Experiment Research on Basic Performance of Alkali-activated Slag Ceramsite Concrete
-
摘要:
为了解决碱矿渣胶凝材料收缩过大限制其应用的问题,将陶粒和陶砂掺入碱矿渣胶凝材料中形成碱矿渣陶粒混凝土.完成了252个碱矿渣陶粒混凝土试件的试验,考虑了水灰比、砂率、粉煤灰质量分数、水玻璃模数、氧化钠质量分数等关键参数对碱矿渣陶粒混凝土抗压强度和干缩率的影响.试验结果表明,碱矿渣陶粒混凝土的28 d边长为100 mm立方体的抗压强度为45~55 MPa,碱矿渣陶粒混凝土的28 d干燥收缩率为1.8×10-4~4.4×10-4.当水灰比、粉煤灰质量分数、水玻璃模数、氧化钠质量分数增大时,抗压强度减小,干缩率增大;砂率增大时,抗压强度增大,干缩率减小.
Abstract:In order to solve the problem of big shrinkage which restricted the application of alkali-activated slag binding material, the ceramsite and ceramic sand can be mixed with the alkali-activated slag binding material and formed the alkali-activated slag ceramsite concrete, the shrinkage can be effectively reduced. The experiments of 252 alkali-activated slag ceramsite concrete specimens were completed, and five parameters were changed including the water cement ratio, sand ratio, the fraction of fly ash, the modulus of sodium silicate, the fraction of sodium oxide, the change rules of cube compressive strength and prism dry shrinkage with these parameters of alkali-activated slag ceramsite concrete were obtained. The cube compressive strength of alkali-activated slag ceramsite concrete was 45-55 MPa, which the side length was 100 mm, the drying shrinkage rate of alkali-activated slag ceramsite concrete was 1.8×10-4-4.4×10-4. The research results show that the cube compressive strength decreases, drying shrinkage rate increases with the water cement ratio, the fraction of fly ash, the modulus of sodium silicate, the fraction of sodium oxide increasing; the cube compressive strength increases, drying shrinkage rate decreases with sand ratio increasing.
-
碱矿渣胶凝材料是以工业副产品——高炉矿渣为原材料,采用适当的碱性激发剂激发,经搅拌而成的胶凝材料.相关文献[1-9]表明,地聚物具有良好的耐高温性能,碱矿渣胶凝材料属于人造地聚物.朱晶[10]的研究表明,在经历600、800 ℃高温后,碱矿渣胶凝材料抗压强度仍有常温时的60%~80%.碱矿渣胶凝材料收缩较大是制约其发展的缺点之一.将陶粒和陶砂加入碱矿渣胶凝材料中形成碱矿渣陶粒混凝土.陶粒和陶砂作为骨料,相同体积的混凝土下,掺加陶粒和陶砂使得胶凝材料减少,因收缩主要是胶凝材料引起,骨料不会收缩,所以可以有效减小碱矿渣胶凝材料的收缩,而且陶粒和陶砂生产过程中经历了高温,应不影响碱矿渣胶凝材料的耐高温性能.
国内外对碱矿渣胶凝材料和碱矿渣混凝土的研究较多,但缺乏关于碱矿渣陶粒混凝土的研究.碱矿渣胶凝材料净浆40 mm×40 mm×160 mm的28 d抗压强度可达80 MPa[11-12]以上,也有学者[13-14]配制出28 d立方体抗压强度超过80 MPa的碱矿渣混凝土.国内外学者研究表明[15-18],碱矿渣胶凝材料净浆的干缩是水泥浆的2~6倍,碱矿渣混凝土的干缩也有普通混凝土的1.2~1.9倍.碱矿渣胶凝材料收缩较大,主要体现在化学收缩和干燥收缩[15].本文主要研究碱矿渣陶粒混凝土的干燥收缩.
本文中碱矿渣陶粒混凝土的配合比是配合后续试验选用的,笔者为在后续试验中使用碱矿渣陶粒混凝土制备空心砌块,结合实际生产中空心砌块的生产方法,配制了干硬性的碱矿渣陶粒混凝土,本文配合比的混凝土塌落度均为0.本文将研究水灰比、砂率、粉煤灰质量分数、水玻璃模数、氧化钠质量分数5个参数对碱矿渣陶粒混凝土的立方体抗压强度和干燥收缩等基本性能的影响.水灰比指用水量与矿渣和粉煤灰总量的比值,因为水化过程中,水玻璃中的结晶水和自由水也会参与反应,用水量应包括水玻璃中含有的水;砂率指陶砂占陶粒和陶砂总和的体积分数;钠水玻璃的分子式为Na2O·nSiO2,其中n指水玻璃模数.
1. 原材料性能与试验方法
1.1 原材料
矿渣:所用矿渣来自山东济宁生产厂家的S95级矿渣,矿渣比表面积为349 m2/kg,其化合物的质量分数如表 1所示.
表 1 矿渣的质量分数Table 1. Mass fraction of slag% 矿渣成分 SiO2 Al2O3 CaO Fe2O3 K2O MgO Na2O P2O5 SO3 数值 36.08 10.22 42.01 0.33 0.71 8.27 0.41 0.02 1.95 粉煤灰:所用粉煤灰来自哈尔滨生产厂家的Ⅰ级粉煤灰,其主要化合物的质量分数如表 2所示.
表 2 粉煤灰的质量分数Table 2. Mass fraction of fly ash% 矿渣成分 SiO2 Al2O3 CaO Fe2O3 K2O MgO Na2O P2O5 SO3 数值 49.98 20.08 10.99 8.16 1.59 0.68 0.69 0.16 1.23 水玻璃:试验采用液态钠水玻璃,含水率50.7%,模数3.2.
氢氧化钠:试验采用固态氢氧化钠(分析纯),氢氧化钠质量分数≥96%.
1.2 试验方法
立方体抗压强度试验采用的试件尺寸为100 mm×100 mm×100 mm,在油压压力试验机上进行.参考规范[19]、梅琳[15]和廖佳庆[18]的试验方法,干燥收缩采用的试件尺寸为100 mm×100 mm×400 mm,每组2个试件,采用手持式收缩测量仪测量收缩值.试验中每天都对试件进行测量,一直测到28 d龄期为止,得到28 d的总干缩率及其随时间变化的曲线.
考察各参数影响的配合比见表 3.水灰比和砂率都是影响混凝土性能的重要因素,而水玻璃模数、氧化钠质量分数和粉煤灰的质量分数对碱矿渣胶凝材料性能的影响十分重要.
表 3 碱矿渣陶粒混凝土配合比Table 3. Mix proportion of alkali-activated slag ceramsite concreteg 编号 矿渣 粉煤灰 陶粒粗骨料
(10~16 mm)陶粒粗骨料
(5~10 mm)陶砂 水玻璃 氢氧化钠 水 A 1 000 0 671.5 287.8 1 700.6 289.9 64.5 168.5 S35L40 1 000 0 732.6 314.0 1 511.6 289.9 64.5 168.5 S38L40 1 000 0 732.6 314.0 1 511.6 289.9 64.5 198.5 S40L40 1 000 0 732.6 314.0 1 511.6 289.9 64.5 218.5 S35L35 1 000 0 793.6 340.1 1 322.7 289.9 64.5 168.5 S35L50 1 000 0 610.5 261.6 1 889.5 289.9 64.5 168.5 F2 800 200 671.5 287.8 1 700.6 289.9 64.5 168.5 F4 600 400 671.5 287.8 1 700.6 289.9 64.5 168.5 F6 400 600 671.5 287.8 1 700.6 289.9 64.5 168.5 F8 200 800 671.5 287.8 1 700.6 289.9 64.5 168.5 M12N6 1 000 0 671.5 287.8 1 700.6 217.4 48.4 213.9 M12N10 1 000 0 671.5 287.8 1 700.6 362.3 80.6 123.2 M14N6 1 000 0 671.5 287.8 1 700.6 253.2 43.5 194.1 M14N8 1 000 0 671.5 287.8 1 700.6 338.2 58.1 142.1 M14N10 1 000 0 671.5 287.8 1 700.6 422.7 72.6 90.2 M16N6 1 000 0 671.5 287.8 1 700.6 289.9 38.7 174.3 M16N8 1 000 0 671.5 287.8 1 700.6 386.5 51.6 115.8 M16N10 1 000 0 671.5 287.8 1 700.6 483.1 64.5 57.2 注:表中编号A为基准试件,水灰比为0.35,砂率为45%,粉煤灰质量分数0%,水玻璃模数1.2,氧化钠质量分数8%;编号S35L40、S38L40、S40L40、S35L35为水灰比和砂率改变的试件.例如,S40L40为水质比0.40,砂率0.40;编号F2、F4、F6、F8表示粉煤灰质量分数分别为20%、40%、60%、80%;编号M12N6、M12N10、M12N6、M14N8、M14N10、M16N6、M16N8、M16N10表示水玻璃模数和氧化钠质量分数改变的试件,例如,M14N8为水玻璃模数1.4、氧化钢质量分数8%. 2. 碱矿渣陶粒混凝土的立方体抗压强度
2.1 水灰比、砂率对碱矿渣陶粒混凝土立方体抗压强度的影响
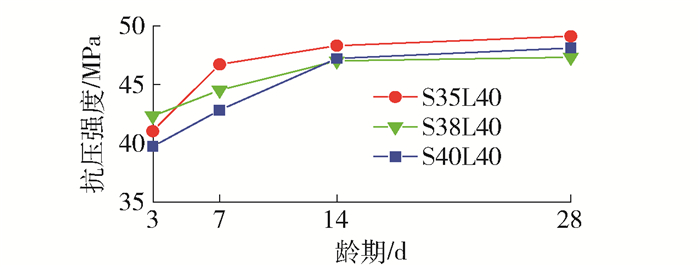
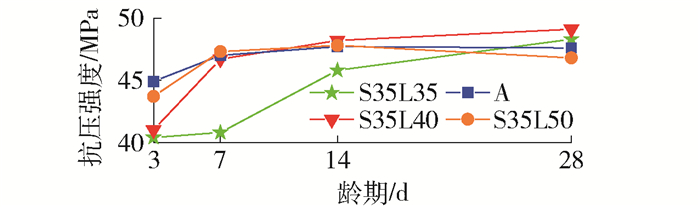
由图 1可以看出,随着龄期的增长,不同水灰比的碱矿渣陶粒混凝土的强度都有增长,水灰比为0.35、0.38、0.40的3组试件3 d强度都达到40 MPa以上,此后强度增长日趋缓慢.水灰比介于0.35~0.40时,水灰比越小,碱矿渣陶粒混凝土抗压强度越高,原因可能是水灰比增大后,碱激发溶液的碱浓度降低,硅酸根离子的浓度降低,延缓了矿渣的水化,浆体结构中的孔隙率也会增大,导致抗压强度降低. 14~28 d强度增长十分微小,甚至会有强度下降的现象出现,有学者研究表明[20],碱矿渣胶凝材料的后期强度出现下降的现象.早期强度出现了水灰比低的强度反而高的现象,原因可能是选取的水灰比差距较小.
由图 2可以看出,砂率影响下的各组试件3 d强度可达40 MPa以上,此后强度增长日趋缓慢,试件S35L50的28 d强度与14 d强度相比有所降低.从早期强度来看,砂率越大,抗压强度越高.原因可能是砂率增大后砂浆能更好地填补粗骨料间的空隙,提高了混凝土的密实性,因而提高了强度;但砂率增大后,骨料的比表面积增大,相同胶凝材料用量下,骨料表面的水泥浆量变少,骨料间胶结力降低,降低了强度.
2.2 粉煤灰质量分数对碱矿渣陶粒混凝土立方体抗压强度的影响
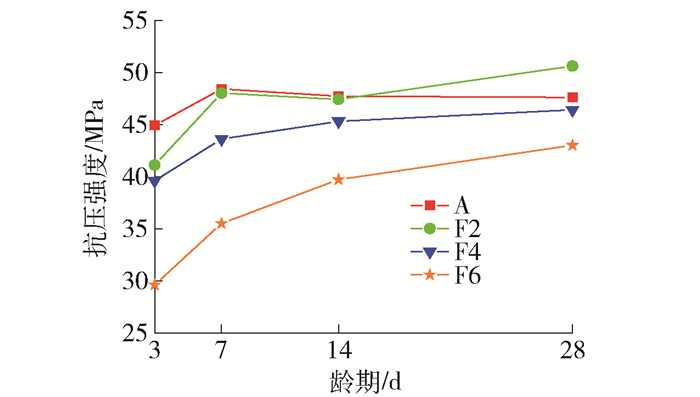
粉煤灰质量分数对碱矿渣陶粒混凝土立方体抗压强度的影响结果如图 3所示.
由图 3可以看出,粉煤灰质量分数越小,抗压强度越高,早期强度相差较大,随着龄期增长,强度相差越来越小.试件F2的抗压强度超过了试件F0,其他试件粉煤灰比例越高,抗压强度越低.原因可能是粉煤灰相比矿渣含有相对较少的氧化钙,活性较低,不易激发,水化早期参与反应程度低,后期粉煤灰的火山灰效应会对强度增长有较大贡献,所以当粉煤灰质量分数较小时,抗压强度可能比纯矿渣激发还要高,粉煤灰质量分数的最佳掺量在20%左右.
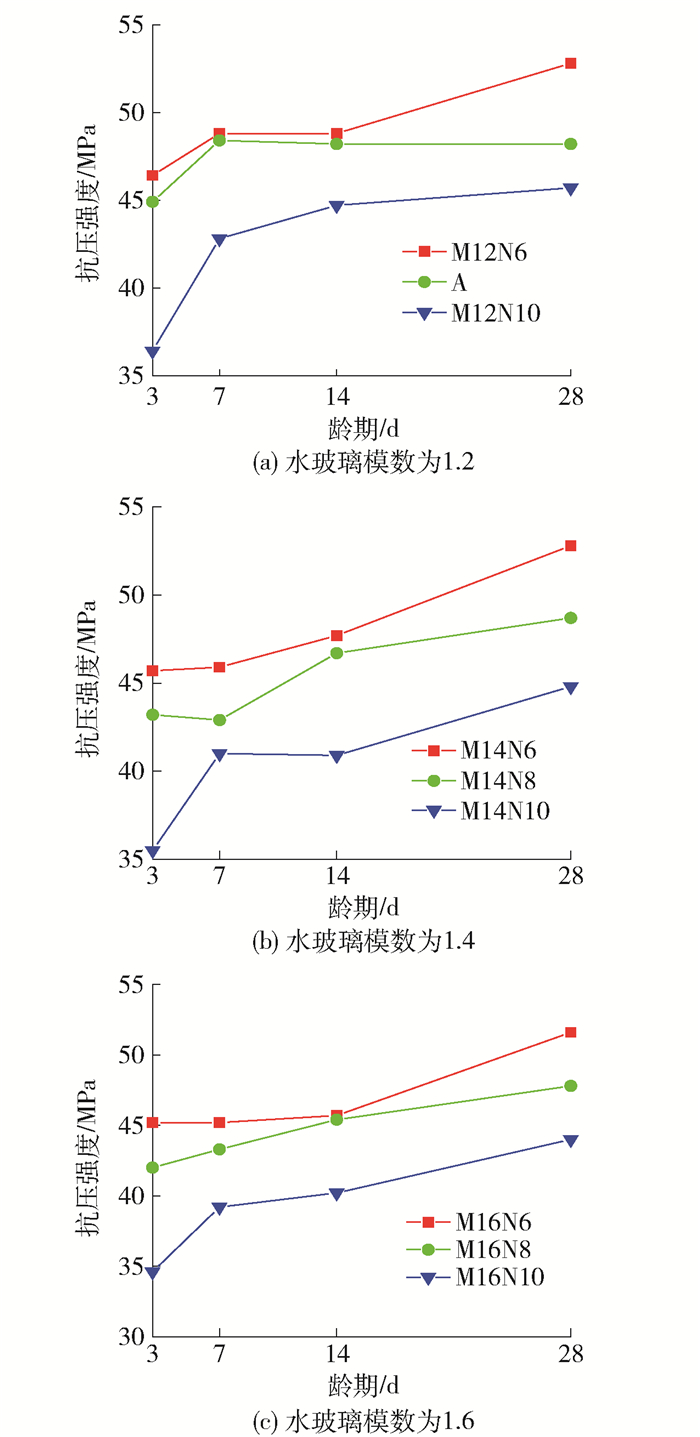
2.3 水玻璃模数和氧化钠质量分数对碱矿渣陶粒混凝土立方体抗压强度的影响
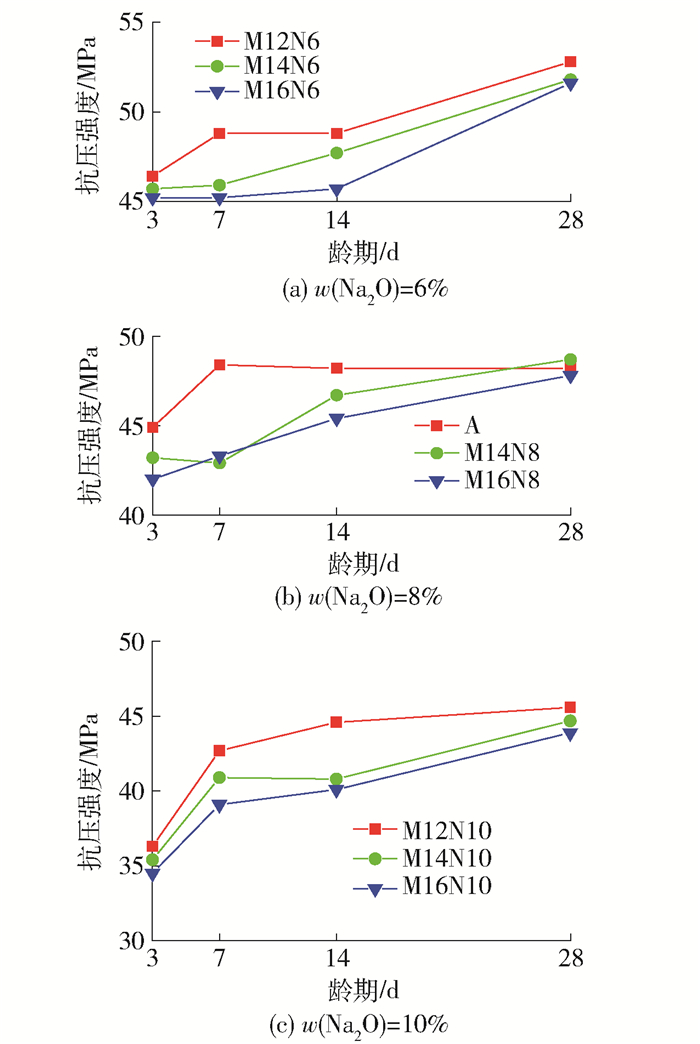
水玻璃模数和氧化钠质量分数对碱矿渣陶粒混凝土立方体抗压强度的影响分别见图 4、5.可以看出,随着龄期的增长,不同配合比的碱矿渣陶粒混凝土的强度都有增长,3 d强度就达到了28 d强度的80%以上.当氧化钠质量分数相同时,水玻璃模数越大,抗压强度相对越低.当水玻璃模数相同时,氧化钠质量分数越高,强度越低.这是由于氧化钠质量分数增大后,溶液碱性增大,水化反应迅速进行,在表面形成一层水化产物,阻止反应进一步进行,使得水化产物结构不致密,孔隙增多.
3. 碱矿渣陶粒混凝土的干缩性能
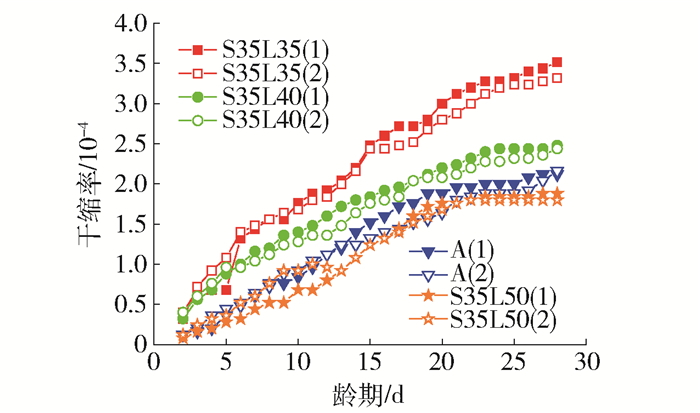
3.1 水灰比、砂率对碱矿渣混凝土干燥收缩的影响
水灰比、砂率对碱矿渣陶粒混凝土干缩率的影响规律见图 6、7.
由图 6可以看出,水灰比越大,干缩率越大.水灰比增大可能导致试件内的自由水和易脱离的结合水变多,毛细孔量更小,使干缩增大. 3组试件都是在开始的几天内收缩增长较大,随着龄期增长,干缩率增长越来越缓慢. 3组试件在28 d时,干缩仍在增长,会继续测量,但在本文中未列入.根据梅琳[15]的研究,普通硅酸盐水泥混凝土的水灰比为0.4、砂率为33%,28 d的干缩率大约为1.20×10-4,可见不同水灰比下的碱矿渣陶粒混凝土28 d干缩率大约为普通混凝土的2.0~3.6倍.矿渣混凝土的干缩之所以比普通混凝土大,是因为矿渣混凝土的孔中小孔比例相对更大,而干缩主要是小孔中水分散失引起的[18].
由图 7可以看出,在骨料总体积不变的情况下,砂率越大,干缩率越小.砂率增大后,砂浆能更好地填补粗骨料间的空隙,提高了混凝土的密实性,硬化后抵抗变形能力更强.同时,骨料的比表面积增大,骨料间胶凝材料减少,从而降低了孔隙率,减少了水分散失.本文砂率为35%时,碱矿渣陶粒混凝土28 d干缩率大约为普通混凝土的2.9倍.
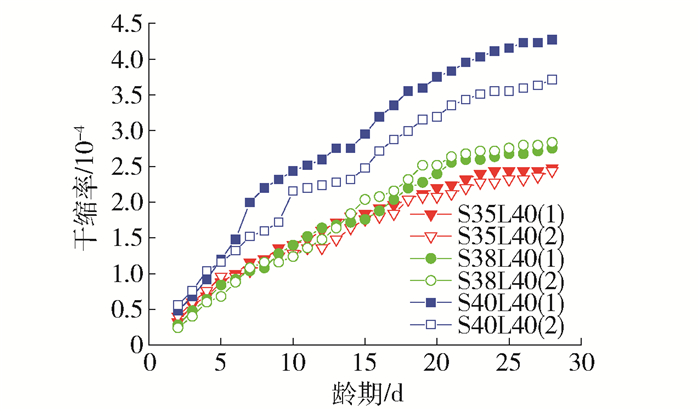
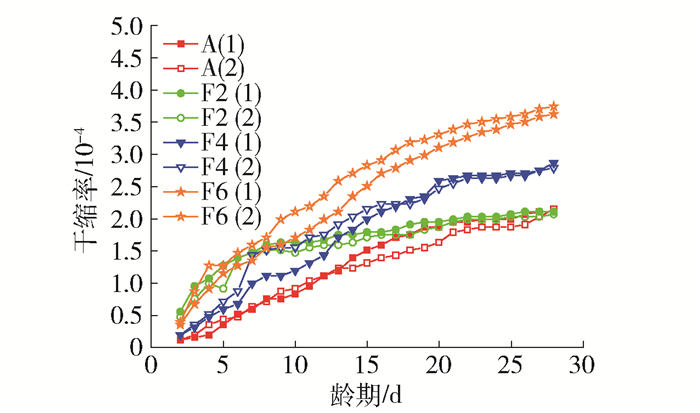
3.2 粉煤灰质量分数对碱矿渣陶粒混凝土干燥收缩的影响
粉煤灰质量分数对碱矿渣陶粒混凝土干缩率的影响见图 8.
由图 8可以看出,粉煤灰质量分数为20%时,与不加入粉煤灰时差别不大,粉煤灰质量分数超过20%时,粉煤灰比例越大,干缩率越大.粉煤灰对混凝土性能的影响与粉煤灰本身的性能有很大关系,如果掺入的粉煤灰需水量比较大,水的消耗更快,可能会导致干缩变大.粉煤灰的需水量比与粉煤灰的细度、烧失量和颗粒形态有关.粉煤灰的细度越低、烧失量越小、球形颗粒含量越大,需水量比越小[21].加入粉煤灰后碱矿渣陶粒混凝土28 d干缩率大约为普通凝土的1.8~3.1倍.
3.3 水玻璃模数和氧化钠质量分数对碱矿渣陶粒混凝土干燥收缩的影响
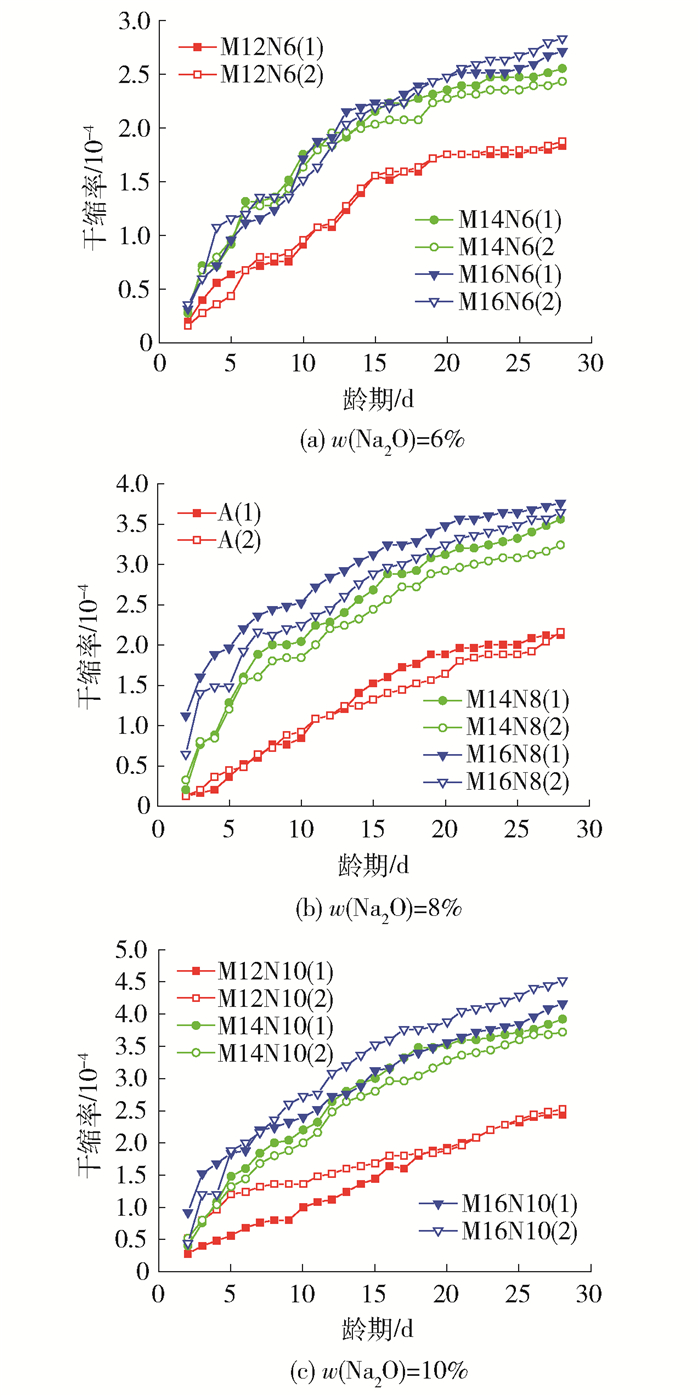
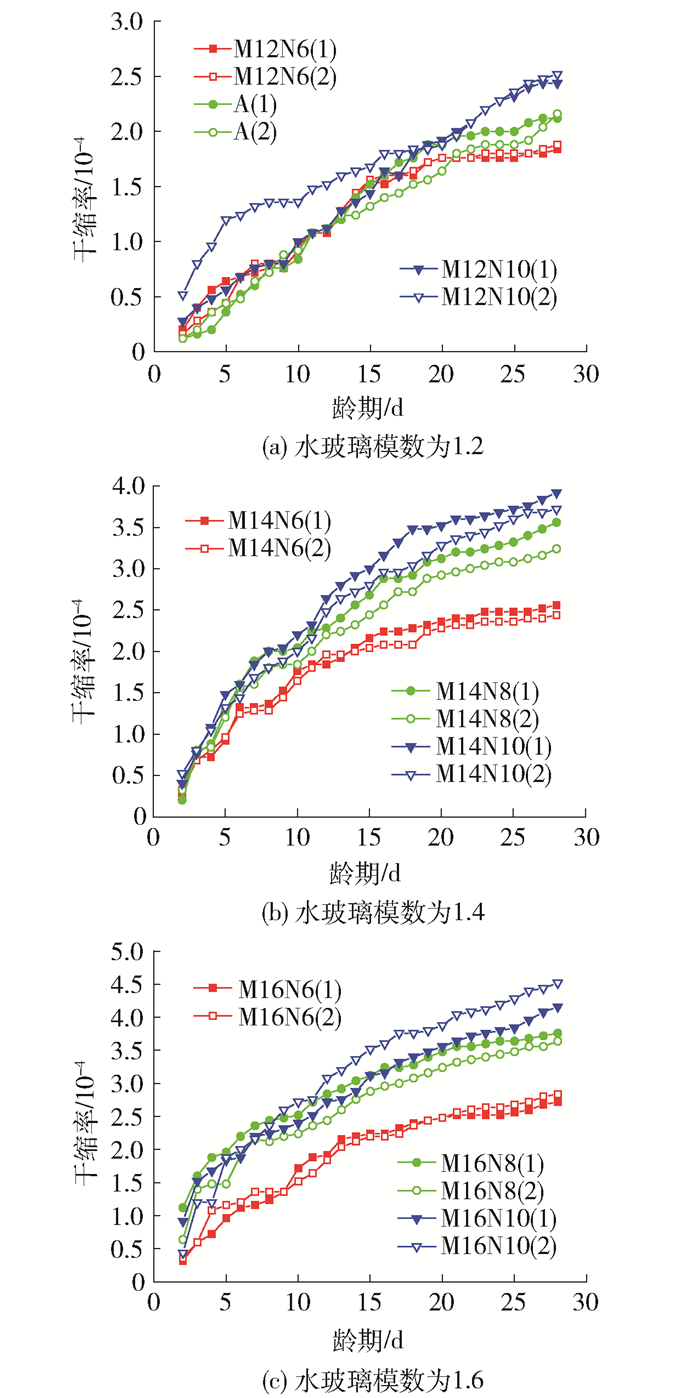
水玻璃模数和氧化钠质量分数对碱矿渣陶粒混凝土干缩率的影响见图 9、10.
由图 9、10可以看出:试件的水玻璃模数越大,氧化钠质量分数越大,干缩率越大.当氧化钠质量分数不变时,水玻璃模数增大,则需增加激发剂的总量,激发剂的碱浓度增大;水玻璃模数不变时,氧化钠质量分数增大,激发剂的碱浓度增大,综合考虑,两者都会增大碱浓度,碱浓度的增大使得干燥收缩增大.原因可能是溶液碱浓度增大后,水化反应迅速,水化产物形成了一层保护层,阻止了反应进一步进行,水化产物结构不致密,水化反应产生的胶凝孔增多,导致一定体积的试件水分散失变快,干燥收缩增大.相同配比的2个试件干缩相差较大可能是装模振实时的质量导致的.
3.4 降低干燥收缩率的措施
由以上试验结果可知,碱矿渣陶粒混凝土的干缩仍旧大于普通混凝土,可通过以下措施尝试进一步降低碱矿渣陶粒混凝土的干燥收缩率.
1) 掺加需水量较小的粉煤灰
降低粉煤灰的需水量比应避免磨细时间过长,选用烧失量较小的粉煤灰.
2) 在养护过程中给试件洒水
干燥收缩主要来源于水分的散失,可通过在养护过程中洒水来补充水分或采用蒸汽养护.
3) 配制和易性更好、密实度更高的碱矿渣陶粒混凝土.
本文为配合后续试验中砌块的生产,选用了干硬性混凝土,可通过配制工作性更好、密实度更高的混凝土来减小干燥收缩.
4. 结论
本文选择水灰比、砂率、粉煤灰质量分数、水玻璃模数、氧化钠质量分数5个参数,研究了碱矿渣陶粒混凝土抗压性能和干燥收缩随上述参数的变化规律,得到以下结论:
1) 水灰比介于0.35~0.40时,水灰比越小,立方体抗压强度越高,干缩率越小.
2) 砂率介于35%~50%时,砂率越大,干缩率越大,早期强度越高.
3) 粉煤灰质量分数介于20%~80%时,粉煤灰质量分数越大,抗压强度越低,干缩率越大.
4) 水玻璃模数介于1.2~1.6,氧化钠质量分数介于6%~10%时,水玻璃模数越大,氧化钠质量分数越高,抗压强度越低,干缩率越大.
5) 可通过降低粉煤灰的需水量、洒水养护和蒸汽养护、提高混凝土的工作性和密实度来降低干缩率.
-
表 1 矿渣的质量分数
Table 1 Mass fraction of slag
% 矿渣成分 SiO2 Al2O3 CaO Fe2O3 K2O MgO Na2O P2O5 SO3 数值 36.08 10.22 42.01 0.33 0.71 8.27 0.41 0.02 1.95 表 2 粉煤灰的质量分数
Table 2 Mass fraction of fly ash
% 矿渣成分 SiO2 Al2O3 CaO Fe2O3 K2O MgO Na2O P2O5 SO3 数值 49.98 20.08 10.99 8.16 1.59 0.68 0.69 0.16 1.23 表 3 碱矿渣陶粒混凝土配合比
Table 3 Mix proportion of alkali-activated slag ceramsite concrete
g 编号 矿渣 粉煤灰 陶粒粗骨料
(10~16 mm)陶粒粗骨料
(5~10 mm)陶砂 水玻璃 氢氧化钠 水 A 1 000 0 671.5 287.8 1 700.6 289.9 64.5 168.5 S35L40 1 000 0 732.6 314.0 1 511.6 289.9 64.5 168.5 S38L40 1 000 0 732.6 314.0 1 511.6 289.9 64.5 198.5 S40L40 1 000 0 732.6 314.0 1 511.6 289.9 64.5 218.5 S35L35 1 000 0 793.6 340.1 1 322.7 289.9 64.5 168.5 S35L50 1 000 0 610.5 261.6 1 889.5 289.9 64.5 168.5 F2 800 200 671.5 287.8 1 700.6 289.9 64.5 168.5 F4 600 400 671.5 287.8 1 700.6 289.9 64.5 168.5 F6 400 600 671.5 287.8 1 700.6 289.9 64.5 168.5 F8 200 800 671.5 287.8 1 700.6 289.9 64.5 168.5 M12N6 1 000 0 671.5 287.8 1 700.6 217.4 48.4 213.9 M12N10 1 000 0 671.5 287.8 1 700.6 362.3 80.6 123.2 M14N6 1 000 0 671.5 287.8 1 700.6 253.2 43.5 194.1 M14N8 1 000 0 671.5 287.8 1 700.6 338.2 58.1 142.1 M14N10 1 000 0 671.5 287.8 1 700.6 422.7 72.6 90.2 M16N6 1 000 0 671.5 287.8 1 700.6 289.9 38.7 174.3 M16N8 1 000 0 671.5 287.8 1 700.6 386.5 51.6 115.8 M16N10 1 000 0 671.5 287.8 1 700.6 483.1 64.5 57.2 注:表中编号A为基准试件,水灰比为0.35,砂率为45%,粉煤灰质量分数0%,水玻璃模数1.2,氧化钠质量分数8%;编号S35L40、S38L40、S40L40、S35L35为水灰比和砂率改变的试件.例如,S40L40为水质比0.40,砂率0.40;编号F2、F4、F6、F8表示粉煤灰质量分数分别为20%、40%、60%、80%;编号M12N6、M12N10、M12N6、M14N8、M14N10、M16N6、M16N8、M16N10表示水玻璃模数和氧化钠质量分数改变的试件,例如,M14N8为水玻璃模数1.4、氧化钢质量分数8%. -
[1] PURDON A O. The action of alkalis on blast-furnace slag[J]. Journal of the Society of Chemical Society, 1940(59): 191. http://www.researchgate.net/publication/284685480_The_action_of_alkalis_on_blast-furnace_slag
[2] 吴怡婷, 施惠生.制备土聚水泥中若干因素的影响[J].水泥, 2003(3): 1-3. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SNIZ200303000.htm WU Y T, SHI H S. The influence of several factors on the preparation of polymer cement soil[J]. Cement, 2003(3): 1-3. (in Chinese) http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SNIZ200303000.htm
[3] 王旻, 覃维祖.化学激发胶凝材料用于碳纤维加固混凝土柱的研究[J].施工技术, 2007(36): 73-75. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SGJS200703024.htm WANG M, QIAN W Z. The research on chemical excitation gelled materials used to reinforced concrete column with carbon fiber[J]. The Construction Technology, 2007(36): 73-75. (in Chinese) http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SGJS200703024.htm
[4] CHENG T W, CHIU J P. Fire-resistant geopolymers produced by granulated blast furnace slag[J]. Minerals Engineering, 2003(16): 205-210. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0892687503000086
[5] DAVIDOVITS J. Geopolymers, green chemistry and sustainable development solutions[M]. Saint Quentin: Geopolymer Insitute, 2005: 145-232.
[6] FODEN A J. Mechanical properties and material characterization of polysialate structural composites[D]. New Brunswick: Rutgers University, 1999: 38-173. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/35164637_Mechanical_properties_and_material_characterization_of_polysialate_structural_composites
[7] DAVIDOVITS J. Geopolymers and geopolymeric materials[J]. Journal of Thermal Analysis, 1989(35): 429-441. doi: 10.1007/BF01904446
[8] XU H, VAN DEVENTER J S J. The geopolymerization of alumino-silicate minerals[J]. International Journal of Mineral Processing, 2000(59): 247-266. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0301751699000745
[9] PALOMO A, MACIAS A, BLANCO M T, et al. Physical, chemical and mechanical characterization of geopolymers[C]//Proceeding of the 9th International Congress on the Chemistry of Cement. New Delhi: National Council for Cement and Building Materials, 1992(5): 505-511.
[10] 朱晶. 碱矿渣胶凝材料耐高温性能及其在工程中应用基础研究[D]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工业大学, 2014. http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-10213-1014084882.htm ZHU J. The research on high temperature resistant performance and basic application in engineering of alkali-activated slag cementitious materials[D]. Harbin: Harbin Institute of Technology, 2014. (in Chinese) http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-10213-1014084882.htm
[11] MALOLEPSZY J, NOCUN-WCZELIK W. Microcalorimetric studies of slag alkaline binders[J]. Journal of Thermal Analysis and Calorimetry, 1988(33): 431-444. doi: 10.1007%2FBF01913919.pdf
[12] FERNANDEZ-JIMENEZ A, PUERTAS F. Structure of calcium silicate hydrates formed in alkaline-activated slag: influence of the type of alkaline activator[J]. The Journal of American Ceramic Society, 2003(33): 2031-2036. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/229875616_Structure_of_Calcium_Silicate_Hydrates_Formed_in_Alkaline-Activated_Slag_Influence_of_the_Type_of_Alkaline_Activator
[13] 史才军, 何富强, FERNANDEZ-JIMENEZ A等.碱激发水泥的类型与特点[J].硅酸盐学报, 2012, 40(1): 69-75. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GXYB201201013.htm SHI C J, HE F Q, FERNANDEZ-JIMENEZ A, et al. Types and characteristics of alkali-activated slag cement[J]. Journal of Chinese Ceramics Society, 2012, 40(1): 69-75. (in Chinese) http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GXYB201201013.htm
[14] 廖佳庆.配制参数对碱矿渣混凝土强度影响研究[J].福建建材, 2009(3): 8-17. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-FJJC200903007.htm LIAO J Q. The research on the influence of preparation parameters on the strength of alkali-activated slag concrete[J]. Fujian Building Materials, 2009(3): 8-17. (in Chinese) http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-FJJC200903007.htm
[15] 梅琳. 碱矿渣混凝土干缩性能及改善措施研究[D]. 重庆: 重庆大学, 2010. http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-10611-2010216556.htm MEI L. Research on the drying performance and improving measures of alkali-activated slag concrete[D]. Chongqing: Chongqing University, 2010. (in Chinese) http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-10611-2010216556.htm
[16] BAKHAREV T. Geopolymeric materials prepared using Class F fly ash andelevated temperature curing[J]. Cement and Concrete Research, 2005(35): 1224-1232. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/240402871_Geopolymeric_Materials_Prepared_Using_Class_F_Fly_Ash_and_Elevated_Temperature_Curing
[17] CENGIZ D A, CAHIT B. Influence of activator on the strength and drying shrinkage of alkali-activated slag mortar[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2009(23): 548-555. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/229413578_Influence_of_Activator_on_the_Strength_and_Drying_Shrinkage_of_Alkali-Activated_Slag_Mortar
[18] 廖佳庆. 碱矿渣水泥与混凝土化学收缩和干缩行为研究[D]. 重庆: 重庆大学, 2007. http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-10611-2007179289.htm LIAO J Q. Research on the chemical shrinkage and drying shrinkage behavior of alkali-activated slag cement and concrete[D]. Chongqing: Chongqing University, 2007. (in Chinese) http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-10611-2007179289.htm
[19] 中华人民共和国住房和城乡建设部. 普通混凝土长期性能和耐久性能试验方法标准: GB/T 50082—2009[S]. 北京: 中国建筑工业出版社, 2009. [20] 姜奉华. 碱激发矿渣微粉胶凝材料的组成、结构和性能的研究[D]. 西安: 西安建筑科技大学, 2008. http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-10703-2009136234.htm JIANG F H. Research on the composition, structure and performance of the alkali-activated slag-fines cementitious materials[D]. Xi'an: Xi'an University of Architecture and Technology, 2008. (in Chinese) http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-10703-2009136234.htm
[21] 张雪, 陈仕国, 王群英, 等.粉煤灰需水量比的影响因素及降低措施[J].华电技术, 2016, 38(8): 3-7. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SLDL201608002.htm ZHANG X, CHEN S G, WANG Q Y, et al. The influence factors and reducing measures of water demand ratio of fly ash[J]. Huadian Technology, 2016, 38(8): 3-7. (in Chinese) http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SLDL201608002.htm
-
期刊类型引用(7)
1. 邱继生,杨占鲁,关虓,邢敏,张程华,秦卿. 煤矸石陶粒混凝土微观孔结构特征及抗压强度. 西安科技大学学报. 2020(01): 110-117 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 郑文忠,邹梦娜,王英. 碱激发胶凝材料研究进展. 建筑结构学报. 2019(01): 28-39 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 郑文忠,焦贞贞,王英,黄文宣,赵宇健. 碱激发矿渣陶砂砂浆砌筑的砌体弯曲受拉性能试验. 哈尔滨工业大学学报. 2019(06): 33-39 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 李东辉,王英,郑文忠. 碱激发矿渣陶粒混凝土砌块高温后力学性能. 哈尔滨工业大学学报. 2019(06): 46-50 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 郑文忠,焦贞贞,赵宇健,王英. 碱矿渣陶砂砂浆砌筑的砌体轴心受拉性能试验. 哈尔滨工程大学学报. 2019(06): 1036-1042 .  百度学术
百度学术
6. 马砺,高宇,向崎,魏高明,任立峰. 泡沫掺量对快硬水泥固化充填特性的影响. 煤矿安全. 2018(05): 67-70 .  百度学术
百度学术
7. 郑文忠,焦贞贞,王英,黄文宣,赵宇健. 碱激发矿渣陶粒混凝土空心砌块砌体抗剪试验. 哈尔滨工业大学学报. 2018(12): 165-170 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(9)



 下载:
下载: