对瞬时油耗较高,但从距离度量而言,车辆处于高速运行时百公里油耗较低,因此,出行时应尽量绕避拥堵路段.从运行工况来看,加速工况相对于其他工况燃油消耗较高,对车辆总油耗的贡献也较大;特别在起步时,油耗显著升高,因此,应尽量避免频繁起停车辆.各局部条件下,单一因素影响下的车辆累积油耗分布及百公里油耗具有一定的相似性.影响车辆油耗的3种因素重要性排序为交通条件>运行工况>道路条件,表明缓解道路拥堵是减少道路车辆运行能耗的重要手段;而在驾驶出行时,应首先重点关注路况,尽量绕避拥堵路段,其次减少频繁加减速、频繁起停车辆,以减少车辆燃油消耗.
2) 考虑出租车长时、长距的运行特征,本文基于出租车运行数据开展研究,所获得的北京市城市快速路油耗分布特征具有一定的代表性,对城市整体交通能耗把控具有一定的参考价值;同时,针对道路油耗影响因素的研究也可为节能减排策略的制定及应用实施提供数据支持.
-
表 1 不同道路条件下交通条件速度区间及瞬时油耗
Table 1 Speed range and instantaneous fuel consumption of different traffic conditions under different road type
道路条件 低速区间 中速区间 高速区间 速度区间/
(km·h-1)瞬时油耗/
(L·h-1)速度区间/
(km·h-1)瞬时油耗/
(L·h-1)速度区间/
(km·h-1)瞬时油耗/
(L·h-1)基本路段 [0, 26] 1.80 (26,50] 2.64 (50, 100] 3.13 上坡 [0, 23] 1.86 (23, 47] 2.87 (47, 100] 3.38 下坡 [0, 28] 1.67 (28, 51] 2.66 (51, 100] 2.35 弯道 [0, 26] 1.68 (26, 50] 2.54 (50, 100] 3.02 表 2 工况定义
Table 2 Definition of driving modes
工况类型 工况定义 怠速 完全停止,速度=0 km/h,加速度=0 km/(h·s) 匀速 匀速段内速度振幅<1 km/h 加速 起步 起始速度<3 km/h,整体趋势为加速,加速段内允许<2 s的匀速段 加速 整体趋势为加速,加速段内允许<2 s的匀速段 减速 整体趋势为减速,减速段内允许<2 s的匀速段 -
[1] 周荣贵, 邢惠臣.公路纵坡与汽车运行速度油耗之间的关系[J].公路交通科技, 1993, 10(1):15-24 http://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?filename=gljk199301003&dbname=CJFD&dbcode=CJFQ ZHOU R G, XING H C. On the relation betweent vehicle speed fuel consumption and longitudinal gradient[J]. Journal of Highway and Transportation Research and Development, 1993, 10(1):15-24. (in Chinese) http://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?filename=gljk199301003&dbname=CJFD&dbcode=CJFQ
[2] 白崤. 汽车驾驶节能技术研究[D]. 西安: 长安大学, 2011 http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-11941-1011185060.htm BAI X. Research on driving energy-saving technology[D]. Xi'an:Chang'an University, 2011. (in Chinese) http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-11941-1011185060.htm
[3] 王莹, 于谦, 李铁柱, 等.公交车辆节能减排驾驶技术研究[J].交通运输工程与信息学报, 2013, 11(2):114-120 http://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?filename=jtgc201302021&dbname=CJFD&dbcode=CJFQ WANG Y, YU Q, LI T Z, et al. Study on energy-saving driving skills of city bus[J]. Journal of Transportation Engineering and Information, 2013, 11(2):114-120. (in Chinese) http://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?filename=jtgc201302021&dbname=CJFD&dbcode=CJFQ
[4] 赵晓华, 姚莹, 伍毅平, 等.基于主成分分析与BP神经元网络的驾驶能耗组合预测模型研究[J].交通运输系统工程与信息, 2016, 16(5):185-191 http://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?filename=ysxt201605028&dbname=CJFD&dbcode=CJFQ ZHAO X H, YAO Y, WU Y P, et al. Prediction model of driving energy consumption based on PCA and BP network[J]. Journal of Transportation Systems Engineering and Information Technology, 2016, 16(5):185-191. (in Chinese) http://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?filename=ysxt201605028&dbname=CJFD&dbcode=CJFQ
[5] 彭美春, 李嘉如, 胡红斐.营运货车道路运行油耗及碳排放因子研究[J].汽车技术, 2015(4):37-40 http://edu.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/Detail/qcjs201504008 PENG M C, LI J R, HU H F. Research on fuel consumption & carbon emission factor of road freight trucks[J]. Automobile Technology, 2015(4):37-40. (in Chinese) http://edu.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/Detail/qcjs201504008
[6] KWON J, ROUSSEAU A, SHARER P. Analyzing the uncertainty in the fuel economy prediction for the EPA MOVES binning methodology[J]. SAE, 2007, 2007-01-0280.
[7] 杨延相, 蔡晓林, 杜青, 等.天津市道路汽车行驶工况的研究[J].汽车工程, 2002, 24(3):200-204 http://www.cqvip.com/QK/91525X/200203/6370888.html YANG Y X, CAI X L, DU Q, et al. Investigation into vehicle driving mode in Tianjing[J]. Automobile Engineering, 2002, 24(3):200-204. (in Chinese) http://www.cqvip.com/QK/91525X/200203/6370888.html
[8] 曾诚, 蔡凤田, 刘莉, 等.不同驾驶操作方法下的汽车运行燃料消耗量分析[J].交通节能与环保, 2010(2):23-26 http://www.wenkuxiazai.com/doc/826924ff700abb68a982fb6a.html ZENG C, CAI F T, LIU L, et al. Analysis of fuel consumption in automobile operation under different driving methods[J]. Energy Conservation & Environmental Protection in Transportation, 2010(2):23-26. (in Chinese) http://www.wenkuxiazai.com/doc/826924ff700abb68a982fb6a.html
[9] 彭玲玲. 城市公交车节能减排综合应用研究[D]. 武汉: 武汉理工大学, 2009 http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-10497-2009106388.htm PENG L L. Comprehensive application research on reducing fuel consumption and exhaust emission of city buses[D]. Wuhan:Wuhan University of Technology, 2009. (in Chinese) http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-10497-2009106388.htm
-
期刊类型引用(3)
1. 周涛,李毅军,孙琴梅,任瀚堃,刘怡,张振豪. 大数据驱动下的山地城市道路条件对车辆碳排放影响研究. 交通运输系统工程与信息. 2023(05): 172-183 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 邵春福,甄理,刘兵,董春娇,骆冠良. 基于竞争路径选择的HOT车道费率优化模型. 北京交通大学学报. 2021(01): 98-104 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 吴华意,黄蕊,游兰,向隆刚. 出租车轨迹数据挖掘进展. 测绘学报. 2019(11): 1341-1356 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(9)



 下载:
下载: