Diversity of Bacteria and Functional Bacteria in MBR Shortcut Nitrification System Treating Late Landfill Leachate
-
摘要:
为了处理晚期垃圾渗滤液,利用膜生物反应器(membrane bioreactor,MBR)实现了稳定亚硝化.分别构建总细菌通用克隆文库和针对亚硝化功能菌氨氧化菌(ammonia oxidizing bacteria,AOB)的功能基因——amoA基因的克隆文库,来研究稳定期亚硝化系统中微生物多样性.从16S rDNA克隆文库中随机挑选82个阳性克隆子进行序列测定,将测序结果与Genbank中已有模式菌株的序列进行比对后发现,亚硝化系统中主要有4个优势菌群,分别是Proteobacteria类群(64.65%)、未培养菌(uncultured bacterium)类群(18.3%)、Bacteroidetes类群(9.76%)、Firmicutes类群(7.32%).构建针对AOB的amoA功能基因的克隆文库,从文库中挑选73个阳性克隆子进行序列测定,经序列比对后发现在系统中仅检测到了亚硝化单胞菌属(Nitrosomonas)和未培养菌,分别占41.1%和58.9%.这表明系统中起到亚硝化作用的微生物种群主要是亚硝化单胞菌属(Nitrosomonas).此外,未培养细菌的大量存在表明,系统中还存在着丰富的微生物资源等待进一步的开发利用.
-
关键词:
- 晚期垃圾渗滤液 /
- 膜生物反应器(MBR) /
- 亚硝化 /
- 克隆文库 /
- 微生物群落结构
Abstract:In order to find the better method to deal with late landfill leachate, the stable partial nitrification system was operated in the MBR (membrane bioreactor). The microbial community structure of the stable partial nitrification phase was investigated by the total bacterial clone library and the cloning library of ammonia oxidizing bacteria (AOB) functional gene amoA. 82 positive clones were selected randomly from 16S rDNA clone library and their sequence was determined. The results show that there are four dominant bacterium groups in the stable partial nitrification phase:Proteobacteria (64.65%), uncultured bacterium (18.3%), Bacteroidetes (9.76%), and Firmicutes (7.32%). Building on the cloning library of AOB's functional gene amoA, 73 positive clones were selected from the library and their sequence was also determined. Compared with basic local alignment search tool(BLAST), the results show that only the Nitrosomonas and Uncultured bacterium are detected in the system, and their proportion is 41.1% and 58.9%, respectively. This phenomenon show that the number of Nitrosomonas is maximum in this system. At the same time, the existence of many unknown bacterial species showed that there are a large number of microbial resources in the system and needing further development.
-
垃圾渗滤液具有高氨氮、成分复杂, 并且含有毒性有机物和重金属等[1-2]特点.依据填埋时间的长短, 垃圾渗滤液分为早期、中期和晚期.晚期垃圾渗滤液为典型的高氨氮、低碳氮比污水, 可生化性较差,其中含有的毒性有机物以及重金属等物质会对系统的微生物多样性造成影响[3-4].晚期垃圾渗滤液的这些水质特点,使得利用微生物反应器对其进行脱氮处理成为难点.
采用亚硝化与厌氧氨氧化(anaerobic ammonium oxidation,ANAMMOX)组合技术脱氮已经越来越多地被应用到高氨氮、低碳氮比污水的处理中.该组合工艺能够实现脱氮的关键是亚硝化的实现及稳定运行.氨氧化菌(ammonia oxidizing bacteria, AOB)是世代周期较长的自养菌[5], 其快速富集则是实现稳定亚硝化的关键.采用膜生物反应器(membrane bioreactor,MBR)工艺可快速实现亚硝化. Xue等[6]在限氧条件下启动MBR的亚硝化处理模拟废水, 并考察了亚硝化影响因素.然而目前, 针对晚期垃圾渗滤液的MBR亚硝化的研究较少[7], 对其稳定运行情况下微生物多样性分析的报道更为罕见.而微生物在亚硝化过程中起着至关重要的作用, 对系统中微生物多样性及群落结构的分析有助于深入了解亚硝化机理, 从而为亚硝化的稳定运行提供指导.
分子生物学技术的深入发展,克服了传统微生物技术培养周期长、工作量大、无法分离未培养微生物等局限,而分子生物学技术在水处理方向的应用,使对处理系统中微生物种类和遗传信息多样性的研究进入一个新的阶段. 16S rDNA克隆文库技术在无须对微生物进行纯种分离的情况下,可以通过提取样品中微生物DNA或直接在原位对微生物进行检测分析[8].克隆文库通过测定目标序列并与已知序列进行比对确定微生物的种属,并根据文库中克隆子出现频率确定样品中种群组成比例. Shen等[9]考察了MBR运行300 d的亚硝化性能及其微生物群落变化.本实验拟在MBR中逐步实现晚期垃圾渗滤液原液的亚硝化, 并结合克隆文库技术对稳定运行的MBR亚硝化系统中总细菌及功能菌AOB的群落结构进行分析, 以期为晚期垃圾渗滤液亚硝化系统中细菌菌群及功能菌的研究提供一定参考, 并指导运行.
1. 材料与方法
1.1 实验装置与样品采集
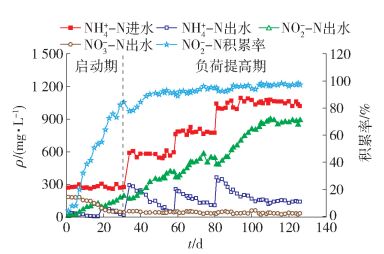
实验采用膜生物反应器, 反应器的有效容积为25 L.内置孔径为0.1 μm、面积为0.5 m2的聚偏氟乙烯中空纤维膜.实验进出水通过可编程逻辑控制系统进行控制, 产水方式采用恒通量过滤间歇抽吸方式, 膜通量为2.28 L/(m2·h), 抽吸周期为10 min(8 min抽吸, 2 min停止).膜组件下部设置曝气装置, 采用转子流量计控制曝气量为40~160 L/h.通过膜压力(transmembrane pressure,TMP)判断膜污染程度.反应器安装真空表(津制00000578型, 天津)测量膜内压力.温度控制在(30±1) ℃, 水力停留时间设置为22 h.实验中采用的垃圾渗滤液为北京某垃圾填埋厂的渗滤液, 填埋年限大于5 a, 为晚期渗滤液.具体水质如表 1所示. MBR反应器在105 d时已经实现晚期垃圾渗滤液原液的亚硝化并稳定运行, 此时,系统出水NO2--N质量浓度为866.14 mg/L, NO2--N积累率为98.22%;在105~126 d的平均出水NO2--N质量浓度为871.25 mg/L, 平均NO2--N积累率为97.18%.具体运行数据如图 1所示,取稳定运行时期(120 d时)的污泥进行克隆文库分析.
表 1 垃圾渗滤液水质情况Table 1. Quality of landfill leachate项目 ρ/(mg·L-1) pH NH4+-N NO2--N NO3--N COD 碱度 范围 900~1 500 0~2 0~8 2 000~4 000 6 000~10 000 7.5~8.5 1.2 试验方法
1.2.1 DNA提取
取适量泥样于1.5 mL Ep管中, 12 000 r/min离心5 min, 弃上清液.用分析天平称取0.2~0.3 g离心后泥样于一支新的Ep管中, 用于提取细菌DNA.采用Ezup柱式基因组DNA抽提试剂盒(上海生工)进行DNA提取. DNA提取完成以后, 用1.2%琼脂糖凝胶跑胶验证是否提取成功.剩余的DNA置于-20 ℃保存.
1.2.2 聚合酶链式反应(polymerase chain reaction, PCR)扩增
以提取的DNA作为模板, 分别进行通用克隆文库和AOB克隆文库的PCR扩增,PCR扩增中所采用的引物、扩增体系以及反应条件如表 2所示.
表 2 克隆文库中PCR扩增条件Table 2. Amplification conditions of PCR in clone library分析手段 引物名称 引物碱基序列(5′-3′) PCR反应体系(50 μL) PCR反应条件 全细菌克隆文库 27F/1492R 27F:AGAGTTTGA-TCCTGGCTCAG
1492R:TACGGYTAC-CTTGTTACGACTT10×PCRbuffer 5 μL, dNTP(2.5 mmol/L) 1 μL, 27F(20 μmol/L)和1492R(20 μmol/L)各1 μL, Taq DNA聚合酶0.5 μL, DNA 0.5 μL, 加超纯水至50 μL 首先95 ℃预变性1.5 min; 其次95 ℃变性0.5 min, 60 ℃退火0.5 min, 72 ℃延伸2 min, 5个循环; 之后95 ℃变性0.5 min, 55 ℃退火0.5 min, 72 ℃延伸2 min, 5个循环; 之后进行15个循环:95 ℃变性0.5 min, 50 ℃退火0.5 min, 72 ℃延伸2 min; 最后60 ℃延伸10 min AOB
克隆文库amoA-1F/
amoA-2RamoA-1F:GGGGTTTC-TACTGGTGGT
amoA-2R:CCCCTCKGS-AAAGCCTTCTTC10×PCRbuffer 5 μL, dNTP(2.5 mmol/L) 2 μL, amoA-1F (20 μmol/L)和amoA-2R(20 μmol/L)各1 μL, Taq DNA聚合酶0.5 μL, DNA 2 μL, 加超纯水至50 μL 94 ℃预变性5 min; 之后进行35个循环:94 ℃变性30 s,55 ℃退火1 min, 72 ℃延伸1 min; 72 ℃延伸10 min PCR反应在MyiQ Real-time PCR扩增仪(美国, Bio-Rad)上进行.扩增时做空白对照, 对照组除不加DNA模板外, 其他实验组分与实验组相同.反应结束后, 取5 μL PCR产物跑胶验证目的基因片段长度是否正确.
1.2.3 克隆、转化和16S rDNA克隆文库的构建
采用DNA胶回收试剂盒(上海生工)将PCR产物进行切胶纯化, 将纯化后产物与pMD18-T载体(Takara)连接, 连接体系(10 μL):PCR产物, 3 μL; pMD18-T Vector, 1 μL; SolutionI, 5 μL; 灭菌超纯水, 1 μL.将连接液混合均匀, 在16 ℃条件下反应4 h后将连接液全部转入Ecoli DH5α感受态细胞(Takara,Japan)中.将混合液涂布在含Amp/X-Gal/IPTG的LB固体培养基上, 37 ℃条件下培养16~24 h后进行阳性克隆子筛选.其中,白斑为具有氨苄青霉素抗性的阳性菌落, 蓝斑为不具氨苄青霉素抗性的阴性菌落.挑选其中的白斑菌落来进行克隆文库的构建, 并对挑选出的阳性克隆子进行菌落PCR以剔除假阳性及假阴性克隆子.最后对用Hha I(Takara, Japan)限制性内切酶对阳性克隆子进行酶切.反应条件为37 ℃, 4 h.酶切反应在PCR仪中进行.酶切后的产物用3%琼脂糖凝胶电泳检测, 并在凝胶成像仪中进行拍照观察, 根据成像结果中的酶切带型划操作分类单元(operational taxonomic units,OTU).每个OTU挑取2~3个代表克隆子送到北京中美泰和技术公司进行测序.
1.2.4 16S rDNA基因克隆文库统计学性分析
基因文库的库容值(C)可以用来表示微生物基因文库多样性的覆盖率.理论上, 当C为100%时表示该基因文库涵盖了样品中所有的微生物种类, 库容值越高说明库的覆盖率越高.库容值计算公式[10]为
$$C = 1 - {n_1}/N$$ 式中:N为基因文库的总克隆子数;n1为仅有一个克隆子的OTU数目.利用Shannon-Wiener指数(H)对基因文库的序列做多样性指数分析, 计算公式为
$$H = - \sum {{P_i}{\rm{ln}}{P_i}} $$ 式中Pi为每个物种样本数量占总样本数量的比例. Margalef物种丰富度指数的计算公式为
$${d_{{\rm{Ma}}}} = \frac{{S - 1}}{{{\rm{ln}}\;N}}$$ 式中:dMa表示Margalef物种丰富度指数; S表示物种丰富度; N表示基因文库的克隆数.均匀度计算公式为
$$\begin{array}{l} E = H/{H_{{\rm{max}}}}\\ {H_{{\rm{max}}}} = {\rm{ln}}\;S \end{array}$$ 式中S为物种丰富度, 表示样本中的物种数量, 等于单个文库中OTU个数.
1.2.5 系统发育树的构建
将测得的序列利用NCBI网站上的Blast在线程序与Genbank中模式菌株序列进行比对, 并下载同源性相对较高的序列.采用MEGA5.0软件中的邻接算法构建系统发育树, 分析污泥样品中的微生物种类和分类地位.利用Bootstraps来分析评估系统发育树的稳定性, 树的节点通过非参数支持率计算(进行1 000次重复运算).
2. 结果与分析
2.1 DNA提取和PCR扩增
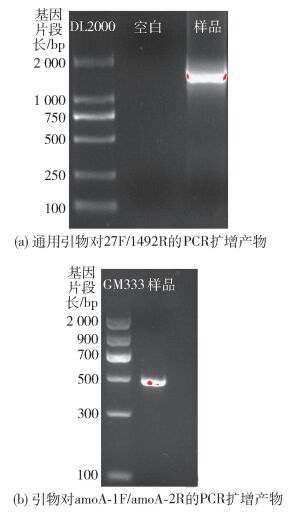
利用试剂盒提取细菌DNA以后, 经1.2%琼脂糖凝胶电泳检测, 在凝胶成像系统中拍照采集图像, 与Marker比对后可知DNA片段长度约为23 kb.采用通用引物对27F/1492R和AOB功能基因amoA的引物对amoA-1F/amoA-2R进行PCR扩增以后得到的目的基因片段长度分别约为1 500、500 bp, 如图 2所示.均满足试验要求.
2.2 16S rDNA通用克隆文库构建与细菌多样性分析
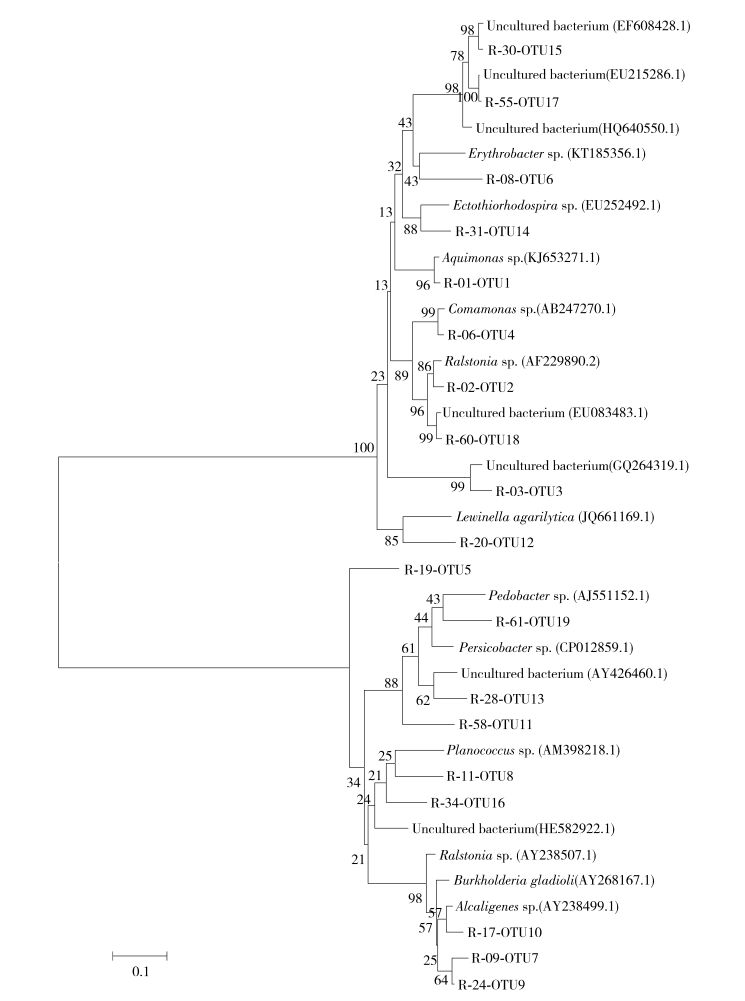
在构建MBR亚硝化系统细菌通用克隆文库时, 对随机挑取的82个阳性克隆子进行酶切分型, 得到19个酶切类型.每个酶切类型选取2~3个克隆子进行测序, 将得到的序列利用BLAST在线程序进行序列同源性比对, 将序列相同的克隆子划分为一个OTU,共得到19个OTU.对克隆文库进行统计学分析, 得到基因文库多样性覆盖率、Shannon-Wiener指数、Simpson指数、均匀度以及物种丰富度指数,如表 3所示.通用克隆文库分析结果如表 4所示.污泥样品通用克隆文库系统发育树如图 3所示.
表 3 克隆文库酶切类型的多样性Table 3. Diversity of restriction endonuclease types in 16S rDNA clone libraryOTU种类 库容大小/% Shannon-Wiener指标 Simpson指标 均匀度 丰富度 19 91.50 2.528 2 0.890 5 0.858 6 4.084 6 表 4 MBR亚硝化系统样品主要细菌16S rDNA克隆文库分析结果Table 4. Data of bacterial 16S rDNA clone library constructed with sample in MBROTU
编号每种OTU所
含克隆子个数每种OTU
百分比/%Genbank中最大相似度细菌
(NCBI登录号)相似
度/%所属细菌类群 OTU1 8 9.76 Aquimonas sp. BUT-1(KJ653271.1) 95 γ-Proteobacteria OTU2 1 1.22 Ralstonia sp. P-4CB2(AF229890.2) 97 β-Proteobacteria OTU3 1 1.22 未培养菌(GQ264319.1) 98 未培养菌 OTU4 3 3.66 Comamonas sp. IA-30(AB247270.1) 93 β-Proteobacteria OTU5 3 3.66 未培养菌(HQ640550.1) 99 未培养菌 OTU6 9 10.98 Erythrobacter sp. B809(KT185356.1) 82 α-Proteobacteria OTU7 1 1.22 Burkholderia gladioli strain 1993027208(AY268167.1) 92 β-Proteobacteria OTU8 1 1.22 未培养菌(HE582922.1) 99 未培养菌 OTU9 20 24.39 Ralstonia sp. 80 (AY238507.1) 98 β-Proteobacteria OTU10 5 6.10 Alcaligenes sp. 92(AY238499.1) 92 β-Proteobacteria OTU11 5 6.10 Persicobacter sp. JZB09(CP012859.1) 82 Bacteroidetes OTU12 2 2.44 Lewinella agarilytica strain r31(JQ661169.1) 82 Bacteroidetes OTU13 2 2.44 未培养菌(AY426460.1) 90 未培养菌 OTU14 6 7.32 Ectothiorhodospira sp. AM4(EU252492.1) 90 γ-Proteobacteria OTU15 6 7.32 未培养菌(EF608428.1) 99 未培养菌 OTU16 6 7.32 Planococcus sp. EP09(AM398218.1) 85 Firmicutes OTU17 1 1.22 未培养菌(EU215286.1) 99 未培养菌 OTU18 1 1.22 未培养菌(EU083483.1) 97 未培养菌 OTU19 1 1.22 Pedobacter sp. An13(AJ551152.1) 85 Bacteroidetes 由表 3可知克隆文库的库容值为91.50%, 这表明该克隆文库的库容值较大, 文库覆盖率较高, 具有较好的代表性. Shannon-Wiener指数为2.528 2,表明MBR亚硝化系统中存在比例较高的优势菌属.
序列比对的结果表明, MBR亚硝化系统稳定期细菌通用克隆文库中的19个OTU分别属于细菌域的4个主要类群.分别是变形菌类群(Proteobacteria,64.65%)、拟杆菌类群(Bacteroidetes,9.76%)、厚壁菌类群(Firmicutes,7.32%)和未培养菌(uncultured bacterium,18.3%),这些微生物类群已在多种污水处理系统中被发现为优势菌属[11-12]. Muyzer等[13]研究发现, 利用目前的分子生物学手段只能检测到某些优势菌群, 而优势菌群的存在导致了微生物结构的相对简单化.
变形菌类群(Proteobacteria)在微生物系统中占64.65%, 是系统中的绝对优势菌属, Snaidr等[14]研究发现,活性污泥池中的优势菌群主要为变形菌(Proteobacteria)类群.变形菌均为革兰氏阴性菌,是系统中COD的主要降解者,且包含多种代谢类型.大部分变形菌既能够在有氧条件下进行呼吸作用,又能在厌氧/缺氧条件下进行发酵,能够以有机物作为碳源,是典型的兼性异养菌.变形菌门根据核糖体RNA序列划分为5个纲, 分别用希腊字母α、β、γ、δ和ε命名.研究结果表明, 在反应系统实现稳定亚硝化时, β-Proteobacteria数量最多,占36.59%, γ-Proteobacteria次之, 占17.08%, α-Proteobacteria最少, 占10.98%.大部分的β-Proteobacteria可在厌氧或缺氧环境中存活,其中某些菌属还可以利用H2、氨氮、CH4和挥发性脂肪酸进行新陈代谢[15].系统中检测到的β-Proteobacteria的代表菌属包括丛毛单胞菌属(Comamonas)、产碱杆菌属(Alcaligenes)、罗尔斯通氏菌属(Ralstonia)以及伯克霍尔德氏菌(Burkholderia).其中, 丛毛单胞菌属(Comamonas)是常见的反硝化菌属, 该菌属已经被研究发现能够降解多种难降解的环境污染物.由于基因背景的差异, 不同丛毛单胞菌能够降解的污染物不同, 同时降解途径和降解方式也不一样,对此研究者做了大量研究. Boon等[16]、Khan等[17]研究发现丛毛单胞菌属(Comamonas)可以利用难降解的芳香族化合物进行新陈代谢.刘志培等[18]将苯胺作为Comamonas acidovorans AN3的唯一碳、氮源, 推测出该菌降解苯胺的代谢途径. Schleheck等[19]研究了菌株Comamonas testosteroni KF-1降解3, 4-磺苯基丁酸盐的代谢途径.产碱杆菌属(Alcaligenes)是污水处理系统中常见的异养硝化菌. Anderson等[20]研究鉴定产碱杆菌属(Alcaligenes)中一株粪产碱杆菌(Alcaligenes faecalis)为异养硝化细菌, 该菌能在低碳条件下发生硝化,也可以在有机环境中进行硝化.王成林等[21]从人工湿地中分离出一株异养硝化菌, 经16S rDNA鉴定后为产碱杆菌属(Alcaligenes).关于罗尔斯通氏菌属(Ralstonia)以及伯克霍尔德氏菌(Burkholderia gladioli)脱氮除磷的报道较少, 这些细菌的脱氮作用还有待作进一步研究.反应器中丛毛单胞菌属(Comamonas)以及产碱杆菌属(Alcaligenes)等菌属的存在, 使亚硝化系统中还可能存在一些其他脱氮途径,如同步硝化反硝化途径.
拟杆菌类群(Bacteroidetes)在系统中约占9.76%.拟杆菌是化能异养菌, 能够降解纤维素、淀粉、蛋白质、脂类等大分子有机物[22].另有研究指出, 拟杆菌广泛存在于厌氧条件的污水处理系统[23]. MBR亚硝化系统中随着污泥质量浓度的提高会造成菌胶团内部溶解氧过低, 在菌胶团会形成微厌氧环境, 这促进了拟杆菌作为优势菌的形成.
厚壁菌类群(Firmicutes)在微生物系统中占7.32%.其中经测序比对得到的代表菌属Planococcus sp.属于芽孢杆菌类群(Bacillus).芽孢杆菌(Bacillus)广泛分布于自然界中, 能够产生孢子, 在恶劣环境中能够休眠, 故有很强的生命力.芽孢杆菌(Bacillus)已经被报道能够降解多种污染物.曾地刚等[24]通过研究枯草芽孢杆菌(Bacillus subtilis)对于养殖废水的净化作用, 发现该类细菌对COD、亚硝酸盐、H2S均有显著去除作用; 邵晴[25]针对养殖水体, 分离得到一株高效氨氮降解菌和一株高效反硝化菌, 经16S rDNA鉴定分别为解淀粉芽孢杆菌(Bacillus amyloliquefaciens)和枯草芽孢杆菌(Bacillus subtilis).陈尚智等[26]通过研究枯草芽孢杆菌(Bacillus subtilis)对微污染水体的净化作用, 也证实了芽孢杆菌(Bacillus)对COD、氨氮、亚氮、硝氮具有显著去除作用. Yang等[27]分离得到一株能够同时进行异养硝化和好氧反硝化的细菌,经16S rDNA鉴定为短小芽孢杆菌(Bacillus pumilus), 并对其脱氮性能进行了研究.以上可知, 芽孢杆菌(Bacillus)对于降解有机污染物和污水脱氮除磷具有巨大潜力.目前, 芽孢杆菌(Bacillus)多用于处理水产养殖废水, 其在污水处理方面的应用还有待进一步研究.
系统中另一优势菌属为未培养菌, 这表明MBR亚硝化系统中还存在着无法估量的微生物资源, 有待进一步研究.另外, 在序列同源性研究中, 一般认为细菌16S rDNA序列同源性低于97%即属于不同的种[28].实验结果表明, 系统中仍有58.54%的菌属序列与对比序列同源性低于97%.这也进一步说明了该系统中还有相当一部分微生物资源有待进一步发掘.
2.3 亚硝化功能菌克隆文库构建及细菌多样性分析
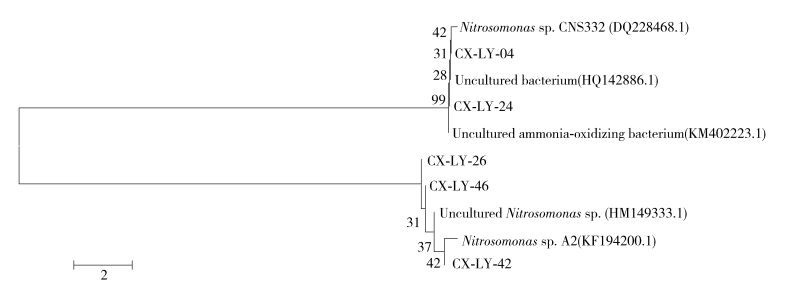
在构建的反应系统16S rDNA通用克隆文库中, 变形菌类群(Proteobacteria)为绝对优势菌属, 多数脱氮菌及固氮菌也都分布在这一菌群.如污水系统中常见的好氧反硝化菌丛毛单胞菌(Comamonas)、硝化菌产碱杆菌(Alcaligenes)、异养硝化-好氧反硝化菌芽孢杆菌(Bacillus)、固氮菌伯克霍尔德氏菌(Burkholderia gladioli)等.这些具有脱氮功能的细菌多数为异养菌.这些类群的存在表明处理晚期垃圾渗滤液的MBR亚硝化系统中同时存在好氧反硝化、异养硝化和同步硝化反硝化等多种脱氮途径, 它们对系统中的氮损失具有一定的贡献率.然而, 在以上文库中并没有检测到常见的AOB和亚硝酸盐氧化菌(nitrite oxidizing bacteria,NOB), 这是由于自养菌繁殖速度慢, 世代周期长, 相对异养菌在数量上并不占优势.因此, 为了更好地分析系统中相对数量较少的AOB, 采用针对AOB功能基因amoA的引物对进行PCR特异性扩增, 构建AOB克隆文库.采用限制性内切酶Hha I对随机挑取的73个阳性克隆子进行酶切分型, 每个酶切类型选2~3个代表克隆子送去测序, 测得序列经比对后得到5个OTU. AOB克隆文库分析结果如表 5所示. AOB系统发育树见图 4.
表 5 MBR系统样品AOB克隆文库分析结果Table 5. Data of AOB clone library constructed with sample in MBROTU
编号每种OTU所
含克隆子个数每种OTU
百分比/%Genbank中最大相似度细菌
(NCBI登录号)相似
度/%所属细菌类群 OTU1 35 47.95 未培养菌(HQ142886.1) 99 未培养菌 OTU2 1 1.37 未培养的ammonia-oxidizing bacterium(KM402223.1) 99 未培养菌 OTU3 7 9.59 未培养的Nitrosomonas sp. (HM149333.1) 88 未培养菌 OTU4 1 1.37 Nitrosomonas sp.A2(KF194200.1) 84 γ-Proteobacteria OTU5 29 39.73 Nitrosomonas sp.CNS332(DQ228468.1) 88 γ-Proteobacteria 在AOB克隆文库中检测到两大优势菌群, 分别是亚硝化单胞菌(Nitrosomonas,41.1%)和未培养菌(58.9%),而并未检测到传统的硝化菌属——亚硝化杆菌属(Nitrosococcus)和亚硝化螺菌属(Nitrosospira).这一研究结果也与前人的研究结果相符.邵军等[29]采用变性梯度凝胶电泳(denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis,DGGE)技术研究垃圾渗滤液处理系统中微生物群落演替过程, 经测序得到的AOB仅有亚硝化单胞菌(Nitrosomonas). Limpiyakorn等[30]利用PCR-DGGE、克隆文库以及荧光定量PCR技术研究对比了在不同季节情况下12种不同污泥样品中AOB的多样性,结果表明:在所有样品中均检测到了亚硝化单胞菌属(Nitrosomonas),并且只在A2O工艺的污泥样品中检测到了除亚硝化单胞菌属(Nitrosomonas)外的其他亚硝化菌. Limpiyakorn等[31]还研究了不同氨氮质量浓度下污泥样品中AOB的多样性,利用分子生物学手段仅在污泥中检测到了亚硝化单胞菌属(Nitrosomonas).因此,在处理晚期垃圾渗滤液的MBR亚硝化系统中起到亚硝化作用的菌属是亚硝化单胞菌属(Nitrosomonas).
3. 结论
1) 通过构建MBR亚硝化系统细菌通用克隆文库, 得知系统中优势菌属主要包括4个类群, 分别是Proteobacteria(64.65%)、未培养菌(18.3%)、Bacteroidetes(9.76%)和Firmicutes(7.32%).
2) 通过构建MBR亚硝化系统AOB克隆文库分析系统中的脱氮功能菌, 结果表明, 在系统中起到亚硝化作用的氨氧化菌(AOB)主要是亚硝化单胞菌(Nitrosomonas).同时, 好氧反硝化菌丛毛单胞菌属(Comamonas)、硝化菌产碱杆菌属(Alcaligenes)等菌的存在, 揭示了系统中除了短程硝化和传统脱氮途径外, 还可能存在其他新型脱氮途径.
3) 在细菌通用克隆文库中检测到未培养菌占18.3%, 在AOB克隆文库中也有58.9%的未培养菌.这一结果表明, 系统中还蕴藏着丰富的微生物资源, 有待进一步的研究.
-
表 1 垃圾渗滤液水质情况
Table 1 Quality of landfill leachate
项目 ρ/(mg·L-1) pH NH4+-N NO2--N NO3--N COD 碱度 范围 900~1 500 0~2 0~8 2 000~4 000 6 000~10 000 7.5~8.5 表 2 克隆文库中PCR扩增条件
Table 2 Amplification conditions of PCR in clone library
分析手段 引物名称 引物碱基序列(5′-3′) PCR反应体系(50 μL) PCR反应条件 全细菌克隆文库 27F/1492R 27F:AGAGTTTGA-TCCTGGCTCAG
1492R:TACGGYTAC-CTTGTTACGACTT10×PCRbuffer 5 μL, dNTP(2.5 mmol/L) 1 μL, 27F(20 μmol/L)和1492R(20 μmol/L)各1 μL, Taq DNA聚合酶0.5 μL, DNA 0.5 μL, 加超纯水至50 μL 首先95 ℃预变性1.5 min; 其次95 ℃变性0.5 min, 60 ℃退火0.5 min, 72 ℃延伸2 min, 5个循环; 之后95 ℃变性0.5 min, 55 ℃退火0.5 min, 72 ℃延伸2 min, 5个循环; 之后进行15个循环:95 ℃变性0.5 min, 50 ℃退火0.5 min, 72 ℃延伸2 min; 最后60 ℃延伸10 min AOB
克隆文库amoA-1F/
amoA-2RamoA-1F:GGGGTTTC-TACTGGTGGT
amoA-2R:CCCCTCKGS-AAAGCCTTCTTC10×PCRbuffer 5 μL, dNTP(2.5 mmol/L) 2 μL, amoA-1F (20 μmol/L)和amoA-2R(20 μmol/L)各1 μL, Taq DNA聚合酶0.5 μL, DNA 2 μL, 加超纯水至50 μL 94 ℃预变性5 min; 之后进行35个循环:94 ℃变性30 s,55 ℃退火1 min, 72 ℃延伸1 min; 72 ℃延伸10 min 表 3 克隆文库酶切类型的多样性
Table 3 Diversity of restriction endonuclease types in 16S rDNA clone library
OTU种类 库容大小/% Shannon-Wiener指标 Simpson指标 均匀度 丰富度 19 91.50 2.528 2 0.890 5 0.858 6 4.084 6 表 4 MBR亚硝化系统样品主要细菌16S rDNA克隆文库分析结果
Table 4 Data of bacterial 16S rDNA clone library constructed with sample in MBR
OTU
编号每种OTU所
含克隆子个数每种OTU
百分比/%Genbank中最大相似度细菌
(NCBI登录号)相似
度/%所属细菌类群 OTU1 8 9.76 Aquimonas sp. BUT-1(KJ653271.1) 95 γ-Proteobacteria OTU2 1 1.22 Ralstonia sp. P-4CB2(AF229890.2) 97 β-Proteobacteria OTU3 1 1.22 未培养菌(GQ264319.1) 98 未培养菌 OTU4 3 3.66 Comamonas sp. IA-30(AB247270.1) 93 β-Proteobacteria OTU5 3 3.66 未培养菌(HQ640550.1) 99 未培养菌 OTU6 9 10.98 Erythrobacter sp. B809(KT185356.1) 82 α-Proteobacteria OTU7 1 1.22 Burkholderia gladioli strain 1993027208(AY268167.1) 92 β-Proteobacteria OTU8 1 1.22 未培养菌(HE582922.1) 99 未培养菌 OTU9 20 24.39 Ralstonia sp. 80 (AY238507.1) 98 β-Proteobacteria OTU10 5 6.10 Alcaligenes sp. 92(AY238499.1) 92 β-Proteobacteria OTU11 5 6.10 Persicobacter sp. JZB09(CP012859.1) 82 Bacteroidetes OTU12 2 2.44 Lewinella agarilytica strain r31(JQ661169.1) 82 Bacteroidetes OTU13 2 2.44 未培养菌(AY426460.1) 90 未培养菌 OTU14 6 7.32 Ectothiorhodospira sp. AM4(EU252492.1) 90 γ-Proteobacteria OTU15 6 7.32 未培养菌(EF608428.1) 99 未培养菌 OTU16 6 7.32 Planococcus sp. EP09(AM398218.1) 85 Firmicutes OTU17 1 1.22 未培养菌(EU215286.1) 99 未培养菌 OTU18 1 1.22 未培养菌(EU083483.1) 97 未培养菌 OTU19 1 1.22 Pedobacter sp. An13(AJ551152.1) 85 Bacteroidetes 表 5 MBR系统样品AOB克隆文库分析结果
Table 5 Data of AOB clone library constructed with sample in MBR
OTU
编号每种OTU所
含克隆子个数每种OTU
百分比/%Genbank中最大相似度细菌
(NCBI登录号)相似
度/%所属细菌类群 OTU1 35 47.95 未培养菌(HQ142886.1) 99 未培养菌 OTU2 1 1.37 未培养的ammonia-oxidizing bacterium(KM402223.1) 99 未培养菌 OTU3 7 9.59 未培养的Nitrosomonas sp. (HM149333.1) 88 未培养菌 OTU4 1 1.37 Nitrosomonas sp.A2(KF194200.1) 84 γ-Proteobacteria OTU5 29 39.73 Nitrosomonas sp.CNS332(DQ228468.1) 88 γ-Proteobacteria -
[1] BODZE M, LOBOS MOYSA E, ZAMOROWSKA M. Removal of organic compounds from municipal landfill leachate in a membrane bioreactor[J]. Desalination, 2006, 198(1):16-23. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0011916406011040
[2] FARAH N A, CHRISTOPHER Q L. Treatment of landfill leachate using membrane bioreactors:a review[J]. Desalination, 2012, 287(8):41-54. https://www.infona.pl/resource/bwmeta1.element.elsevier-3a692f6c-fe13-34bb-9f22-43871acc6eaf
[3] STUCZYNSKI T I, MCCARTY G W, SIEBIELEC G. Response of soil microbiological activities to cadmium, lead, and zinc salt amendments[J]. Journal of Environmental Quality, 2003, 32(4):1346-1355. doi: 10.2134/jeq2003.1346
[4] KARGI F, KONYA I. COD, para-chlorophenol and toxicity removal from para-chlorophenol containing synthetic wastewater in an activated sludge unit[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2006, 132(2/3):226-231. http://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S0304389405005844
[5] STROUS M, HEIJNEN J J, KUENEN J G, et al. The sequencing batch reactor as a powerful tool for the study of slowly growing anaerobic ammonium-oxidizing microorganisms[J]. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 1998, 50(5):589-596. doi: 10.1007/s002530051340
[6] XUE Y, YANG F, LIU S, et al. The influence of controlling factors on the start-up and operation for partial nitrification in membrane bioreactor[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2009, 100(3):1055-1060. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2008.07.052
[7] 李芸, 熊向阳, 李军, 等.膜生物反应器处理晚期垃圾渗滤液亚硝化性能及其抑制动力学分析[J].中国环境科学, 2016, 36(2):419-427 http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGHJ201602019.htm LI Y, XIONG X Y, LI J, et al. Performance and inhibition kinetics of membrane bioreactor in treatment of advanced landfill leachate[J]. China Environmental Science, 2016, 36(2):419-427. (in Chinese) http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGHJ201602019.htm
[8] WIDADA J, NOJIRI H, OMORI T. Recent developments in molecular techniques for identification and monitoring of xenobiotic-degrading bacteria and their catabolic genes in bioremediation[J]. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 2002, 60(1):45-59. doi: 10.1007%2Fs00253-002-1072-y
[9] SHEN L, YUAN Y, MENG F. Reactor performance and microbial ecology of a nitritation membrane bioreactor[J]. Journal of Membrane Science, 2014, 462(462):139-146. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0376738814002208
[10] 伍阳. 膜反应器脱氮除磷及细菌16S rDNA多样性研究[D]. 雅安: 四川农业大学, 2008: 18-19 WU Y. Study on the diversity of nitrogen and phosphorus removal bacterium in membrane reactor by 16S rDNA.[D]. Yaan:Sichuan Agricultural University, 2008:18-19. (in Chinese)
[11] HUANG L N, ZHU S, ZHOU H, et al. Molecular phylogenetic diversity of bacteria associated with the leachate of a closed municipal solid waste landfill[J]. FEMS Microbiol Lett, 2005, 242(2):297-303. doi: 10.1016/j.femsle.2004.11.021
[12] KAPLEY A, PRASAD S, PUROHIT H. Changes in microbial diversity infed-batch reactor operation with wastewater containing nitroaromatic residues[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2007, 98(13):2479-2484. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2006.09.012
[13] MUYZER G. DGGE/TGGE a method for identifying genes from natural ecosystems[J]. Current Opinion in Microbiology, 1999, 2(3):317-322. doi: 10.1016/S1369-5274(99)80055-1
[14] SNAIDR J, AMANN R, HUBER I, et al. Phylogenetic analysis and in situ identification of bacteria in activated sludge[J]. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 1997, 63(7):2884-2896. http://aem.asm.org/cgi/reprint/63/7/2884.pdf
[15] XIA S, LI J, WANG R, et al. Tracking composition and dynamics of nitrification and denitrification microbial community in a biofilm reactor by PCR-DGGE and combining fish with flow cytometry[J]. Biochemical Engineering Journal, 2010, 49(3):370-378. doi: 10.1016/j.bej.2010.01.013
[16] BOON N, GORIS J, DE VOS P, et al. Genetic diversity among 3-chloroaniline and aniline-degrading strains of the Comamonadaceae[J]. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 2001, 67(3):1107-1115. doi: 10.1128/AEM.67.3.1107-1115.2001
[17] KHAN S T, HORIBA Y, YAMAMOTO M, et al. Members of the family Comamonadaceae as primary poly (3-hydroxybutyrate-co-3-hydroxyvalerate) degrading deni-trifiers in activated sludge asrevealed by a polyphasic approach[J]. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 2002, 68(7):3206-3214. doi: 10.1128/AEM.68.7.3206-3214.2002
[18] 刘志培, 杨惠芳, 周培瑾.食酸丛毛单胞菌AN3菌株降解苯胺代谢途径的研究[J].微生物学报, 1999, 39(5):448-453 http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-WSXB199905009.htm LIU Z P, YANG H F, ZHOU P J. Study on the degradat-ion of aniline by the strain of Comamonas acidovorans AN3[J]. Acta Microbiologica Sinica, 1999, 39(5):448-453. (in Chinese) http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-WSXB199905009.htm
[19] SCHLEHECK D, VON NETZER F, FLEISCHMANN T, et al. The missing link in linear alkylbenzenesulfonate surfactant degradation:4-sulfoacetophenone as atransient intermediate in the degradation of 3-(4-Sulfophenyl) utyrate by Comamonastestosteroni KF-1[J]. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 2010, 76(1):196-202. doi: 10.1128/AEM.02181-09
[20] ANDERSON I C, POTH M, HOMSTEAD J, et al. A comparison of NO and N2O production by the autotrophic nitrifier Nitorsomonas europaea and the heterotrophic nitrifier Alcaligenes faecalis[J]. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 1993, 59(11):3525-3533.
[21] 王成林, 周巧红, 王亚芬.一株异养硝化细菌的分离鉴定及其亚硝化作用研究[J].农业环境科学学报, 2008, 27(3):1146-1150 http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-NHBH200803055.htm WANG C L, ZHOU Q H, WANG Y F. Isolation and identification of a heterotrophic nitrification bacteria and its role in the study of partial nitrification[J]. Journal of Agro-environment Science, 2008, 27(3):1146-1150. (in Chinese) http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-NHBH200803055.htm
[22] HILL V R, KAHLER A M, JOTHIKUMAR N, et al. Multistate evaluation of an ultrafiltration-based procedure for simultaneous recovery of enteric microbes in 100-liter tap water samples[J]. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 2007, 73(13):4218-4225. doi: 10.1128/AEM.02713-06
[23] CHOUARI R, LE PASLIER D, DAEGELEN P, et al. Novel predominant archaeal and bacterial groups revealed by molecular analysis of an anaerobic sludge digester[J]. Environmental Microbiology, 2005, 7(8):1104-1115. doi: 10.1111/emi.2005.7.issue-8
[24] 曾地刚, 雷爱莹, 彭敏, 等.枯草芽孢杆菌的分离及其净化水质的研究[J].水利渔业, 2007, 27(6):1003-1278 http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SCAN200706026.htm ZENG D G, LEI A Y, PENG M, et al. Isolation of Bacillus subtilis and study on its role of purification water[J]. Reservoir Fisheries, 2007, 27(6):1003-1278. (in Chinese) http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SCAN200706026.htm
[25] 邵晴. 氨氮和亚硝态氮降解菌的研究[D]. 无锡: 江南大学, 2008: 19-41 SHAO Q. Study on the degradation of ammonia nitrogen and nitrite nitrogen[D]. Wuxi:Jiangnan University, 2008:19-41. (in Chinese)
[26] 陈尚智, 胡勇有.枯草芽孢杆菌对微污染水体的净化作用[J].环境科学学报, 2011, 31(8):1594-1601 http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJXX201108007.htm CHEN S Z, HU Y Y. Purification of micro polluted water by Bacillus subtilis[J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 2011, 31(8):1594-1601. (in Chinese) http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJXX201108007.htm
[27] YANG X P, WANG S M, ZHANG D W, et al. Isolation and nitrogen removal characteristics of an aerobic heterotrophic nitrifying-denitrifying bacterium, Bacillus subtilis, A1[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2011, 102(2):854-862. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2010.09.007
[28] GIOVANNONI S J, MULLINS T D, FIELD K G. Microbial diversity in oceanic systems:rRNA approaches to the study of unculturable microbes[M]. Berlin:Springer, 1995:217-248.
[29] 邵军, 孙海美, 孙卫玲, 等.垃圾渗滤液处理系统中微生物群落结构变化研究[J].北京大学学报, 2010, 46(3):435-441 http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-BJDZ201003022.htm SHAO J, SUN H M, SUN W L, et al. Study on the microbial community structure in landfill leachate treatment system[J]. Journal of Peking University, 2010, 46(3):435-441. (in Chinese) http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-BJDZ201003022.htm
[30] LIMPIYAKORN T, SHINOHARA Y, KURISU F, et al. Communities of ammonia-oxidizing bacteria in activated sludge of various sewage treatment plants in Tokyo[J]. Fems Microbiology Ecology, 2006, 54(2):205-217.
[31] LIMPIYAKORN T, KURISU F, SAKAMOTO Y, et al. Effects of ammonium and nitrite on communities and populations of ammonia-oxidizing bacteria in laboratory-scale continuous-flow reactors[J]. Fems Microbiology Ecology, 2007, 60(3):501-512. doi: 10.1111/fem.2007.60.issue-3



 下载:
下载: